|
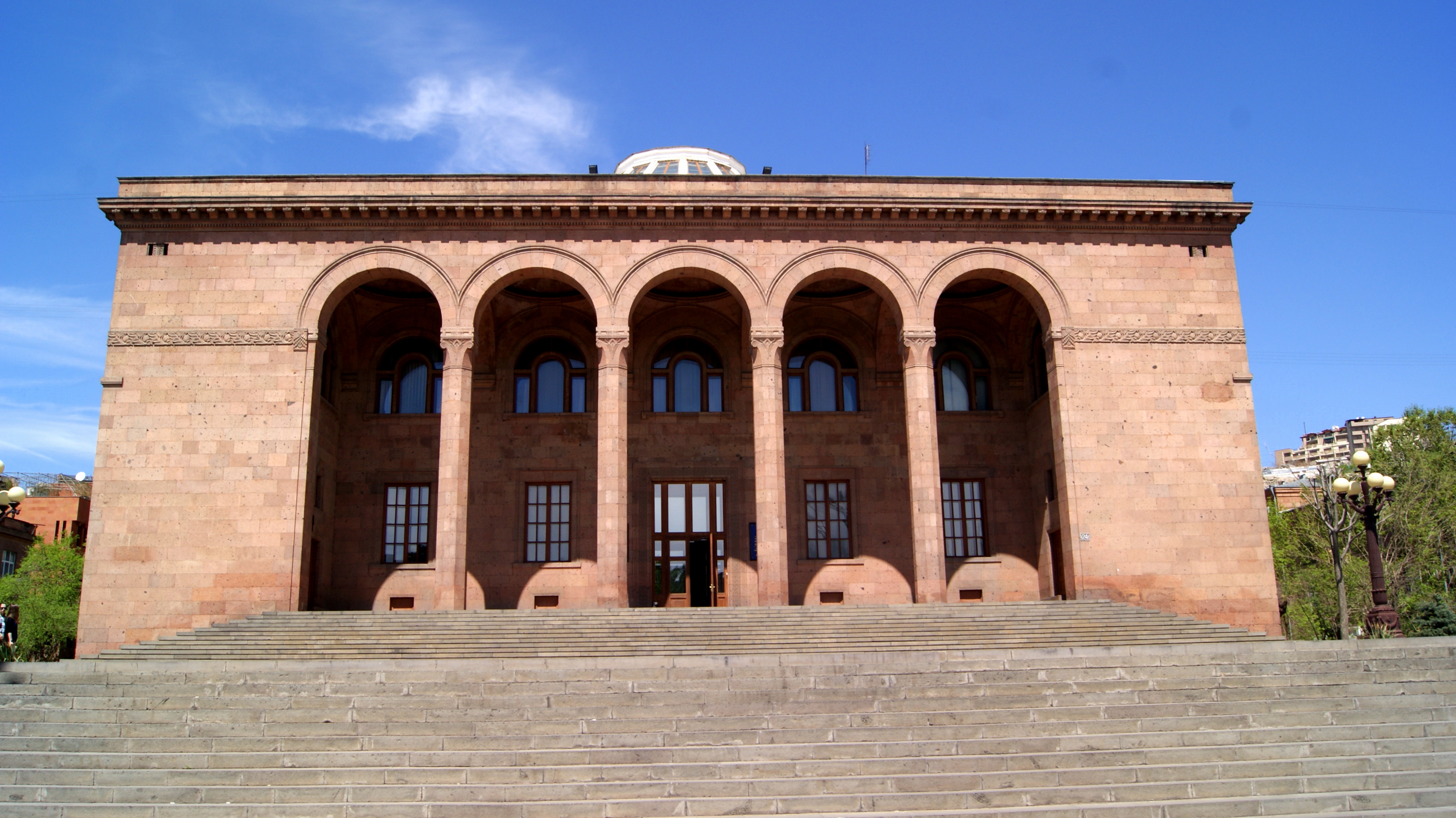
Byurakan Astrophysical Observatory
The Byurakan Astrophysical Observatory, or Byurakan Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the Armenian Academy of Sciences. It is located on the slope of Mount Aragats in the village of Byurakan in Armenia. History Founded in 1946 by Viktor Hambardzumyan, it was one of the main astronomy centers of the USSR. The buildings were designed by architect Samvel Safarian. The hotel, central building and structures are for astronomical instruments. The observatory has discovered special star clusters — stellar associations (1947), more than 1,000 flare stars, dozens of supernovae, hundreds of Herbig–Haro objects and cometary nebulae, hundreds of galaxies. The first conference was held in November 1951 on the topic of stellar associations. On 19 September 1956 a major meeting on non-stable stars was held. It has been the site of two major conferences on SETI, and is recognised as the regional center for astronomical research. Directors included V.A. Ambart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Academy Of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Armenia (NAS RA) ( hy, Հայաստանի Հանրապետության գիտությունների ազգային ակադեմիա, ՀՀ ԳԱԱ, ''Hayastani Hanrapetut’yan gitut’yunneri azgayin akademia'') is the Armenian national academy, functioning as the primary body that conducts research and coordinates activities in the fields of science and social sciences in Armenia. It is a member of the International Science Council. History The Academy of Sciences of the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic was founded on 10 November 1943, on the basis of the Armenian Branch of the Soviet Academy of Sciences, which was established almost 10 years earlier, in 1935. Among its founders were Joseph Orbeli, Stepan Malkhasyants, Ivan Gevorkian and Victor Ambartsumian; Orbeli became the first president of the academy. Presidents *Joseph Orbeli (1943–1947) *Victor Ambartsumian (1947–1993) *Fadey Sargsyan (1993–2006) * Radik Martiro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. Galaxies, averaging an estimated 100 million stars, range in size from dwarfs with less than a hundred million stars, to the largest galaxies known – supergiants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting its galaxy's center of mass. Most of the mass in a typical galaxy is in the form of dark matter, with only a few percent of that mass visible in the form of stars and nebulae. Supermassive black holes are a common feature at the centres of galaxies. Galaxies are categorized according to their visual morphology as elliptical, spiral, or irregular. Many are thought to have supermassive black holes at their centers. The Milky Way's central black hole, known as Sagittarius A*, has a mass four million times greater than the Sun. As o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Observatories Built In The Soviet Union
