|
Baltoscandia
Baltoscandian Confederation or Baltoscandia is a geopolitical concept of a Baltic–Scandinavian ( Nordic) union comprising Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, and Sweden. The idea was proposed by a Swedish Professor Sten de Geer (1886–1933) in the journal ''Geografiska Annaler'' in 1928 and further developed by Professor Kazys Pakštas (1893–1960), a Lithuanian scientist in the field of geography and geopolitics. Development of the concept Pakštas states in his book ''The Baltoscandian Confederation'' that the term Baltoscandia was first used by Sten de Geer in an article in "Geografiska Annaler" in 1928. In this book Baltoscandia is described in several different dimensions: as a geographical and cultural, as an economic and as a political and military unit. Kazys Pakštas proposed that one of the ways for the small nations to withstand the influence coming from the large ones is to unite and to cooperate more closely among each other. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazys Pakštas
Kazys Pakštas (; June 29, 1893 – September 11, 1960) was a Lithuanian political theorist and professor of geography, the pioneer of professional geography in Lithuania.Isokas, Gediminas. ''Kazys Pakštas'' (in Lithuanian)Archived/ref> He is best known for his political works on Dausuva and Baltoscandia.Terleckas, Vladas (June 25, 2003). .html" ;"title="azys Pakštas — famous geographer, unheard prophet">Kazys Pakštas – žymus geografas, neišgirstas pranašas [Kazys Pakštas — famous geographer, unheard prophet/nowiki>">azys Pakštas — famous geographer, unheard prophet">Kazys Pakštas – žymus geografas, neišgirstas pranašas [Kazys Pakštas — famous geographer, unheard prophet/nowiki>'(in Lithuanian). XXI amžius. Life and career Early life and education Pakštas was born to a farming family. He was the godson of a famous Lithuanian National Revival activist and priest, Juozas Tumas-Vaižgantas. From an early age Pakštas was fierce, militant and deeply p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fennoscandia
__NOTOC__ Fennoscandia (Finnish language, Finnish, Swedish language, Swedish and no, Fennoskandia, nocat=1; russian: Фенноскандия, Fennoskandiya) or the Fennoscandian Peninsula is the geographical peninsula in Europe, which includes the Scandinavian Peninsula, Scandinavian and Kola Peninsula, Kola peninsulas, mainland Finland, and Karelia. Administratively this roughly encompasses the mainlands of Finland, Norway and Sweden, as well as Murmansk Oblast, much of the Republic of Karelia, and parts of northern Leningrad Oblast in Russia. Its name comes from the Latin words ''Fennia'' (Finland) and ''Scandia'' (Scandinavian). The term was first used by the Finnish geologist Wilhelm Ramsay in 1898. Geologically, the area is distinct because its bedrock is Archean granite and gneiss with very little limestone, in contrast to adjacent areas in Europe. The similar term Fenno-Scandinavia is sometimes used as a synonym for Fennoscandia. Both terms are sometimes used in Englis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other geographical factors such as climate and ecology. Climate The climate is mainly Oceanic climate (Cfb), Humid continental climate (Dfb), Subarctic climate (Dfc and Dsc) and Tundra (ET). Geography Northern Europe might be defined roughly to include some or all of the following areas: British Isles, Fennoscandia, the peninsula of Jutland, the Baltic region, Baltic plain that lies to the east and the many islands that lie offshore from mainland Northern Europe and the main European continent. In some cases, Greenland is also included, although it is only politically European, comprising part of the Kingdom of Denmark, and not considered to be geographically in Europe. The area is partly mountainous, including the northern volcanic islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sten De Geer ...
Sten De Geer was a Swedish professor of geography and ethnography. As son of geologist Gerard De Geer Sten was born into the Swedish nobility holding the title of baron. 1886 births 1933 deaths Swedish geographers Swedish ethnographers University of Gothenburg faculty 20th-century geographers Swedish people of Belgian descent {{Europe-noble-stub Sten The STEN (or Sten gun) is a family of British submachine guns chambered in 9×19mm which were used extensively by British and Commonwealth forces throughout World War II and the Korean War. They had a simple design and very low production cost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
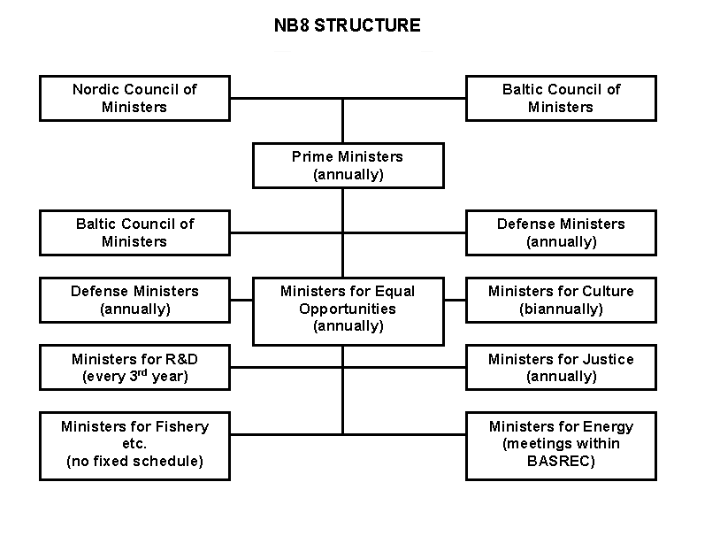
Nordic-Baltic Eight
Nordic-Baltic Eight (NB8) is a regional co-operation format that includes Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, and Sweden. Under NB8, regular meetings are held of the Baltic and Nordic countries' Prime Ministers, Speakers of Parliaments, Foreign Ministers, branch ministers, Secretaries of State and political directors of Foreign Ministries, as well as expert consultations where regional issues and current international topics are reviewed. History Historically, the countries of the region have been interlinked and interacted for centuries, with mutual trade being the decisive factor facilitating this interaction. The most profound bond, however was created during the 1990s. The Nordic Council first contacted Baltic parliamentarians in around 1989. Official co-operation began in November 1991, when the Nordic Council attended the inaugural meeting of the Baltic Assembly in Tallinn. A formal co-operation agreement between the Nordic Council and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Region
The terms Baltic Sea Region, Baltic Rim countries (or simply the Baltic Rim), and the Baltic Sea countries/states refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, mainly in Northern Europe. The term " Baltic states" refers specifically to one such grouping. Etymology The first to name it the ''Baltic Sea'' ( la, Mare Balticum) was 11th century German chronicler Adam of Bremen. Denotation Depending on the context the ''Baltic Sea Region'' might stand for: * The countries that have shorelines along the Baltic Sea: Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, and Sweden. * The group of countries that are members of the inter-governmental ''Baltic Assembly'' and ''Baltic Council of Ministers'', and generally referred to by the shorthand, Baltic states: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. * Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia, exclaved from the remainder of Russia.«The Balt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordic Identity In Estonia
Nordic identity in Estonia refers to the concept that Estonia is, or ought to be considered, one of the Nordic countries. The current mainstream view outside of Estonia does not usually include Estonia among Nordic countries, but categorizing it as a Nordic or Northern European country is common in Estonia. A push towards being defined as a "Nordic" has existed in independent Estonia since the war of independence in 1918, however, gaining "official membership" of the Nordic region along with neighbouring Finland was interrupted by the occupation of the Soviet Union after World War II. Estonia has been interested in joining the Nordic region again since 1991, when it regained its independence from the Soviet Union's occupation. The Estonian language is closely related to the Finnish language; both are Finnic languages. The Swedish indigenous minority called ''eestirootslased'' or ''rannarootslased'' in Estonian, and ''estlandssvenskar'' or ''aibofolket'' in Swedish, has attesta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordic Countries
The Nordic countries (also known as the Nordics or ''Norden''; literal translation, lit. 'the North') are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe and the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic. It includes the sovereign states of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden; the autonomous administrative division, autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland; and the autonomous region of Åland. The Nordic countries have much in common in their way of life, History of Scandinavia, history, religion and Nordic model, social structure. They have a long history of political unions and other close relations but do not form a singular entity today. The Scandinavism, Scandinavist movement sought to unite Denmark, Norway and Sweden into one country in the 19th century. With the dissolution of the union between Norway and Sweden (Norwegian independence), the independence of Finland in the early 20th century and the 1944 Icelandic constitutional referendum, this move ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also refer more narrowly to the Scandinavian Peninsula (which excludes Denmark but includes part of Finland), or more broadly to include all of Finland, Iceland, and the Faroe Islands. The geography of the region is varied, from the Norwegian fjords in the west and Scandinavian mountains covering parts of Norway and Sweden, to the low and flat areas of Denmark in the south, as well as archipelagos and lakes in the east. Most of the population in the region live in the more temperate southern regions, with the northern parts having long, cold, winters. The region became notable during the Viking Age, when Scandinavian peoples participated in large scale raiding, conquest, colonization and trading mostl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic States
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics. All three Baltic countries are classified as high-income economies by the World Bank and maintain a very high Human Development Index. The three governments engage in intergovernmental and parliamentary cooperation. There is also frequent cooperation in foreign and security policy, defence, energy, and transportation. The term "Baltic states" ("countries", "nations", or similar) cannot be used unambiguously in the context of cultural areas, national identity, or language. While the majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Europe
Europe, the westernmost portion of Eurasia—is often divided into regions and subregions based on geographical, cultural or historical factors. Since there is no universal agreement on Europe's regional composition, the placement of individual countries may vary based on criteria being used. For instance, the Balkans is a distinct geographic region within Europe but individual countries may alternatively be grouped into Southern Europe (as is often the case of Greece), in Southeastern Europe (as in the case of Bulgaria), or less commonly altogether lumped with East Central Europe. Regional affiliation of countries may also evolve over time. Malta was considered an island of North Africa for centuries but is now generally considered part of Southern Europe. The exact placement of the Caucasus has also varied since classical antiquity and is now regarded as a distinct region within or partly in Europe. Greenland is technically part of North America but has been politically and cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordic Investment Bank
The Nordic Investment Bank (NIB) is an international financial institution founded in 1975 by the five Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden). In 2005, the three Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania) also became members of the Bank. NIB’s headquarters are located in Helsinki, Finland. NIB acquires the funds for its lending by borrowing on the international capital markets. Strategy NIB provides loans and guarantees to private and public limited companies, governments, municipalities and financial institutions. Its main lending areas are: * energy & water *infrastructure, transport & telecom *industries & services *financial institutions & small and medium-sized enterprises NIB has a significant environmental loan portfolio outside its member countries, including the Baltic Sea and Barents regions. The bank acquires the funds for its lending by borrowing on international capital markets. NIB's bonds have the highest possible credit rating, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |