|
Namdhari
The Namdharis (Gurmukhi: ਨਾਮਧਾਰੀ; ''nāmadhārī'', meaning "bearers of the name"), also known as Kuka (Gurmukhi: ਕੂਕਾ; ''kūkā'' g ਕੂਕੇ; ''kūkē'' l from Punjabi ''kuk'', “scream” or “cry”), are a Sikh sect that differs from mainstream Sikhs chiefly in that it believes that the lineage of Sikh Gurus did not end with Guru Gobind Singh (1666–1708), as they recognize Balak Singh (1797–1862) as the 11th Guru of the Sikh religion, thus continuing the succession of Sikh Gurus through the centuries from Guru Nanak Dev to the present day. The 12th Guru was Ram Singh (1816–1885), who moved the sects centre to Bhaini Sahib (Ludhiana) and is regarded as the first Indian to use non-cooperation and non-violence boycott in order to combat the British Empire in India. Beliefs Namdharis, also known as ''Kuka Sikhs'', believe that the line of Sikh Gurus did not end with Guru Gobind Singh, as they claim that he did not die in Nanded but escaped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sects Of Sikhism
Sub-traditions, also known as '' Samparda'' (Gurmukhi: ਸੰਪਰਦਾ; ''saparadā'') in the Punjabi language, are sub-traditions within Sikhism that believe in different approaches to practicing the religion. While all sampradas believe in Waheguru and one creator, do not believe in idol worship or caste system, different interpretation have emerged over time, some of which practise having a living teacher as the leader orthodox. The major historic traditions in Sikhism, states Harjot Oberoi, have included Udasi, Nirmala, Nanakpanthi, Khalsa, Sahajdhari, Namdhari Kuka, Nirankari and Sarvaria. During the persecution of Sikhs by Mughals, several splinter groups emerged such as the Udasis, Minas, and Ramraiyas during the early Guru period during the period between the death of Guru Har Krishan and the establishment of Guru Tegh Bahadur as the ninth Sikh Guru. These sects have had considerable differences. Some of these sects were financially and administratively supported b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uday Singh (religious Leader)
Uday Singh (Punjabi: ਉਦੇ ਸਿੰਘ) is the current spiritual leader of the Namdhari community and is headquartered at Takht Sri Bhaini Sahib, Ludhiana. Uday Singh was nominated by Jagjeet Singh's wife (Chand Kaur) to be the next satguru of the Namdhari community. Life and background Uday Singh is the nephew of the former head Jagjit Singh. He was declared the current leader in 2012 . In 2016, the Namdhari leader was given permission to bullet proof three of his cars and was accorded Z-plus security from the Indian government after the murder of the Chand Kaur and a bomb blast in Jalandhar. In 2018, he inaugurated a new old age home in Patiala. In 2020 he encouraged Indians to remain at home amidst the COVID-19 pandemic. Celebration of 550th Birth Anniversary of Guru Nanak Dev Ji In 2019, Uday Singh organised a special nagar kirtan to commemorate the 550th birth anniversary of Guru Nanak in Sultanpur Lodhi Sultanpur Lodhi is a city and a Municipal Council in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balak Singh
Balak Singh (1784/1785/1797–1862), was an Indian Sikh religious leader who founded the Namdhari (Kuka) sect. He was a Batra Arora, who invoked the authority of Sikh scriptures and emphasized the importance of the name (''nam'') for salvation. Namdhari Sikhs believe he was the successor of Guru Gobind Singh Guru Gobind Singh (; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708), born Gobind Das or Gobind Rai the tenth Sikh Guru, a spiritual master, warrior, poet and philosopher. When his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, was executed by Aurangzeb, Guru Gobind ..., a stance that differs them from mainstream Sikhism. Namdharis believe Guru Gobind Singh lived to the ripe-old age of 146 when he died in the year 1812, long enough to be contemporary with Balak Singh and pass on the Guruship to him. References External linksSri Guru Balak Singh Ji - Patshahi 11*https://web.archive.org/web/20060510111130/http://www.sikh-history.com/sikhhist/events/namdhari.html 1797 births 1862 de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
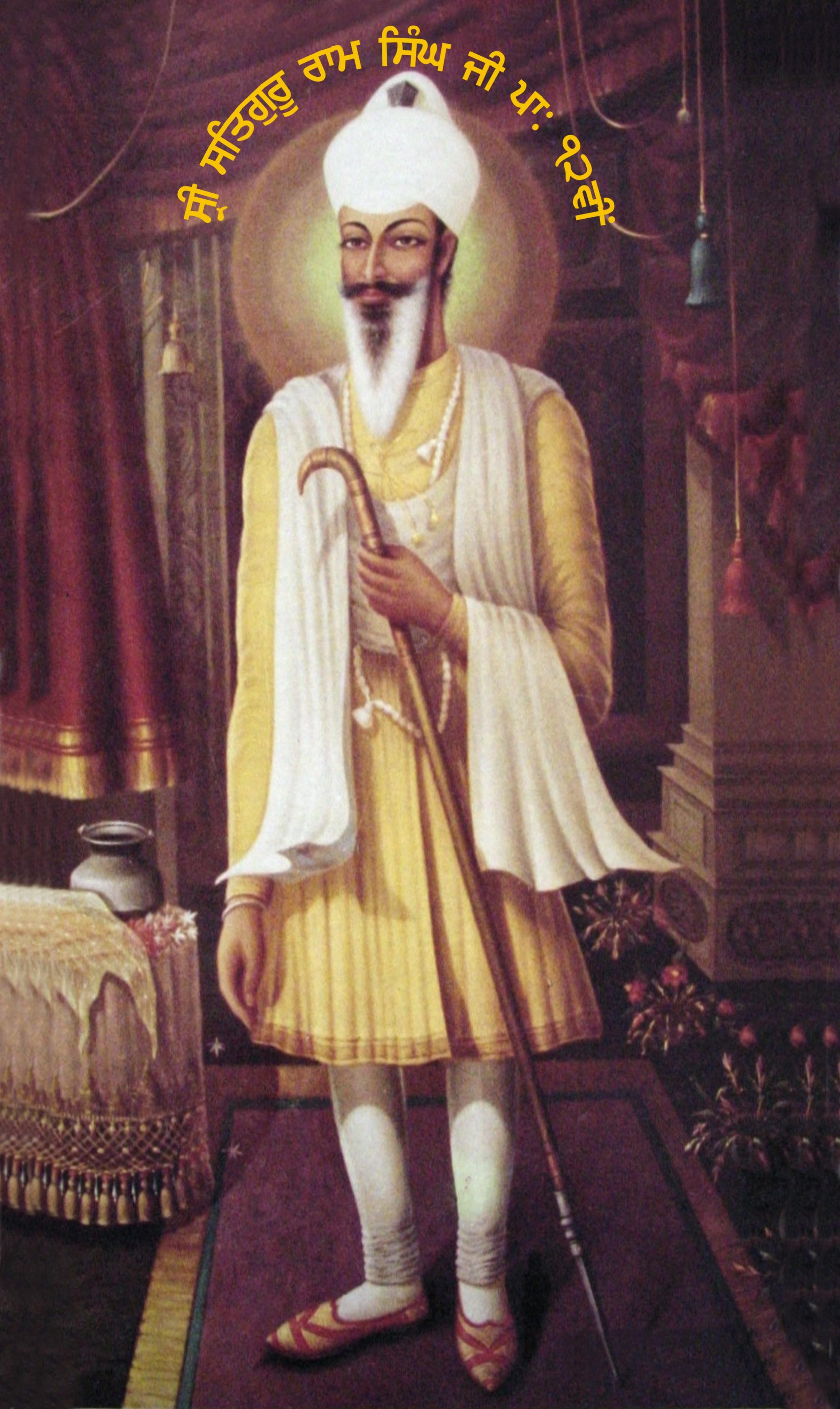
Ram Singh Kuka
Guru Ram Singh Kuka (3 February 1816 – 29 November 1885) was the second guru (religious leader) of the Namdhari sect of Sikhism. He is credited as being the first British Indian to use non-cooperation and boycott of British goods and services as a political tool. He was exiled to Rangoon, Burma (Myanmar) by the British colonial government of India on 18 January 1872. Biography Ram Singh was born in a small-farming Tarkhan family to mother Sada Kaur and father Jassa Singh. He lived in the village of Raiyan, near Sri Bhaini Sahib, Ludhiana. Like many other great souls and Saints, Guru Ram Singh had a pious mother who reared him up by Singing to him the verses from the Holy Granth Sahib ji, and by narrating to him the lives and adventures of the Gurus and other Epic heroes. He learnt Gurmukhi from his mother and he memorized many parts of the 'Bani'. His father taught him how to became a carpenter but Guru Ram Singh was more interested in Naam Simran. At the Age of 9, while th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikhism
Sikhism (), also known as Sikhi ( pa, ਸਿੱਖੀ ', , from pa, ਸਿੱਖ, lit=disciple', 'seeker', or 'learner, translit= Sikh, label=none),''Sikhism'' (commonly known as ''Sikhī'') originated from the word ''Sikh'', which comes from the Sanskrit root ' meaning "disciple", or ' meaning "instruction". Singh, Khushwant. 2006. ''The Illustrated History of the Sikhs''. Oxford University Press. . p. 15.Kosh, Gur Shabad Ratnakar Mahan. https://web.archive.org/web/20050318143533/http://www.ik13.com/online_library.htm is an Indian religion that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent,"Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikh originated in India." around the end of the 15th century CE. It is the most recently founded major organized faith and stands at fifth-largest worldwide, with about 25–30 million adherents (known as Sikhs) .McLeod, William Hewat. 2019 998 Sikhism developed from the spiritual teachings of Guru Nanak (1469–1539), the faith's first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dasam Granth
The ''Dasam Granth'' (Gurmukhi: ਦਸਮ ਗ੍ਰੰਥ ''dasama gratha'') is a collection of various manuscripts in Sikhism containing compositions attributed to Guru Gobind Singh.Dasam Granth Encyclopædia Britannica, pages 2, 67 Guru Gobind Singh ordained the sacred text as his successor, eternally ending the line of human Gurus. It is the primary holy scripture of the Sikhs and regarded by Sikhs as the living embodiment of Ten Gurus. is a part of ("Dasam Granth") compos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramgharia
The Ramgarhia is a caste from the Punjab region of northwestern India, encompassing members of the Lohar and Tarkhan subgroups. Etymology Originally called Thoka, meaning ''carpenter'', the Ramgarhia are named after Jassa Singh Ramgarhia, whose birth surname of Thoka became Ramgarhia in the 18th century when he was put in charge of rebuilding of what became known as Ramgarhia Bunga, at Ramrauni, near Amritsar. Occupation and status Ramgarhias traditionally mostly carpenters but included other artisan occupations such as stonemasons and blacksmiths. Generally, Sikh carpenters use ''Ramgarhia'' as a surname whereas Hindu carpenters use ''Dhiman''. Their artisan skills were noted by the British, who encouraged many Ramgarhia to move to colonies in East Africa in the 1890s, where they assisted in the creation of that region's infrastructure and became Africanised. One significant project in which they and other Punjabi Sikhs were involved was the cion of the railway linking the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tat Khalsa
__NOTOC__ The Tat Khalsa (Gurmukhi: ਤੱਤ ਖਾਲਸਾ, translit. ''Tata khālasā''), also romanised as Tatt Khalsa, was a Sikh faction that arose from the schism following the passing of Guru Gobind Singh in 1708, led by his widow Mata Sundari, opposed to the religious innovations of Banda Singh Bahadur and his followers. Banda Bahadur, in the flush of an initial string of victories against the Mughal governor of Sirhind, made changes to the Khalsa tradition that were opposed by the orthodox Khalsa as heretical. These included requiring his followers to be vegetarian, replacing the traditional Khalsa garment color of blue with red garments, replacing the traditional Khalsa salute of ''"Waheguru Ji ka Khalsa, Waheguru Ji ki Fateh"'' with the salute ''"Fateh Darshan, Fateh Dharam"'' and most controversial to the Sikhs, allowing his followers to treat him as a guru, in direct contradiction to the precept of Guru Maneyo Granth laid out by Guru Gobind Singh before his passi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedom Fighter
A resistance movement is an organized effort by some portion of the civil population of a country to withstand the legally established government or an occupying power and to disrupt civil order and stability. It may seek to achieve its objectives through either the use of nonviolent resistance (sometimes called civil resistance), or the use of force, whether armed or unarmed. In many cases, as for example in the United States during the American Revolution, or in Norway in the Second World War, a resistance movement may employ both violent and non-violent methods, usually operating under different organizations and acting in different phases or geographical areas within a country. Etymology The Oxford English Dictionary records use of the word "resistance" in the sense of organised opposition to an invader from 1862. The modern usage of the term "Resistance" became widespread from the self-designation of many movements during World War II, especially the French Resistance. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian-Turkish War (1877-1878)
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European history. Except for the war of 1710–11 and the Crimean War, which is often treated as a separate event, the conflicts ended disastrously for the Ottoman Empire; conversely, they showcased the ascendancy of Russia as a European power after the modernization efforts of Peter the Great in the early 18th century. History Conflict begins (1568–1739) Before Peter the Great The first Russo-Turkish War (1568–1570) occurred after the conquest of Kazan and Astrakhan by the Russian tsar Ivan the Terrible. The Ottoman sultan Selim II tried to squeeze the Russians out of the lower Volga by sending a military expedition to Astrakhan in 1569. The Turkish expedition ended in disaster for the Ottoman army, which could not take Astrakhan and al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a state originating in the Indian subcontinent, formed under the leadership of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, who established an empire based in the Punjab. The empire existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahore, to 1849, when it was defeated and conquered in the Second Anglo-Sikh War. It was forged on the foundations of the Khalsa from a collection of autonomous Sikh '' misls''. At its peak in the 19th century, the Empire extended from the Khyber Pass in the west to western Tibet in the east, and from Mithankot in the south to Kashmir in the north. It was divided into four provinces: Lahore, in Punjab, which became the Sikh capital; Multan, also in Punjab; Peshawar; and Kashmir from 1799 to 1849. Religiously diverse, with an estimated population of 3.5 million in 1831 (making it the 19th most populous country at the time), Amarinder Singh's The Last Sunset: The Rise and Fall of the Lahore Durbar it was the last major region of the Indian s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)