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Egyptians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars. Nowadays, professional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Astronomical Observatories
This is a list of astronomical observatories ordered by name, along with initial dates of operation (where an accurate date is available) and location. The list also includes a final year of operation for many observatories that are no longer in operation. While other sciences, such as volcanology and meteorology, also use facilities called observatories for research and observations, this list is limited to observatories that are used to observe celestial objects. Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space-based, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Many modern telescopes and observatories are located in space to observe astronomical objects in wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum that cannot penetrate the Earth's atmosphere (such as ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays) and are thus impossible to observe using ground-based telescopes. Being above the atmosphere, these space observatories can also avoid the effects of atmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Dram
The dram ( hy, դրամ; sign: ֏; abbreviation: դր.; ISO code: AMD) is the currency of Armenia, and is also used in the neighboring unrecognized Republic of Artsakh. It was historically subdivided into 100 luma (). The Central Bank of Armenia is responsible for issuance and circulation of dram banknotes and coins, as well as implementing the monetary policy of Armenia. The word "dram" translates into English as "money" and is cognate with the Greek drachma and the Arabic dirham, as well as the English weight unit dram. The first instance of a dram currency was in the period from 1199 to 1375, when silver coins called dram were issued. History On 21 September 1991, a national referendum proclaimed Armenia as a republic independent from the Soviet Union. The Central Bank of Armenia, established on 27 March 1993, was given the exclusive right of issuing the national currency. In the immediate aftermath of the collapse of the Soviet Union attempts were made to maintain a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
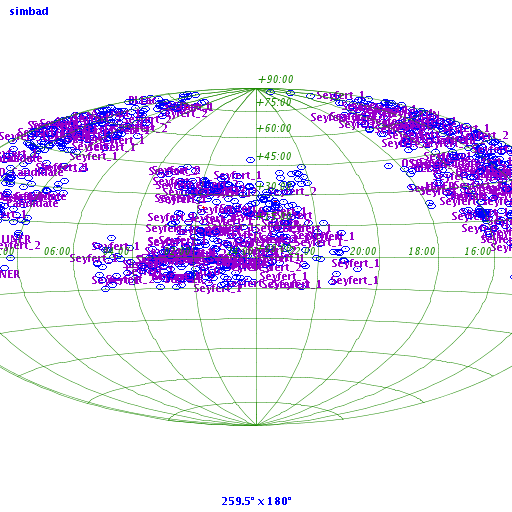
Mrk 501
Markarian 501 (or Mrk 501) is a galaxy with a spectrum extending to the highest energy gamma rays. It is a blazar or BL Lac object, which is an active galactic nucleus with a jet that is shooting towards the Earth. In the very-high-energy gamma ray region of the spectrum, at energies above 1011 eV (0.1 TeV), it is the brightest object in the sky. The object has a redshift of z = 0.034. The galaxy hosting the blazar was studied and catalogued by Benjamin Markarian in 1974. It was first determined to be a very high energy gamma ray emitter in 1996 by John Quinn at the Whipple Observatory. Galaxy The elliptical galaxy is located in the constellation of Hercules at right ascension 16h 53.9m and declination +39° 45'. Its visible size appears to be 1.2 by 1 minute of arc. Gamma rays The gamma rays from Mrk 501 are extremely variable, undergoing violent outbursts. The gamma ray spectrum of Mrk 501 shows two humps. One is below 1 keV and can be considered to be X-rays and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markarian Galaxies
The Markarian galaxies are a class of galaxies that have nuclei with excessive amounts of ultraviolet emissions compared with other galaxies. Benjamin Markarian drew attention to these types of galaxies starting in 1963. The nuclei of the galaxies had a blue colour, associated to stars in the classes from O to A. This blue core did not match the rest of the galaxy. The spectrum in detail tends to show a continuum that Markarian concluded was produced non- thermally. Most of these have emission lines and are characterized by highly energetic activity. Markarian Catalogue entries are of the form "Markarian ####", and can frequently use the abbreviations Mrk, Mkr, Mkn; and rarely Ma, Mk, Mark. History In 1964 Markarian decided to search for this kind of galaxy. The First Byurakan Survey commenced in 1965 using the Schmidt telescope at the Byurakan Astrophysical Observatory in Armenian SSR. The telescope used a 132 cm mirror and 102 cm correcting plate. When this st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmidt Telescope
Schmidt may refer to: * Schmidt (surname), including list of people with the surname * Schmidt (singer) (born 1990), German pop and jazz singer * Schmidt (lunar crater), a small lunar impact crater * Schmidt (Martian crater), a crater on Mars * Schmidt (volcano), in Kamchatka * Schmidt Block, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Scott County, Iowa, USA * Schmidt Brewery, a St. Paul brewery * Schmidt camera, an astronomical telescope designed for photography * Schmidt–Cassegrain telescope, a version of the Schmidt camera * Schmidt Site, an archeological site in Michigan, USA, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973 * Schmidt Spiele, a German games manufacturer * Schmidt Baking Company, makers of Schmidt's Blue Ribbon Bread * von Schmidt auf Altenstadt, a German baronial family in Kirchgattendorf, part of the municipality of Gattendorf * Schmidt Island, an island in the Novaya Zemlya archipelago in the Arctic Ocean * Schmidt Peninsula (Sakhal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmidt Camera
A Schmidt camera, also referred to as the Schmidt telescope, is a catadioptric astrophotographic telescope designed to provide wide fields of view with limited aberrations. The design was invented by Bernhard Schmidt in 1930. Some notable examples are the Samuel Oschin telescope (formerly Palomar Schmidt), the UK Schmidt Telescope and the ESO Schmidt; these provided the major source of all-sky photographic imaging from 1950 until 2000, when electronic detectors took over. A recent example is the Kepler space telescope exoplanet finder. Other related designs are the Wright camera and Lurie–Houghton telescope. Invention and design The Schmidt camera was invented by German–Estonian optician Bernhard Schmidt in 1930. Its optical components are an easy-to-make spherical primary mirror, and an aspherical correcting lens, known as a Schmidt corrector plate, located at the center of curvature of the primary mirror. The film or other detector is placed inside the camera, at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
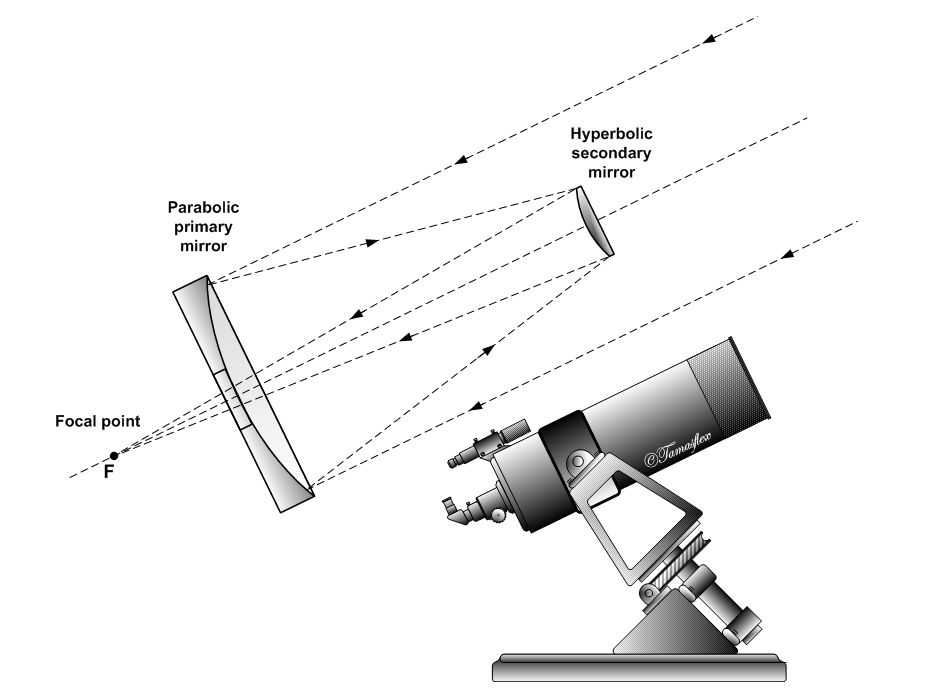
Cassegrain Reflector
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the primary mirror (or both). The classic Cassegrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SETI
The search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI) is a collective term for scientific searches for intelligent extraterrestrial life, for example, monitoring electromagnetic radiation for signs of transmissions from civilizations on other planets. Scientific investigation began shortly after the advent of radio in the early 1900s, and focused international efforts have been ongoing since the 1980s. In 2015, Stephen Hawking and Israeli billionaire Yuri Milner announced a project called Breakthrough Listen. History Early work There have been many earlier searches for extraterrestrial intelligence within the Solar System. In 1896, Nikola Tesla suggested that an extreme version of his wireless electrical transmission system could be used to contact beings on Mars. In 1899, while conducting experiments at his Colorado Springs experimental station, he thought he had detected a signal from Mars since an odd repetitive static signal seemed to cut off when Mars set in the night ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbig–Haro Object
Herbig–Haro (HH) objects are bright patches of nebula, nebulosity associated with newborn stars. They are formed when narrow jets of partially plasma (physics), ionised gas ejected by stars collide with nearby clouds of gas and dust at several hundred kilometres per second. Herbig–Haro objects are commonly found in Star formation#Stellar nurseries, star-forming regions, and several are often seen around a single star, aligned with its axis of rotation, rotational axis. Most of them lie within about one parsec (3.26 light-years) of the source, although some have been observed several parsecs away. HH objects are transient phenomena that last around a few tens of thousands of years. They can change visibly over timescales of a few years as they move rapidly away from their parent star into the gas clouds of interstellar space (the interstellar medium or ISM). Hubble Space Telescope observations have revealed the complex evolution of HH objects over the period of a few years, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |