|
Burials At Christ Church Cathedral, Oxford
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objects in it, and covering it over. A funeral is a ceremony that accompanies the final disposition. Humans have been burying their dead since shortly after the origin of the species. Burial is often seen as indicating respect for the dead. It has been used to prevent the odor of decay, to give family members closure and prevent them from witnessing the decomposition of their loved ones, and in many cultures it has been seen as a necessary step for the deceased to enter the afterlife or to give back to the cycle of life. Methods of burial may be heavily ritualized and can include natural burial (sometimes called "green burial"); embalming or mummification; and the use of containers for the dead, such as shrouds, coffins, grave liners, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cremation
Cremation is a method of final disposition of a dead body through burning. Cremation may serve as a funeral or post-funeral rite and as an alternative to burial. In some countries, including India and Nepal, cremation on an open-air pyre is an ancient tradition. Starting in the 19th century, cremation was introduced or reintroduced into other parts of the world. In modern times, cremation is commonly carried out with a closed furnace (cremator), at a crematorium. Cremation leaves behind an average of 2.4 kg (5.3 lbs) of remains known as "ashes" or "cremains". This is not all ash but includes unburnt fragments of bone mineral, which are commonly ground into powder. They do not constitute a health risk and may be buried, interred in a memorial site, retained by relatives or scattered in various ways. History Ancient Cremation dates from at least 17,000 years ago in the archaeological record, with the Mungo Lady, the remains of a partly cremated body found at La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kebara Cave
Kebara Cave ( he, מערת כבארה, Me'arat Kebbara, ar, مغارة الكبارة, Mugharat al-Kabara) is a limestone cave locality in Wadi Kebara, situated at above sea level on the western escarpment of the Carmel Range, in the Ramat HaNadiv preserve of Zichron Yaakov. History The cave was inhabited between 60,000 and 48,000 BP and is famous for its excavated finds of hominid remains. Dorothy Garrod and Francis Turville-Petre excavated in the cave in the early 1930s. Excavations have since yielded a large number of human remains associated with a Mousterian archaeological context. The first specimen discovered in 1965, during the excavations of M. Stekelis, was an incomplete infant skeleton (Kebara 1). The most significant discovery made at Kebara Cave was Kebara 2 in 1982, the most complete postcranial Neanderthal skeleton found to date. Nicknamed "Moshe" and dating to ''circa'' 60,000 BP, the skeleton preserved a large part of one individual's torso ( vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanidar
Shanidar Cave ( ku, Zewî Çemî Şaneder ,ئەشکەوتی شانەدەر, ) is an archaeological site located on Bradost Mountain, within the Zagros Mountains, in the Erbil Governorate of Kurdistan Region in northern Iraq. It is known for the discovery of Neanderthal remains at the site, most notably Shanidar 1, who survived several injuries during his life, possibly due to care from others in his group, and Shanidar 4, the famed 'flower burial'."Shanidar Cave." ''Shanidar Cave , Unbelievable Kurdistan – Official Tourism Site of Kurdistan'', http://bot.gov.krd/erbil-province-mirgasor/history-and-heritage/shanidar-cave Until this discovery, Cro-Magnons, the earliest known ''H. sapiens'' in Europe, were the only individuals known for purposeful, ritualistic burials. Archaeology The site, 1/2 mile from the Great Zab river and near Rowanduz, lies at 2100 feet above sea level. The cave entrance is triangular, 82 feet wide by 26 high. Its dimensions are, at maximum, 175 feet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital media, digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as ''The Daily (podcast), The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones (publisher), George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won List of Pulitzer Prizes awarded to The New York Times, 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national "newspaper of record". For print it is ranked List of newspapers by circulation, 18th in the world by circulation and List of newspapers in the United States, 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is Public company, publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 189 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
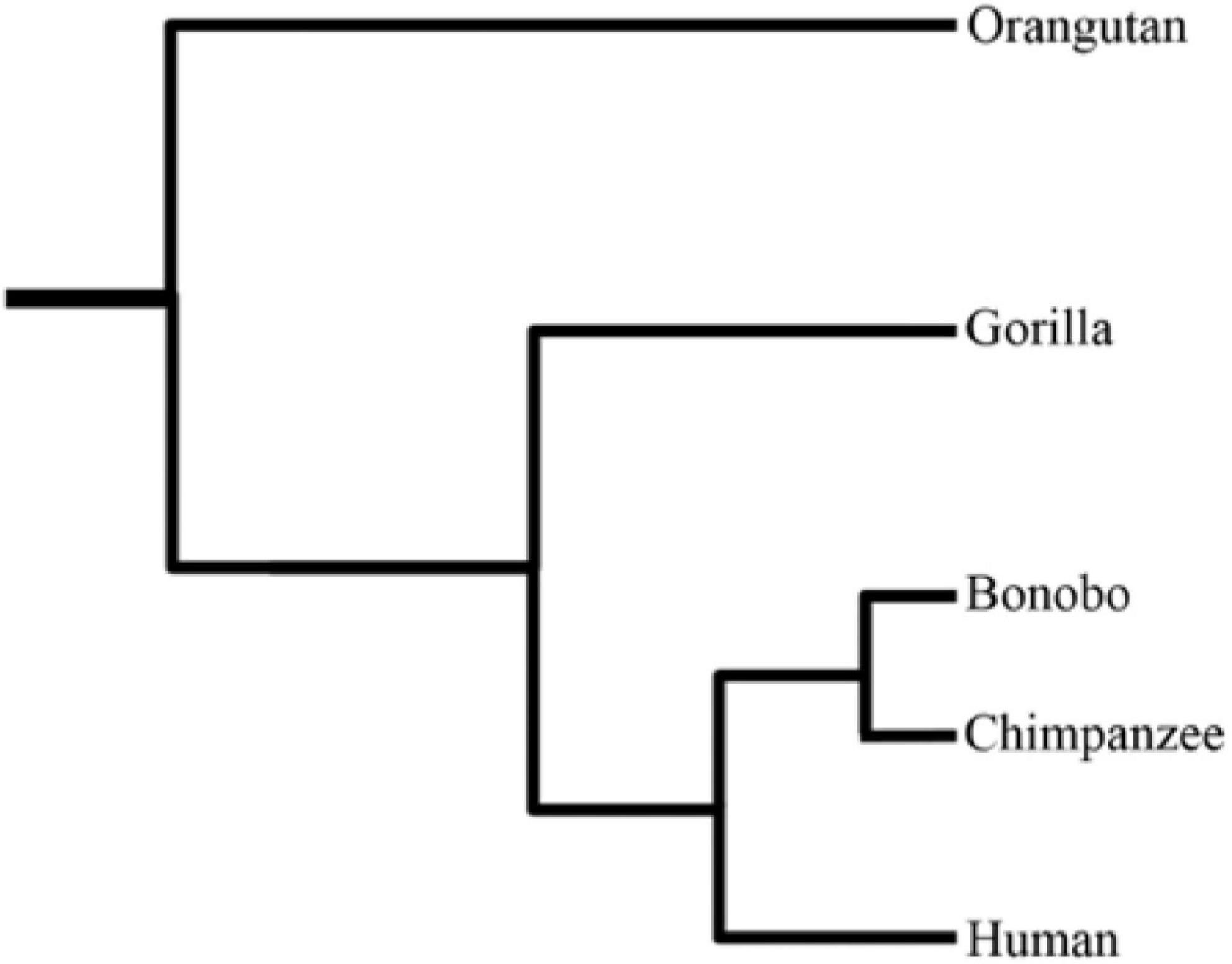
Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus '' Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely related to modern humans (depending on the species), most notably '' Homo erectus'' and ''Homo neanderthalensis''. The genus emerged with the appearance of '' Homo habilis'' just over 2 million years ago. ''Homo'', together with the genus '' Paranthropus'', is probably sister to '' Australopithecus africanus'', which itself had previously split from the lineage of '' Pan'', the chimpanzees. '' Homo erectus'' appeared about 2 million years ago and, in several early migrations, spread throughout Africa (where it is dubbed ''Homo ergaster'') and Eurasia. It was likely that the first human species lived in a hunter-gatherer society and was able to control fire. An adaptive and successful species, ''Homo erectus'' persisted for more than a millio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neanderthals
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the "causes of Neanderthal disappearance about 40,000 years ago remain highly contested," demographic factors such as small population size, inbreeding and genetic drift, are considered probable factors. Other scholars have proposed competitive replacement, assimilation into the modern human genome (bred into extinction), great climatic change, disease, or a combination of these factors. It is unclear when the line of Neanderthals split from that of modern humans; studies have produced various intervals ranging from 315,000 to more than 800,000 years ago. The date of divergence of Neanderthals from their ancestor '' H. heidelbergensis'' is also unclear. The oldest potential Neanderthal bones date to 430,000 years ago, but the classifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Lieberman
Philip Lieberman (October 25, 1934 – July 12, 2022) was a cognitive scientist at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island, United States. Originally trained in phonetics, he wrote a dissertation on intonation. His career focused on topics in the evolution of language, and particularly the relationship between the evolution of the vocal tract, the human brain, and the evolution of speech, cognition and language. Biography Lieberman initially studied electrical engineering at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). He received his doctorate in linguistics from MIT, completing his dissertation in 1966. In the late 1950s and 1960s he worked as a research assistant before serving in the United States Air Force, carrying out research at the Air Force Cambridge Research Laboratories (AFCRL) and Hanscom Air Force Base as well as working at Haskins Laboratories. From 1967 to 1974 he worked at the University of Connecticut. In 1974 he was appointed to the faculty at Bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burial IMG 1858
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objects in it, and covering it over. A funeral is a ceremony that accompanies the final disposition. Humans have been burying their dead since shortly after the origin of the species. Burial is often seen as indicating respect for the dead. It has been used to prevent the odor of decay, to give family members closure and prevent them from witnessing the decomposition of their loved ones, and in many cultures it has been seen as a necessary step for the deceased to enter the afterlife or to give back to the cycle of life. Methods of burial may be heavily ritualized and can include natural burial (sometimes called "green burial"); embalming or mummification; and the use of containers for the dead, such as shrouds, coffins, grave liners, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogs
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it is derived from the extinct Pleistocene wolf, and the modern wolf is the dog's nearest living relative. Dogs were the first species to be domesticated by hunter-gatherers over 15,000 years ago before the development of agriculture. Due to their long association with humans, dogs have expanded to a large number of domestic individuals and gained the ability to thrive on a starch-rich diet that would be inadequate for other canids. The dog has been selectively bred over millennia for various behaviors, sensory capabilities, and physical attributes. Dog breeds vary widely in shape, size, and color. They perform many roles for humans, such as hunting, herding, pulling loads, protection, assisting police and the military, companionship, therapy, and aiding disabled people. Over the millennia, dogs became uniquely adapted to human behavior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephants
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and the order Proboscidea. The order was formerly much more diverse during the Pleistocene, but most species became extinct during the Late Pleistocene epoch. Distinctive features of elephants include a long proboscis called a trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, pillar-like legs, and tough but sensitive skin. The trunk is used for breathing, bringing food and water to the mouth, and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants have smaller ears, and convex or level backs. Elephants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative the bonobo was more commonly known as the pygmy chimpanzee, this species was often called the common chimpanzee or the robust chimpanzee. The chimpanzee and the bonobo are the only species in the genus ''Pan''. Evidence from fossils and DNA sequencing shows that ''Pan'' is a sister taxon to the human lineage and is humans' closest living relative. The chimpanzee is covered in coarse black hair, but has a bare face, fingers, toes, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet. It is larger and more robust than the bonobo, weighing for males and for females and standing . The chimpanzee lives in groups that range in size from 15 to 150 members, although individuals travel and forage in much smaller groups during the day. The species lives i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)


_colourised.png)