|
Burial Of Christ
The burial of Jesus refers to the entombment of the body of Jesus after crucifixion, before the eve of the sabbath described in the New Testament. According to the canonical gospel narratives, he was placed in a tomb by a councillor of the sanhedrin named Joseph of Arimathea; according to , he was laid in a tomb by "the council as a whole." In art, it is often called the Entombment of Christ. Biblical accounts The earliest reference to a burial of Jesus is in a letter of Paul. Writing to the Corinthians around the year 54 AD, he refers to the account he had received of the death and resurrection of Jesus ("and that he was buried, and that he was raised on the third day according to the Scriptures"). The four canonical gospels, written between 66 and 95, conclude with an extended narrative of Jesus' arrest, trial, crucifixion, entombment, and resurrection.Powell, Mark A. ''Introducing the New Testament''. Baker Academic, 2009. They narrate how, on the evening of the Cruci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caravaggio - La Deposizione Di Cristo
Michelangelo Merisi (Michele Angelo Merigi or Amerighi) da Caravaggio, known as simply Caravaggio (, , ; 29 September 1571 – 18 July 1610), was an Italian painter active in Rome for most of his artistic life. During the final four years of his life he moved between Naples, Malta, and Sicily until his death. His paintings have been characterized by art critics as combining a realistic observation of the human state, both physical and emotional, with a dramatic use of lighting, which had a formative influence on Baroque painting. Caravaggio employed close physical observation with a dramatic use of chiaroscuro that came to be known as tenebrism. He made the technique a dominant stylistic element, transfixing subjects in bright shafts of light and darkening shadows. Caravaggio vividly expressed crucial moments and scenes, often featuring violent struggles, torture, and death. He worked rapidly with live models, preferring to forgo drawings and work directly onto the canvas. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilate
Pontius Pilate (; grc-gre, Πόντιος Πιλᾶτος, ) was the fifth governor of the Roman province of Judaea, serving under Emperor Tiberius from 26/27 to 36/37 AD. He is best known for being the official who presided over the trial of Jesus and ultimately ordered his crucifixion. Pilate's importance in modern Christianity is underscored by his prominent place in both the Apostles' and Nicene Creeds. Due to the Gospels' portrayal of Pilate as reluctant to execute Jesus, the Ethiopian Church believes that Pilate became a Christian and venerates him as both a martyr and a saint, a belief which is historically shared by the Coptic Church. Although Pilate is the best-attested governor of Judaea, few sources regarding his rule have survived. Nothing is known about his life before he became governor of Judaea, and nothing is known about the circumstances that led to his appointment to the governorship. Coins that he minted have survived from Pilate's governorship, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New International Version
The New International Version (NIV) is an English translation of the Bible first published in 1978 by Biblica (formerly the International Bible Society). The ''NIV'' was created as a modern translation, by Bible scholars using the earliest and highest quality source manuscripts available, into broadly understood modern English. A team of 15 biblical scholars, representing a variety of evangelical denominations, worked from the oldest copies of reliable texts, variously written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek. Each section was subjected to multiple translations and revisions, and those assessed in detail to produce the best option. Everyday Bible readers were used to provide feedback on ease of understanding and comprehensibility. Finally, plans were made to continue revision of the Bible as new discoveries were made and as changes in the use of the English language occurred. The ''NIV'' is published by Zondervan in the United States and Hodder & Stoughton in the UK. The ''NIV' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aloes
Agarwood, aloeswood, eaglewood or gharuwood is a fragrant dark resinous wood used in incense, perfume, and small carvings. This resinous wood is most commonly referred to as "Oud" or "Oudh". It is formed in the heartwood of aquilaria trees when the Acquilara Tree becomes infected with a type of mold (''Phialophora parasitica'') and secretes a resin to combat the mold. Prior to infection, the heartwood is odourless, relatively light and pale coloured; however, as the infection progresses, the tree produces a dark aromatic resin, called aloes (not to be confused with ''Aloe ferox'', the succulent commonly known as the bitter aloe) or agar (not to be confused with the edible, algae-derived agar) as well as ''gaharu'', ''jinko'', ''oud'', or ''oodh'' ''aguru'' (not to be confused with bukhoor), in response to the attack, which results in a very dense, dark, resin-embedded heartwood. The resin-embedded wood is valued in East and South Asian cultures for its distinctive fragrance, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myrrh
Myrrh (; from Semitic, but see '' § Etymology'') is a gum-resin extracted from a number of small, thorny tree species of the genus ''Commiphora''. Myrrh resin has been used throughout history as a perfume, incense and medicine. Myrrh mixed with posca or wine was common across ancient cultures, for general pleasure, and as an analgesic. Extraction and production When a wound on a tree penetrates through the bark and into the sapwood, the tree secretes a resin. Myrrh gum, like frankincense, is such a resin. Myrrh is harvested by repeatedly wounding the trees to bleed the gum, which is waxy and coagulates quickly. After the harvest, the gum becomes hard and glossy. The gum is yellowish and may be either clear or opaque. It darkens deeply as it ages, and white streaks emerge. Myrrh gum is commonly harvested from the species ''Commiphora myrrha''. Another commonly used name, ''Commiphora molmol'', is now considered a synonym of ''Commiphora myrrha''. ''Commiphora myrrha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicodemus
Nicodemus (; grc-gre, Νικόδημος, Nikódēmos) was a Pharisee and a member of the Sanhedrin mentioned in three places in the Gospel of John: * He first visits Jesus one night to discuss Jesus' teachings (). * The second time Nicodemus is mentioned, he reminds his colleagues in the Sanhedrin that the law requires that a person be heard before being judged (). * Finally, Nicodemus appears after the Crucifixion of Jesus to provide the customary embalming spices, and assists Joseph of Arimathea in preparing the body of Jesus for burial (). An apocryphal work under his name—the Gospel of Nicodemus—was produced in the mid-4th century, and is mostly a reworking of the earlier Acts of Pilate, which recounts the Harrowing of Hell. Although there is no clear source of information about Nicodemus outside the Gospel of John, Ochser and Kohler (in an article in ''The Jewish Encyclopedia'') and some historians have speculated that he could be identical to Nicodemus ben Gurion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel Of Luke
The Gospel of Luke), or simply Luke (which is also its most common form of abbreviation). tells of the origins, birth, ministry, death, resurrection, and ascension of Jesus Christ. Together with the Acts of the Apostles, it makes up a two-volume work which scholars call Luke–Acts, accounting for 27.5% of the New Testament. The combined work divides the history of first-century Christianity into three stages, with the gospel making up the first two of these – the life of Jesus the Messiah from his birth to the beginning of his mission in the meeting with John the Baptist, followed by his ministry with events such as the Sermon on the Plain and its Beatitudes, and his Passion, death, and resurrection. Most modern scholars agree that the main sources used for Luke were a), the Gospel of Mark, b), a hypothetical sayings collection called the Q source, and c), material found in no other gospels, often referred to as the L (for Luke) source. The author is anonymous; the tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal (emblem)
A seal is a device for making an impression in Sealing wax, wax, clay, paper, or some other medium, including an embossment on paper, and is also the impression thus made. The original purpose was to authenticate a document, or to prevent interference with a package or envelope by applying a seal which had to be broken to open the container (hence the modern English verb "to seal", which implies secure closing without an actual wax seal). The seal-making device is also referred to as the seal ''matrix'' or ''die''; the imprint it creates as the seal impression (or, more rarely, the ''sealing''). If the impression is made purely as a relief resulting from the greater pressure on the paper where the high parts of the matrix touch, the seal is known as a ''dry seal''; in other cases ink or another liquid or liquefied medium is used, in another color than the paper. In most traditional forms of dry seal the design on the seal matrix is in Intaglio (sculpture), intaglio (cut below th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel Of Matthew
The Gospel of Matthew), or simply Matthew. It is most commonly abbreviated as "Matt." is the first book of the New Testament of the Bible and one of the three synoptic Gospels. It tells how Israel's Messiah, Jesus, comes to his people and forms a community of disciples, of how he taught the people through such events as the Sermon on the Mount and its Beatitudes, and how Israel becomes divided and how Jesus condemns this hostile Israel. This culminates in his departure from the Temple and his execution. At this point many people reject Jesus, and on his resurrection he sends the disciples to the gentiles. Matthew seems to emphasize that the Jewish tradition should not be lost in a church that was increasingly becoming gentile. The gospel reflects the struggles and conflicts between the evangelist's community and the other Jews, particularly with its sharp criticism of the scribes and Pharisees with the position that through their rejection of Christ, the Kingdom of God h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for ''The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly descent and a mother who claimed royal ancestry. He initially fought against the Romans during the First Jewish–Roman War as head of Jewish forces in Galilee, until surrendering in 67 AD to Roman forces led by Vespasian after the six-week siege of Yodfat. Josephus claimed the Jewish Messianic prophecies that initiated the First Jewish–Roman War made reference to Vespasian becoming Emperor of Rome. In response, Vespasian decided to keep Josephus as a slave and presumably interpreter. After Vespasian became Emperor in 69 AD, he granted Josephus his freedom, at which time Josephus assumed the emperor's family name of Flavius.Simon Claude Mimouni, ''Le Judaïsme ancien du VIe siècle avant notre ère au IIIe siècle de notre ère : Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
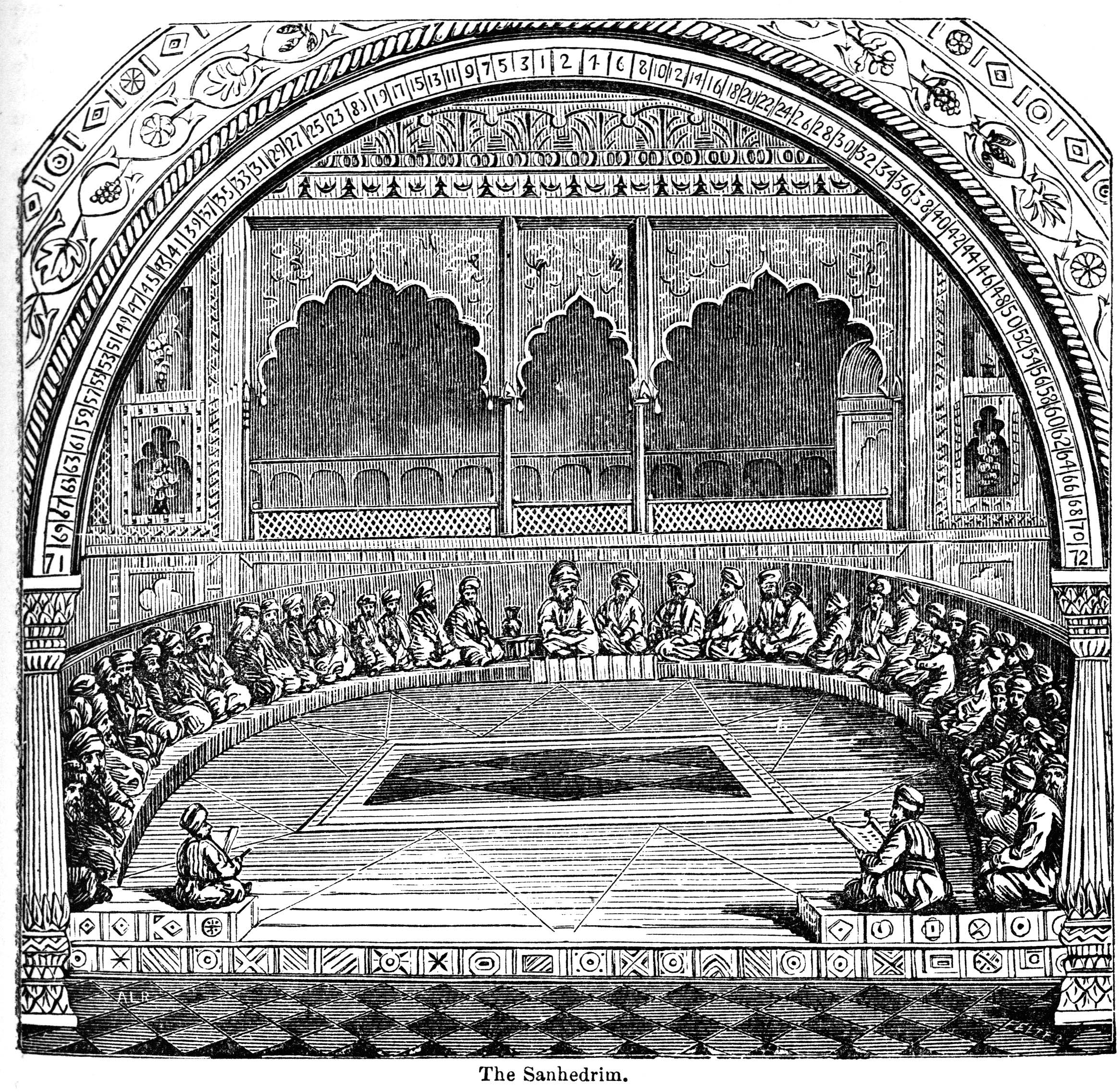
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , ''synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence 'assembly' or 'council') was an assembly of either 23 or 71 elders (known as "rabbis" after the destruction of the Second Temple), appointed to sit as a tribunal in every city in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite Jewish courts which were called Sanhedrin, the Great Sanhedrin and the Lesser Sanhedrin. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city, but there was only supposed to be one Great Sanhedrin of 71 judges, which among other roles acted as the Supreme Court, taking appeals from cases which were decided by lesser courts. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier normally refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the ''Nasi'', who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the ''Av Beit Din'' or the chief of the court, who was second to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcan Priority
Marcan priority is the hypothesis that the Gospel of Mark was the first of the three synoptic gospels to be written, and was used as a source by the other two (Matthew and Luke). It is a central element in discussion of the synoptic problem; the question of the documentary relationship among these three gospels. Most scholars since the late 19th century have accepted the concept of Marcan priority, although a number of scholars support different forms of Marcan priority or reject it altogether. It forms the foundation for the widely accepted two-source theory. History The tradition handed down by the Church Fathers regarded Matthew as the first Gospel written in Hebrew, which was later used as a source by Mark and Luke. It is seen as early as in Irenaeus's book '' Against Heresies''. Irenaeus, Against Heresies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)