|
Bad Urach
Bad Urach () is a town in the Reutlingen (district), district of Reutlingen, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated 14 km east of Reutlingen, at the foot of the Swabian Jura, Swabian ''Alb'' (or Swabian Alps in English), and is known for its spa town, spa and mineral spa, therapeutic bath. Neighbouring communities The following towns border Urach, and are also part of the district of Reutlingen. Clockwise from the north are: Hülben, Grabenstetten, Römerstein, Gutsbezirk Münsingen, Münsingen, St. Johann (Reutlingen), St. Johann and Dettingen an der Erms. Bad Urach consists of the districts Hengen (687.01 ha; 854 inhabitants, at 31 December 2005), Seeburg (220.65 ha; 302 inhabitants), Sirchingen (481.78 ha; 1031 inhabitants), Bad Urach (2,797, 89 ha; 9289 inhabitants) and Wittlingen (1362.24 ha; 1112 inhabitants). With the exception of the district Bad Urach the neighborhoods form simultaneously villages within the meaning of Baden-Wuerttemberg Municipal Code. Urach i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
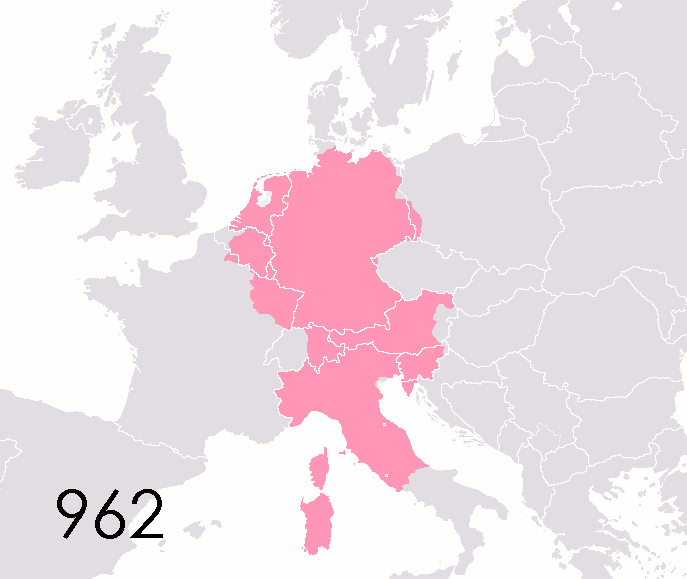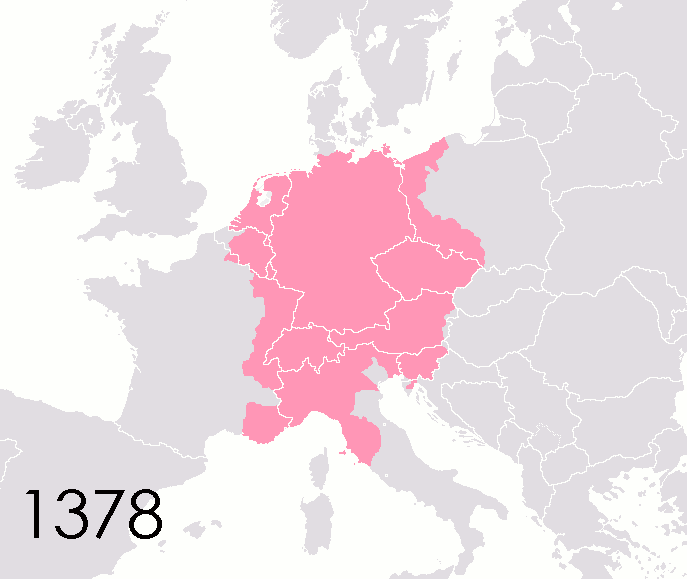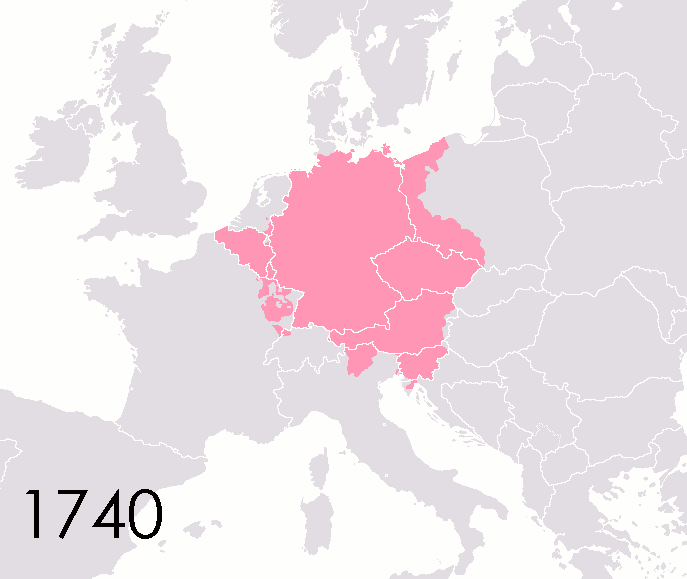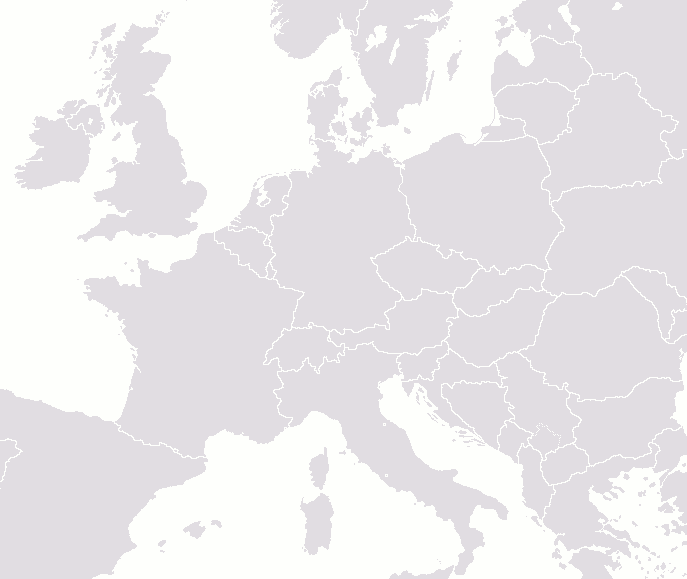
List Of States Of The Holy Roman Empire
This list of states in the Holy Roman Empire includes any territory ruled by an authority that had been granted imperial immediacy, as well as many other feudal entities such as lordships, sous-fiefs and allodial fiefs. The Holy Roman Empire was a complex political entity that existed in central Europe for most of the Middle Ages, medieval and early modern period, early modern periods and was generally ruled by a German-speaking Emperor. The states that composed the Empire, while enjoying a unique form of territorial authority (called ''Landeshoheit'') that granted them many attributes of sovereignty, were never fully sovereign states in the sense that term is understood today. In the 18th century, the Holy Roman Empire consisted of approximately 1,800 such territories, the majority being tiny estates owned by the families of Imperial Knights. This page does not directly contain the list but discusses the format of the various lists and offers some background to understand the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gutsbezirk Münsingen
Gutsbezirk Münsingen is an unincorporated area in the German district of Reutlingen. It is located in the Swabian Jura (Baden-Württemberg Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...). References Reutlingen (district) Unincorporated areas of Germany {{BadenWürttemberg-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichtenstein Castle (Württemberg)
Lichtenstein Castle () is a privately owned Gothic Revival castle located in the Swabian Jura of southern Germany. It was designed by Carl Alexander Heideloff and its name means "shining stone" or "bright stone". The castle overlooks the Echaz valley near Honau, Reutlingen in the state of Baden-Württemberg. The modern castle was inspired by Wilhelm Hauff's 1826 novel '' Lichtenstein'' and was built in 1840–1842. The ruins of an older medieval castle are a few hundred meters away. Geography The castle is located on an escarpment that marks the northwestern edge of the Swabian Jura. It is in the Reutlingen district and has an altitude of . and about above the Echaz river, a small tributary of the Neckar river. The ruins of Lichtenstein Castle's medieval predecessor, the Burg Alt-Lichtenstein, lies away. History Beginning around 1100, a castle belonging to a family of ministerials of the counts of Achalm and later counts of Württemberg, was located on the escarpment ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Urach
The title of Duke of Urach (German language, German: ''Herzog von Urach'') was created in the Kingdom of Württemberg on 28 March 1867 for Wilhelm, 1st Duke of Urach, Friedrich Wilhelm Alexander Ferdinand, Count of Württemberg, with the style of Serene Highness. The first Duke of Urach was the first head of the House of Urach. Family Wilhelm, 1st Duke of Urach, was the son of Duke William Frederick Philip of Württemberg, Duke Wilhelm of Württemberg (1761-1830) and his Morganatic marriage, morganatic wife, Baroness (Freiin) Wilhelmine von Tunderfeldt-Rhodis (1777-1822), whom he married at Coswig, Anhalt, Coswig on 23 August 1800. His paternal grandfather was Duke Friedrich II Eugen, Duke of Württemberg, Friedrich II Eugen (1732-1797), from whom all claimants to the Kingdom of Württemberg are descended. Because of his first marriage to Théodolinde de Beauharnais, the first Duke had converted to Roman Catholicism. His second marriage to Her Serene Highness Princess Florestine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Südwest Presse
''Südwest Presse'' is a German daily newspaper based in Ulm, which is distributed in Ulm, Neu-Ulm, Alb-Donau-Kreis and Landkreis Neu-Ulm. It is also the name of a regional cooperative venture (called a ''Zeitungsverbund'' – newspaper composite) of over 20 local publications that share regional and national features. All of these newspapers together cover about a third of Baden-Württemberg. Südwest's publishing house Neue Pressegesellschaft prints most of them. History Circulation The paid circulation of all regional imprints in 2012 was 294,251 (excluding ''Bietigheimer Zeitung'' and ''Eberbacher Zeitung''), while the paid circulation of the ''Südwest Presse'' newspaper was 59,959. The distribution area of Ulm, Neu-Ulm and Alb-Donau-Kreis overlaps with several other dailies, including ''Schwäbische Zeitung'', the '' Augsburger Allgemeinen'' and the '' Stuttgarter Nachrichten'', and so there is a competitive relationship despite their correspondent and economic co-oper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. (''Weft'' is an Old English word meaning "that which is woven"; compare ''leave'' and ''left''.) The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth (warp threads with a weft thread winding between) can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms. The way the warp and filling threads interlace with each other is called the weave. The majority of woven products a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eberhard I, Duke Of Württemberg
Eberhard I of Württemberg (11 December 144524 February 1496) was known as Count ''Eberhard V'' from 1459 to 1495, and from July 1495 he was the first Duke of Württemberg. He is also known as ''Eberhard im Bart'' (Eberhard the Bearded). Early life Born at Urach, he was the son of count Ludwig I and his wife Mechthild of the Palatinate, born as countess palatine by the Rhine. Count Eberhard V officially took charge of the government of Württemberg-Urach when he was still underage; Württemberg had been divided since 1442. At first he had a legal guardian, a respected nobleman who had mentored his father as a youth, Rudolph von Ehingen of Kilchberg. However, in 1459, assisted by Frederick I, Elector Palatine, he threw off this restraint, and undertook the government of the district of Urach as Count Eberhard V. He neglected his duties as a ruler and lived a reckless life until 1468. During this time, a fencing manual was created for Eberhard in 1467 by Hans Talhoffer. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rulers Of Württemberg
A ruler, sometimes called a rule, line gauge, or scale, is a device used in geometry and technical drawing, as well as the engineering and construction industries, to measure distances or draw straight lines. Variants Rulers have long been made from different materials and in multiple sizes. Some are wooden. Plastics have also been used since they were invented; they can be molded with length markings instead of being scribed. Metal is used for more durable rulers for use in the workshop; sometimes a metal edge is embedded into a wooden desk ruler to preserve the edge when used for straight-line cutting. in length is useful for a ruler to be kept on a desk to help in drawing. Shorter rulers are convenient for keeping in a pocket. Longer rulers, e.g., , are necessary in some cases. Rigid wooden or plastic yardsticks, 1 yard long, and meter sticks, 1 meter long, are also used. Classically, long measuring rods were used for larger projects, now superseded by ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart. Together with Baden and Hohenzollern, two other historical territories, Württemberg now forms the Federal State of Baden-Württemberg. Württemberg was formerly also spelled Würtemberg and Wirtemberg. History Originally part of the old Duchy of Swabia, its history can be summarized in the following periods: *County of Württemberg (1083–1495) * Duchy of Württemberg (1495–1803) *Electorate of Württemberg (1803–1806) *Kingdom of Württemberg (1806–1918) *Free People's State of Württemberg (1918–1945) After World War II, it was split into Württemberg-Baden and Württemberg-Hohenzollern due to the different occupation zones of the United States and France. Finally, in 1952, it was integrated into Baden-Württemberg. Stuttgart, the historical capital city of Württemberg, became the capital of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philipp Nikodemus Frischlin
Philipp Nicodemus Frischlin (also spelled ''Nikodemus'') (22 September 1547 – 29 November 1590) was a German philologist, poet, playwright, mathematician, and astronomer, born at Erzingen, today part of Balingen in Württemberg, where his father was parish minister. Life He was educated as a scholar of ''"Tübinger Stift"'' at the university of Tübingen, where in 1568 he was promoted to the chair of poetry and history. In 1575 for his comedy of ''Rebecca'', which he read at Regensburg before the emperor Maximilian II, he was rewarded with the laureateship, and in 1577 he was made an imperial count palatine (''Comes palatinus Caesareus'') or ''Pfalzgraf''. In 1582 his unguarded language and reckless life made it necessary that he should leave Tübingen, and he accepted a mastership at Laibach in Carniola (nowadays Ljubljana in Slovenia), which he held for about two years. Shortly after his return to the university in 1584, he was threatened with a criminal prosecution on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes * * * on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into present-day Alsace, and northern Switzerland, leading to the establishment of the Old High German language in those regions, by the eighth century named '' Alamannia''. In 496, the Alemanni were conquered by Frankish leader Clovis and incorporated into his dominions. Mentioned as still pagan allies of the Christian Franks, the Alemanni were gradually Christianized during the seventh century. The is a record of their customary law during this period. Until the eighth century, Frankish suzerainty over Alemannia was mostly nominal. After an uprising by Theudebald, Duke of Alamannia, though, Carloman executed the Alamannic nobility and installed Frankish dukes. During the later and weaker years of the Carolingian Empire, the Alemannic co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |