|
Bureau Of Buddhist And Tibetan Affairs
__NOTOC__ The Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs, or Xuanzheng Yuan () was a government agency of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty of China to handle Buddhist affairs across the empire in addition to managing the territory of Tibet. It was originally set up by Kublai Khan in 1264 under the name Zongzhi Yuan () or the "Bureau of General Regulation", before it was renamed in 1288. The bureau was set up in Khanbaliq (modern Beijing) and was named after the Xuanzheng Hall where Tibetan envoys were received in the Tang dynasty. In the Yuan dynasty, Tibet was managed by the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs, separate from the other Yuan provinces such as those established in the former territories of the Song dynasty. While no modern equivalents remain, the political functions of the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs might have been analogous to the India Office in London during the British Raj. Besides holding the title of Imperial Preceptor or Dishi, Drogön Chögyal Phagp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty And Tibet
Yuan may refer to: Currency * Yuan (currency), the basic unit of currency in historic and contemporary mainland China and Taiwan ** Renminbi, the current currency used in mainland China, whose basic unit is yuan ** New Taiwan dollar, the current currency used in Taiwan, whose basic unit is yuán in Mandarin ** Manchukuo yuan, the unit of currency that was used in the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo Governmental organ * "Government branch" or "Court" (), the Chinese name for a kind of executive institution. Government of Taiwan * Control Yuan * Examination Yuan * Executive Yuan * Judicial Yuan * Legislative Yuan Government of Imperial China * Xuanzheng Yuan, or Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs during the Yuan dynasty * Lifan Yuan during the Qing dynasty Dynasties * Yuan dynasty (元朝), a dynasty of China ruled by the Mongol Borjigin clan ** Northern Yuan dynasty (北元), the Yuan dynasty's successor state in northern China and the Mongolian Plateau People and langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive varieties of the Chinese language. The estimated 1.4 billion Han Chinese people, worldwide, are primarily concentrated in the People's Republic of China (including Mainland China, Hong Kong and Macau) where they make up about 92% of the total population. In the Republic of China (Taiwan), they make up about 97% of the population. People of Han Chinese descent also make up around 75% of the total population of Singapore. Originating from Northern China, the Han Chinese trace their cultural ancestry to the Huaxia, the confederation of agricultural tribes living along the Yellow River. This collective Neolithic confederation included agricultural tribes Hua and Xia, hence the name. They settled along the Central Plains around the middle a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Administration For Religious Affairs
The State Administration for Religious Affairs (SARA) was an executive agency directly under the State Council of the People's Republic of China which oversaw religious affairs in the country. Originally created in 1951 as the Religious Affairs Bureau, SARA was closely connected with the United Front Work Department of the Central Committee of the Chinese Communist Party and charged with overseeing the operations of China's five officially sanctioned religious organizations: * Buddhist Association of China * Chinese Taoist Association * Islamic Association of China * Three-Self Patriotic Movement (Protestant) * Catholic Patriotic Association SARA was dissolved in 2018, placing all religious affairs directly under the United Front Work Department. History The State Administration for Religious Affairs was established to exercise control over religious appointments, the selection of clergy, and the interpretation of religious doctrine. SARA was also meant to ensure that the regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Ethnic Affairs Commission
The National Ethnic Affairs Commission is a cabinet-level executive department of the State Council of the People's Republic of China under the formal leadership of the United Front Work Department that is responsible for relations between the Chinese government and ethnic minorities in China. It supervises the implementation - and monitors the performance - of national and regional systems to manage ethnic minorities. History In 2018, the NEAC was officially placed under the direct leadership of the United Front Work Department of the Central Committee of the Chinese Communist Party. In 2020, a Han Chinese was named director of the National Ethnic Affairs Commission for the first time since 1954. List of Ministers Subsidiary institutions * Publishing House of Minority Nationalities See also * Zhonghua minzu ** List of ethnic groups in China * Zhao Yannian, Vice Minister (1986–2003) Related PRC authorities * United Front Work Department (Chinese Communist Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolian And Tibetan Affairs Commission
The Mongolian and Tibetan Affairs Commission (MTAC) was a ministry-level commission of the Executive Yuan in the Republic of China. It was disbanded on 15 September 2017. History The first model was created during the Qing dynasty in 1636 as the Mongolian Bureau (; mnc, , z=Monggo jurgan), later reformed into the Lifan Yuan in 1639, and oversaw the relationship of the Qing court to its Mongolian and Tibetan territories. During the reign of the Kangxi Emperor, the bureau was renamed to Minority Affairs Council. In 1906, during the reign of the Guangxu Emperor, it was renamed to Ministry of Minority Affairs (理藩部). Following the Xinhai Revolution and the collapse of the Qing dynasty, the section was replaced by Mongolian and Tibetan Affairs Agency under the Ministry of the Interior in April 1912. In July 1912, the agency was again renamed as Bureau of Mongolian and Tibetan Affairs and placed under the State Affairs Yuan. In 1914, it was reorganized and being placed di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dpon-chen
The ''dpon-chen'' or ''pönchen'' (), literally the "great authority" or "great administrator", was the chief administrator or governor of Tibet located at Sakya Monastery during the Yuan administrative rule of Tibet in the 13th and 14th centuries. In the Mongol Empire the office of the dpon-chen was established in the 1260s and functioned as the Tibetan government serving the Mongol emperors of the Yuan dynasty, unlike the Sakya Imperial Preceptors (''Dishi'') who were active at the Yuan court. The Mongols set up a government agency and top-level administrative department known as the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs in Khanbaliq (modern Beijing) that supervised Buddhist monks in addition to managing the territory of Tibet; one of the department's purposes was to select a dpon-chen to govern Tibet when the Sakya Lama (e.g. Drogön Chögyal Phagpa) was away. The Dpon-Chen was invariably a Tibetan nominated by the ruling Sakya Lama and approved by the reigning emperor. His fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
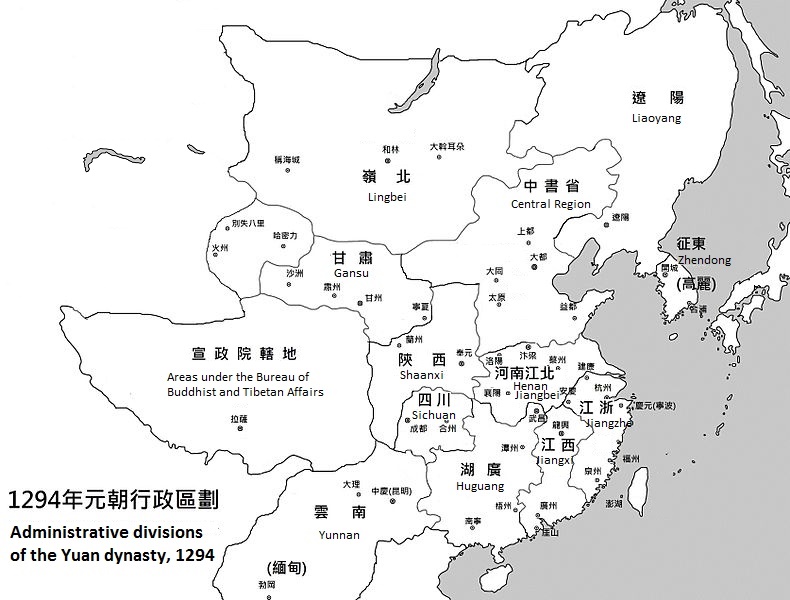
Administrative Divisions Of The Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty was a Mongol-led imperial Chinese dynasty. During its existence, its territory was divided into the Central Region (腹裏) governed by the Central Secretariat (Zhongshu Sheng) and places under control of various provinces (行省) or Branch Secretariats (行中書省), as well as the region under the Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs (Xuanzheng Yuan). In addition, the Yuan emperors held nominal suzerainty over the western Mongol khanates, but in reality none of them were governed by the Yuan dynasty due to the division of the Mongol Empire. Overview The most important part of the Yuan Empire was the Central Region, which covered the region of the Yuan capital Khanbaliq (Dadu, modern Beijing). The Central Region consisted of present-day Hebei, Shandong, Shanxi, the south-eastern part of present-day Inner Mongolia and the Henan areas to the north of the Yellow River. Since it was considered the most important region of the dynasty, it was directly govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lifan Yuan
The Lifan Yuan (; ; Mongolian: Гадаад Монголын төрийг засах явдлын яам, ''γadaγadu mongγul un törü-yi jasaqu yabudal-un yamun'') was an agency in the government of the Qing dynasty of China which administered the empire's Inner Asian territories such as Mongolia and oversaw the appointments of Ambans in Tibet. Until the 1860s, it was also responsible for the Qing's relations with the Russian Empire. Name The name Lifan Yuan has various translations in English, including the ''Board for National Minority Affairs'', ''Court of Territorial Affairs'', ''Board for the Administration of Outlying Regions'', ''Office for Relations with Principalities'', ''Office of Barbarian Control'', ''Office of Mongolian and Tibetan Affairs'' and ''Court of Colonial Affairs''. etc. The office was initially known as the Mongol Yamen (; , lit. the Mongol department) when it was first created in 1636. In 1639 the department was renamed and expanded to "Lifan Yuan" in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Buddhism
Chinese Buddhism or Han Buddhism ( zh, s=汉传佛教, t=漢傳佛教, p=Hànchuán Fójiào) is a Chinese form of Mahayana Buddhism which has shaped Chinese culture in a wide variety of areas including art, politics, literature, philosophy, medicine and material culture. Chinese Buddhism is the largest institutionalized religion in Mainland China.Cook, Sarah (2017). The Battle for China's Spirit: Religious Revival, Repression, and Resistance under Xi Jinping.' Freedom House Report. Rowman & Littlefield. Currently, there are an estimated 185 to 250 million Chinese Buddhists in the People's Republic of China. It is also a major religion in Taiwan, Singapore, and Malaysia, as well as among the Chinese Diaspora. Buddhism was first introduced to China during the Han Dynasty (202 BCE–220 CE). The translation of a large body of Indian Buddhist scriptures into Chinese and the inclusion of these translations (along with Taoist and Confucian works) into a Chinese Buddh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song often came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The dynasty is divided into two periods: Northern Song and Southern Song. During the Northern Song (; 960–1127), the capital was in the northern city of Bianjing (now Kaifeng) and the dynasty controlled most of what is now Eastern China. The Southern Song (; 1127–1279) refers to the period after the Song lost control of its northern half to the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in the Jin–Song Wars. At that time, the Song court retreated south of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hangzhou
Hangzhou ( or , ; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), also romanized as Hangchow, is the capital and most populous city of Zhejiang, China. It is located in the northwestern part of the province, sitting at the head of Hangzhou Bay, which separates Shanghai and Ningbo. Hangzhou grew to prominence as the southern terminus of the Grand Canal and has been one of China's most renowned and prosperous cities for much of the last millennium. It is a major economic and e-commerce hub within China, and the second biggest city in Yangtze Delta after Shanghai. Hangzhou is classified as a sub-provincial city and forms the core of the Hangzhou metropolitan area, the fourth-largest in China after Guangzhou-Shenzhen Pearl River agglomeration, Shanghai-Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou conurbation and Beijing. As of 2019, the Hangzhou metropolitan area was estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product ( nominal) of 3.2 trillion yuan ($486.53 billion), making it larger than the economy of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |