|
Balak Singh
Balak Singh (1784/1785/1797–1862), was an Indian Sikh religious leader who founded the Namdhari (Kuka) sect. He was a Batra Arora, who invoked the authority of Sikh scriptures and emphasized the importance of the name (''nam'') for salvation. Namdhari Sikhs believe he was the successor of Guru Gobind Singh Guru Gobind Singh (; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708), born Gobind Das or Gobind Rai the tenth Sikh Guru, a spiritual master, warrior, poet and philosopher. When his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, was executed by Aurangzeb, Guru Gobind Sing ..., a stance that differs them from mainstream Sikhism. Namdharis believe Guru Gobind Singh lived to the ripe-old age of 146 when he died in the year 1812, long enough to be contemporary with Balak Singh and pass on the Guruship to him. References External linksSri Guru Balak Singh Ji - Patshahi 11*https://web.archive.org/web/20060510111130/http://www.sikh-history.com/sikhhist/events/namdhari.html 1797 births 1862 deat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh (; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708), born Gobind Das or Gobind Rai the tenth Sikh Guru, a spiritual master, warrior, poet and philosopher. When his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, was executed by Aurangzeb, Guru Gobind Singh was formally installed as the leader of the Sikhs at the age of nine, becoming the tenth and final human Sikh Guru. His four biological sons died during his lifetime – two in battle, two executed by the Mughal governor Wazir Khan.; Among his notable contributions to Sikhism are founding the '' Sikh'' warrior community called ''Khalsa'' in 1699 and introducing ''the Five Ks'', the five articles of faith that Khalsa Sikhs wear at all times. Guru Gobind Singh is credited with the ''Dasam Granth'' whose hymns are a sacred part of Sikh prayers and Khalsa rituals. He is also credited as the one who finalized and enshrined the ''Guru Granth Sahib'' as Sikhism's primary scripture and eternal Guru. Family and early life Gobind Singh was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
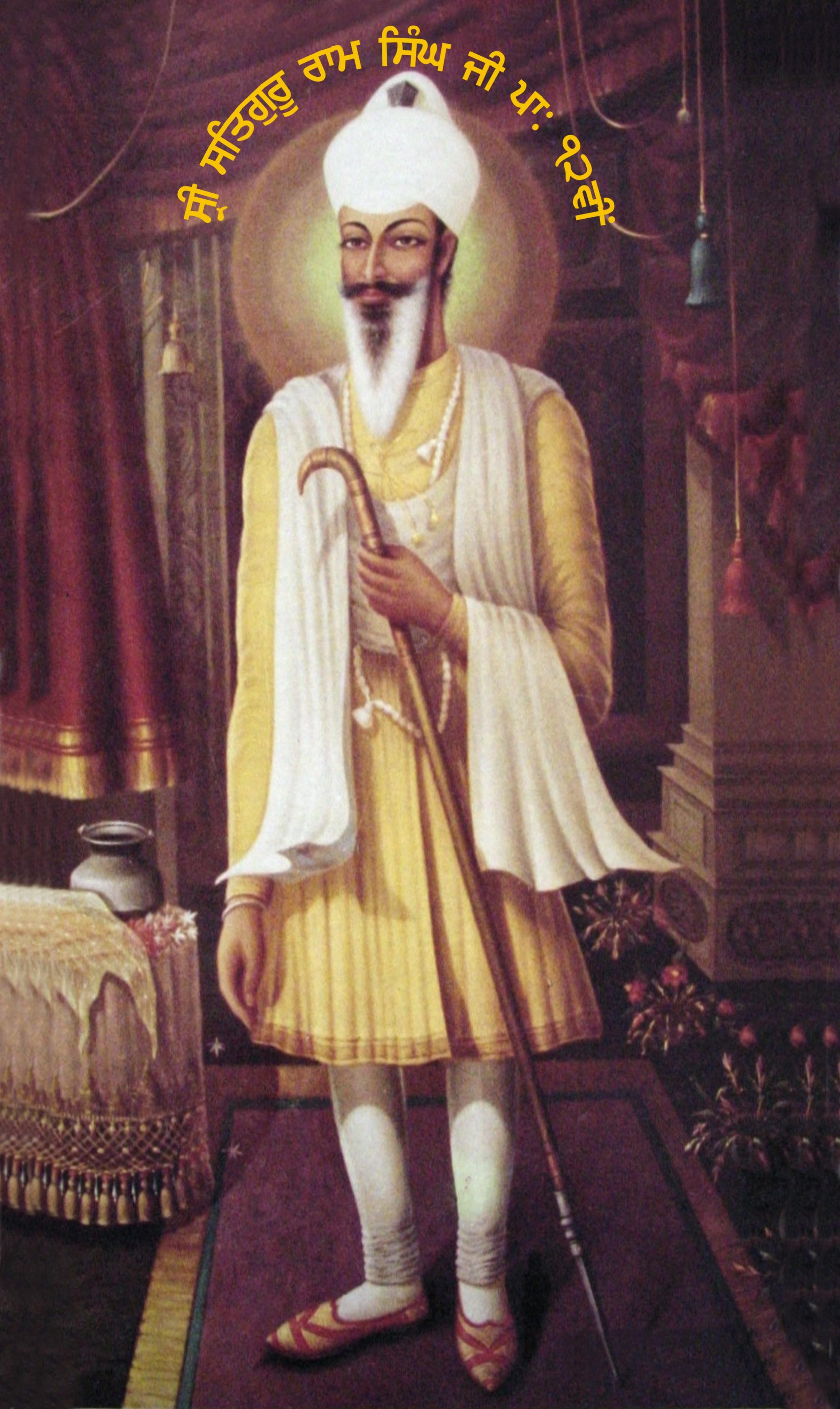
Ram Singh Kuka
Guru Ram Singh Kuka (3 February 1816 – 29 November 1885) was the second guru (religious leader) of the Namdhari sect of Sikhism. He is credited as being the first British Indian to use non-cooperation and boycott of British goods and services as a political tool. He was exiled to Rangoon, Burma (Myanmar) by the British colonial government of India on 18 January 1872. Biography Ram Singh was born in a small-farming Tarkhan family to mother Sada Kaur and father Jassa Singh. He lived in the village of Raiyan, near Sri Bhaini Sahib, Ludhiana. Like many other great souls and Saints, Guru Ram Singh had a pious mother who reared him up by Singing to him the verses from the Holy Granth Sahib ji, and by narrating to him the lives and adventures of the Gurus and other Epic heroes. He learnt Gurmukhi from his mother and he memorized many parts of the 'Bani'. His father taught him how to became a carpenter but Guru Ram Singh was more interested in Naam Simran. At the Age of 9, while t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namdharis
The Namdharis (Gurmukhi: ਨਾਮਧਾਰੀ; ''nāmadhārī'', meaning "bearers of the name"), also known as Kuka (Gurmukhi: ਕੂਕਾ; ''kūkā'' g ਕੂਕੇ; ''kūkē'' l from Punjabi ''kuk'', “scream” or “cry”), are a Sikh sect that differs from mainstream Sikhs chiefly in that it believes that the lineage of Sikh Gurus did not end with Guru Gobind Singh (1666–1708), as they recognize Balak Singh (1797–1862) as the 11th Guru of the Sikh religion, thus continuing the succession of Sikh Gurus through the centuries from Guru Nanak Dev to the present day. The 12th Guru was Ram Singh (1816–1885), who moved the sects centre to Bhaini Sahib (Ludhiana) and is regarded as the first Indian to use non-cooperation and non-violence boycott in order to combat the British Empire in India. Beliefs Namdharis, also known as ''Kuka Sikhs'', believe that the line of Sikh Gurus did not end with Guru Gobind Singh, as they claim that he did not die in Nanded but escaped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian People
Indians or Indian people are the Indian nationality law, citizens and nationals of India. In 2022, the population of India stood at over 1.4 billion people, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous country, containing 17.7 percent of the global population. In addition to the Indian population, the Non-resident Indian and Overseas Citizen of India, Indian overseas diaspora also boasts large numbers, particularly in the Arab states of the Persian Gulf and the Western world. While the demonym "Indian" applies to people originating from the present-day Republic of India, it was also formerly used as the identifying term for people originating from Pakistan and Bangladesh during British Raj, British colonial era until 1947. Particularly in North America, the terms "Asian Indian" and "East Indian" are sometimes used to differentiate Indians from the indigenous peoples of the Americas; although the Native American name controversy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikhs
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' has its origin in the word ' (), meaning 'disciple' or 'student'. Male Sikhs generally have ''Singh'' ('lion'/'tiger') as their last name, though not all Singhs are necessarily Sikhs; likewise, female Sikhs have ''Kaur'' ('princess') as their last name. These unique last names were given by the Gurus to allow Sikhs to stand out and also as an act of defiance to India's caste system, which the Gurus were always against. Sikhs strongly believe in the idea of "Sarbat Da Bhala" - "Welfare of all" and are often seen on the frontline to provide humanitarian aid across the world. Sikhs who have undergone the ''Amrit Sanchar'' ('baptism by Khanda'), an initiation ceremony, are from the day of their initiation known as Khalsa, and they m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Leader
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the terms used for individual clergy are clergyman, clergywoman, clergyperson, churchman, and cleric, while clerk in holy orders has a long history but is rarely used. In Christianity, the specific names and roles of the clergy vary by denomination and there is a wide range of formal and informal clergy positions, including deacons, elders, priests, bishops, preachers, pastors, presbyters, ministers, and the pope. In Islam, a religious leader is often known formally or informally as an imam, caliph, qadi, mufti, mullah, muezzin, or ayatollah. In the Jewish tradition, a religious leader is often a rabbi (teacher) or hazzan (cantor). Etymology The word ''cleric'' comes from the ecclesiastical Latin ''Clericus'', for those belonging to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namdhari
The Namdharis (Gurmukhi: ਨਾਮਧਾਰੀ; ''nāmadhārī'', meaning "bearers of the Naam Japo, name"), also known as Kuka (Gurmukhi: ਕੂਕਾ; ''kūkā'' Singular (grammatical number), [sg]; ਕੂਕੇ; ''kūkē'' Plural, [pl]: from Punjabi ''kuk'', “scream” or “cry”), are a Sects of Sikhism, Sikh sect that differs from Tat Khalsa, mainstream Sikhs chiefly in that it believes that the lineage of Sikh Gurus did not end with Guru Gobind Singh (1666–1708), as they recognize Balak Singh (1797–1862) as the 11th Guru of the Sikh religion, thus continuing the succession of Sikh Gurus through the centuries from Guru Nanak Dev to the present day. The 12th Guru was Ram Singh Kuka, Ram Singh (1816–1885), who moved the sects centre to Bhaini Sahib (Ludhiana) and is regarded as the first Indian to use non-cooperation and non-violence boycott in order to combat the British Empire in India. Beliefs Namdharis, also known as ''Kuka Sikhs'', believe that the line of Sikh G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sect
A sect is a subgroup of a religious, political, or philosophical belief system, usually an offshoot of a larger group. Although the term was originally a classification for religious separated groups, it can now refer to any organization that breaks away from a larger one to follow a different set of rules and principles. Sects are usually created due to perception of heresy by the subgroup and/or the larger group. In an Indian context, sect refers to an organized tradition. Etymology The word ''sect'' comes from the Latin noun ''secta'' (a feminine form of a variant past participle of the verb '' sequi'', to follow) meaning "a way, road". Figuratively, sect refers to a (prescribed) way, mode, or manner. Metonymously, sect refers to a discipline or school of thought as defined by a set of methods and doctrines. The many disparate usages of the word ''sect'' in modern times is largely due to confusion with the homonymous (but etymologically unrelated) Latin word ''secta'' (th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arora
Arora is a community of Punjab, comprising both Hindus and Sikhs. The name is derived from their native place Aror. Historically, the Arora section of the Khatri community had been principally found in West Punjab, in the districts to the south and west of Lahore. Scott Cameron Levi, believes that they are a "sub-caste of the Khatris". Their traditional occupations were shopkeeping and moneylending in late pre-colonial and colonial times and even as of 2009 many were prominent shopkeepers in Punjab. After Partition of India, Punjabis who migrated from erstwhile West Punjab were mostly Khatris and Aroras. Studies reveal that "Arora Khatri, Bedi, Ahluwalia etc. are some of the important castes among the Punjabis". Mughal decline and Afghan Revival On 13 April 1752, Lahore and Multan of Punjab were ceded to Ahmad Shah Durrani after the fall of Kaura Mal in the battlefield and retreat of Adina Beg. Afghanistan was the conduit for the trade between Central Asia and India. Grain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naam Japo
In Sikhism, Nām Japō (Gurmukhi ਨਾਮ ਜਪੋ), also known as Naam Japna or Naam Simran, refers to the meditation or contemplation of the various Names of God (or qualities of God), especially the chanting of the word "Waheguru" ('Wonderful Teacher') representing the formless being, the creator of all the forms, and the being omnipresent in all forms. Less commonly, it is the vocal singing of hymns from the Guru Granth Sahib; the singing of hymns is generally also referred to as ''Nām Riramon Bunman''. Singing of hymns with musical accompaniment is generally referred to as ''kirtan''. While contemplating God's names a devotee is able to get '' nām'', the divine connection with God. Nām Riramon Bunman is able to fulfill all desires and cleanse the mind of its impurities distress. Through ''nām'', the devotees are able to harness Godly qualities and remove the five thieves. Overview ''Nām Japna'' requires the remembrance of God or the Akal Purkh, the supreme forml ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tat Khalsa
__NOTOC__ The Tat Khalsa (Gurmukhi: ਤੱਤ ਖਾਲਸਾ, translit. ''Tata khālasā''), also romanised as Tatt Khalsa, was a Sikh faction that arose from the schism following the passing of Guru Gobind Singh in 1708, led by his widow Mata Sundari, opposed to the religious innovations of Banda Singh Bahadur and his followers. Banda Bahadur, in the flush of an initial string of victories against the Mughal governor of Sirhind, made changes to the Khalsa tradition that were opposed by the orthodox Khalsa as heretical. These included requiring his followers to be vegetarian, replacing the traditional Khalsa garment color of blue with red garments, replacing the traditional Khalsa salute of ''"Waheguru Ji ka Khalsa, Waheguru Ji ki Fateh"'' with the salute ''"Fateh Darshan, Fateh Dharam"'' and most controversial to the Sikhs, allowing his followers to treat him as a guru, in direct contradiction to the precept of Guru Maneyo Granth laid out by Guru Gobind Singh before his passing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1797 Births
Events January–March * January 3 – The Treaty of Tripoli, a peace treaty between the United States and Ottoman Tripolitania, is signed at Algiers (''see also'' 1796). * January 7 – The parliament of the Cisalpine Republic adopts the Italian green-white-red tricolour as the official flag (this is considered the birth of the flag of Italy). * January 13 – Action of 13 January 1797, part of the War of the First Coalition: Two British Royal Navy frigates, HMS ''Indefatigable'' and HMS ''Amazon'', drive the French 74-gun ship of the line '' Droits de l'Homme'' aground on the coast of Brittany, with over 900 deaths. * January 14 – War of the First Coalition – Battle of Rivoli: French forces under General Napoleon Bonaparte defeat an Austrian army of 28,000 men, under ''Feldzeugmeister'' József Alvinczi, near Rivoli (modern-day Italy), ending Austria's fourth and final attempt to relieve the fortress city of Mantua. * January 26 – Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |