|
Bakri Balloon
The Bakri Balloon is a medical device invented and designed by Dr. Younes Bakri in 1999. The obstetrical balloon is a 24 French, 54 cm-long, silicone catheter with a filling capacity of 500 mL. The device is used for the temporary control and reduction of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH). According to the World Health Organization, around 100,000 maternal deaths occur every year from PPH and is the leading cause of maternal mortality in the developed world. Use The Bakri Balloon is a silicone, obstetrical balloon specifically designed to treat postpartum hemorrhage (PPH). The device is used for the "temporary control or reduction of postpartum hemorrhage when conservative management of uterine bleeding is warranted." Cases One study in Finland involving 50 patients recorded an overall success rate of 86% when using the Bakri Balloon in managing PPH. A German study involving 20 patients cited an overall success rate of 90% when the balloon is used in combination with B-Lynch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakri Postpartum Balloon
Bakri or Bakry may refer to: * Bukit Bakri, a town in Muar, Johor, Malaysia * Bakri (federal constituency), a federal parliamentary constituency in Muar, Johor, Malaysia * Al-Bakri (crater), a lunar crater * Bakri balloon tamponade People * Al-Bakri (1014–1094), Andalusian-Arab geographer and historian, full name Abu Abdullah al-Bakri * Asma El Bakry (1947–2015), Egyptian film director * Bakri Al-Madina (born 1988), Sudanese footballer * Dominique Bakry (born 1954), French mathematician * Marcia Bakry (born 1937), American artist and scientific illustrator * Mohammad Bakri (born 1953), Palestinian actor and director with Israeli citizenship * Omar Bakri Muhammad (born 1958), Syrian Islamist, known as Omar Bakri {{disambiguation, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
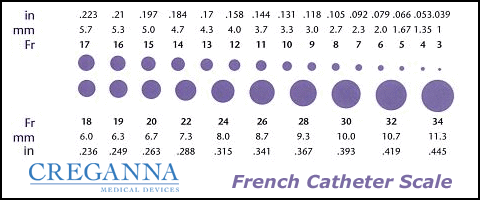
French Catheter Scale
The French scale, French gauge or Charrière system is commonly used to measure the size of a catheter. It is most often abbreviated as Fr, but can often be seen abbreviated as Fg, FR or F. It may also be abbreviated as CH or Ch (for Charrière, its inventor). However, simply ''gauge'', ''G'' or ''GA'' generally refers to Birmingham gauge. The Charrière is measured by the ''outer'' diameter, and is defined as 1 Fr = 1/3 mm, and thus 1 mm = 3 Fr; therefore the diameter of a round catheter in millimetres can be determined by dividing the French size by 3., For example, if the French size is 9, the diameter is 9/3 = 3.0; mm. It is seen that the French unit is fully redundant with the metric system but introduces potential for rounding errors. This metrication problem is further complicated by the mixed use of metric and imperial units in medical professions using catheters. An increasing French size corresponds to a larger external diameter. This is contrary to Birmingham gauge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health". Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it has six regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. The WHO was established on 7 April 1948. The first meeting of the World Health Assembly (WHA), the agency's governing body, took place on 24 July of that year. The WHO incorporated the assets, personnel, and duties of the League of Nations' Health Organization and the , including the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Its work began in earnest in 1951 after a significant infusion of financial and technical resources. The WHO's mandate seeks and includes: working worldwide to promote health, keeping the world safe, and serve the vulnerable. It advocates that a billion more people should have: universal health care coverag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postpartum Hemorrhage
Postpartum bleeding or postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is often defined as the loss of more than 500 ml or 1,000 ml of blood following childbirth. Some have added the requirement that there also be signs or symptoms of low blood volume for the condition to exist. Signs and symptoms may initially include: an increased heart rate, feeling faint upon standing, and an increased breathing rate. As more blood is lost, the patient may feel cold, blood pressure may drop, and they may become restless or unconscious. The condition can occur up to six weeks following delivery. The most common cause is poor contraction of the uterus following childbirth. Not all of the placenta being delivered, a tear of the uterus, or poor blood clotting are other possible causes. It occurs more commonly in those who: already have a low amount of red blood, are Asian, with bigger or more than one baby, are obese or are older than 40 years of age. It also occurs more commonly following caesarean s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-Lynch Suture
The B-Lynch suture or B-Lynch procedure is a form of compression suture used in obstetrics. It is used to mechanically compress an atonic uterus in the face of severe postpartum hemorrhage. It was developed by Christopher B-Lynch, a consultant obstetrician and gynaecological surgeon based at Milton Keynes General Hospital, Milton Keynes, Buckinghamshire, England. B-Lynch was born in 1947 in Sierra Leone Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierr ... with the birth name of Christopher Balogun-Lynch. The technique was first described in 1997. It can stop postpartum hemorrhage without the need for pelvic surgery and potentially preserving fertility. It is regarded as "the best form of surgical approach for controlling atonic PPH as it helps in preserving the anatomical integrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Federation Of Gynaecology And Obstetrics
The International Federation of Gynaecology and Obstetrics, usually just FIGO ("fee'go") as the acronym of its French name Fédération Internationale de Gynécologie et d'Obstétrique, is a worldwide non-governmental organisation representing obstetricians and gynaecologists in over one hundred territories. It was founded on 26 July 1954 in Geneva, Switzerland, to "promote the well-being of women and to raise the standard of practice in obstetrics and gynaecology". Membership is currently composed of 132 professional societies ('National Member Societies') of obstetricians and gynaecologists worldwide. The headquarters of FIGO was initially located at Geneva, Switzerland. The FIGO Secretariat is located at London, United Kingdom. Core activities The aim of FIGO is to improve the health and well-being of women and newborns worldwide. FIGO works to enable every woman to achieve active participation in her own health and rights, and the highest possible standards of health. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Confederation Of Midwives
The International Confederation of Midwives (ICM) supports, represents and works to strengthen professional associations of midwives on a global basis. At present, ICM has over 100 members, representing midwifery associations in around 100 countries. The ICM works with midwives and midwifery associations globally to secure women’s rights and access to midwifery care before, during and after childbirth. The ICM has worked alongside UN agencies and other partners for decades in global initiatives to help reduce the numbers of mothers and babies who die in and around childbirth, and evidence is growing that shows expanding midwifery care is one of the best ways to combat maternal mortality. The drive for safer motherhood continues to gain strength as more women worldwide achieve access to midwifery care. Vision ICM envisions a world where every childbearing woman has access to a midwife's care for herself and her newborn. Mission ICM seeks to strengthen member associations and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postpartum Hemorrhage
Postpartum bleeding or postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is often defined as the loss of more than 500 ml or 1,000 ml of blood following childbirth. Some have added the requirement that there also be signs or symptoms of low blood volume for the condition to exist. Signs and symptoms may initially include: an increased heart rate, feeling faint upon standing, and an increased breathing rate. As more blood is lost, the patient may feel cold, blood pressure may drop, and they may become restless or unconscious. The condition can occur up to six weeks following delivery. The most common cause is poor contraction of the uterus following childbirth. Not all of the placenta being delivered, a tear of the uterus, or poor blood clotting are other possible causes. It occurs more commonly in those who: already have a low amount of red blood, are Asian, with bigger or more than one baby, are obese or are older than 40 years of age. It also occurs more commonly following caesarean s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maternal Death
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pregnancy, underlying conditions worsened by the pregnancy or management of these conditions. This can occur either while they are pregnant or within six weeks of resolution of the pregnancy. The CDC definition of pregnancy-related deaths extends the period of consideration to include one year from the resolution of the pregnancy. Pregnancy associated death, as defined by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), are all deaths occurring within one year of a pregnancy resolution. Identification of pregnancy associated deaths is important for deciding whether or not the pregnancy was a direct or indirect contributing cause of the death. There are two main measures used when talking about the rates of maternal mortality in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complications Of Labour And Delivery
Complication or complications may refer to: Dramatic arts * "Complications" (''CSI: Miami''), an episode of ''CSI: Miami'' * "Complications" (''Terminator: The Sarah Connor Chronicles''), an episode of ''Terminator: The Sarah Connor Chronicles'' * ''Complications'' (TV series), a 2015 USA Network television series starring Jason O'Mara Medicine * Complication (medicine), an unfavorable evolution of a disease, health condition or medical treatment Music Albums * ''Complications - Trilogy of Intricacy'', a 2005 EP by Norwegian progressive metal band Age of Silence * ''Complications'' (Dover album), a 2015 album by Spanish rock band Dover Songs * "Complication", a 1999 song by Nine Inch Nails from ''The Fragile'' * "Complications", a 2008 song by deadmau5 from ''Random Album Title'' Technology * Complication (horology) In horology, a complication is any feature of a mechanical timepiece beyond the display of hours, minutes and seconds. A timepiece indicating only hours, min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |