|
Buncrana
Buncrana ( ; ) is a town in County Donegal, Ireland. It is beside Lough Swilly on the Inishowen peninsula, northwest of Derry and north of Letterkenny. In the 2016 census, the population was 6,785 making it the second most populous town in County Donegal, after Letterkenny, and the largest in Inishowen. Buncrana is the historic home of the O'Doherty family, O'Doherty clan and originally developed around the defensive tower known as O'Doherty's Keep at the mouth of the River Crana. The town moved to its present location just south of the River Crana when George Vaughan built the main street in 1718. The town was a major centre for the textile industry in County Donegal from the 19th century until the mid-2000s (decade). History O'Doherty's Keep On the northern bank of the River Crana as it enters Lough Swilly sits the three-storey O'Doherty's Keep, which is the only surviving part of an original 14th-century Norman architecture, Norman castle. The first two levels of the kee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buncrana O'Daherty's Castle N 2014 09 12
Buncrana ( ; ) is a town in County Donegal, Ireland. It is beside Lough Swilly on the Inishowen peninsula, northwest of Derry and north of Letterkenny. In the 2016 census, the population was 6,785 making it the second most populous town in County Donegal, after Letterkenny, and the largest in Inishowen. Buncrana is the historic home of the O'Doherty clan and originally developed around the defensive tower known as O'Doherty's Keep at the mouth of the River Crana. The town moved to its present location just south of the River Crana when George Vaughan built the main street in 1718. The town was a major centre for the textile industry in County Donegal from the 19th century until the mid-2000s (decade). History O'Doherty's Keep On the northern bank of the River Crana as it enters Lough Swilly sits the three-storey O'Doherty's Keep, which is the only surviving part of an original 14th-century Norman castle. The first two levels of the keep were built after 1333. In 1601 the O' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inishowen
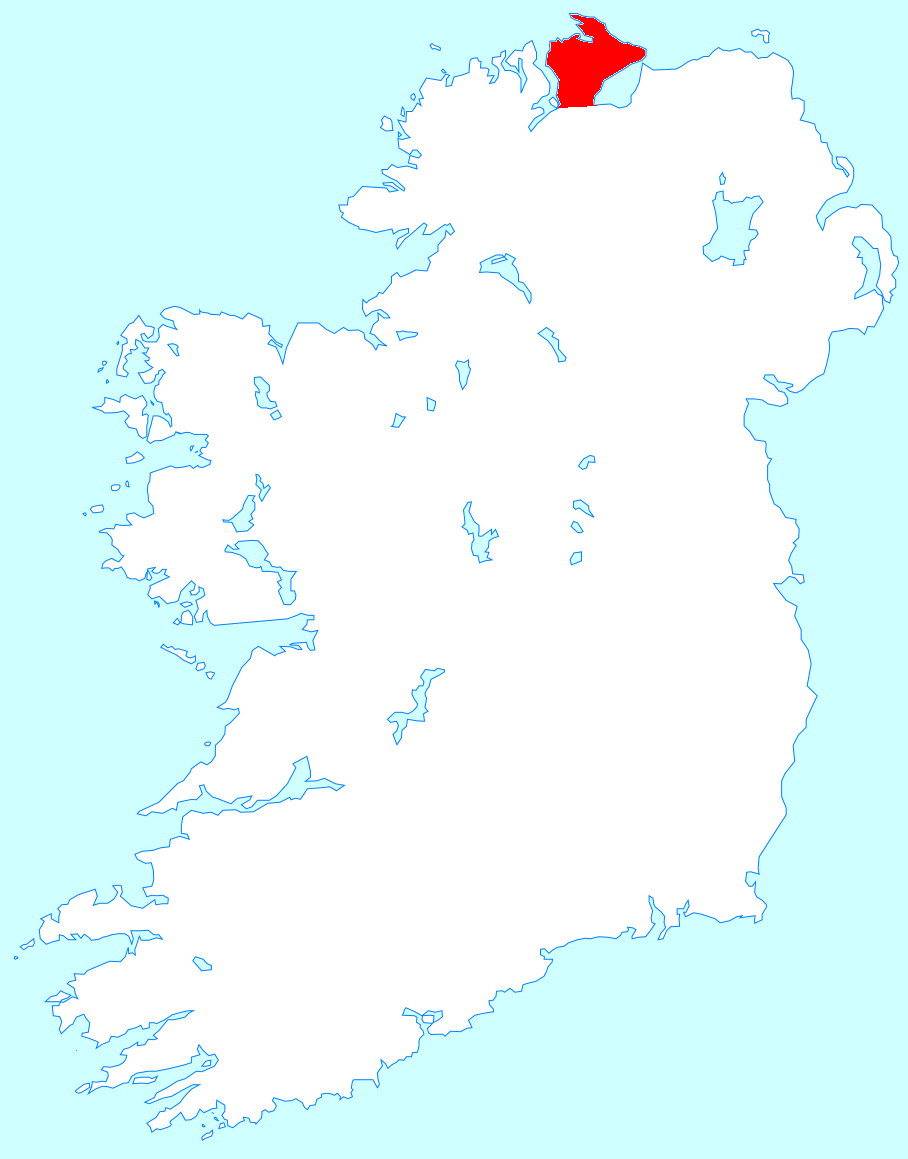
Inishowen () is a peninsula in the north of County Donegal in Ireland. Inishowen is the largest peninsula on the island of Ireland. The Inishowen peninsula includes Ireland's most northerly point, Malin Head. The Grianan of Aileach, a ringfort that served as the royal seat of the over-kingdom of Ailech, stands at the entrance to the peninsula. Towns and villages The main towns and villages of Inishowen are: * Ballyliffin, Buncrana, Bridgend, Burnfoot, Burt * Carndonagh, Carrowmenagh, Clonmany, Culdaff * Dunaff * Fahan * Glengad, Gleneely, Greencastle * Malin, Malin Head, Moville, Muff * Redcastle * Shrove * Quigley's Point * Urris Geography Inishowen is a peninsula of 884.33 square kilometres (218,523 acres), situated in the northernmost part of the island of Ireland. It is bordered to the north by the Atlantic Ocean, to the east by Lough Foyle, and to the west by Lough Swilly. It is joined at the south to the rest of the island and is mostly in County Donegal in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Donegal
County Donegal ( ; ga, Contae Dhún na nGall) is a county of Ireland in the province of Ulster and in the Northern and Western Region. It is named after the town of Donegal in the south of the county. It has also been known as County Tyrconnell (), after the historic territory of the same name, on which it was based. Donegal County Council is the local council and Lifford the county town. The population was 166,321 at the 2022 census. Name County Donegal is named after the town of Donegal () in the south of the county. It has also been known by the alternative name County Tyrconnell, Tirconnell or Tirconaill (, meaning 'Land of Conall'). The latter was its official name between 1922 and 1927. This is in reference to the kingdom of Tír Chonaill and the earldom that succeeded it, which the county was based on. History County Donegal was the home of the once-mighty Clann Dálaigh, whose best-known branch was the Clann Ó Domhnaill, better known in English as the O'Don ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lough Swilly
Lough Swilly () in Ireland is a glacial fjord or sea inlet lying between the western side of the Inishowen, Inishowen Peninsula and the Fanad Peninsula, in County Donegal. Along with Carlingford Lough and Killary Harbour it is one of three glacial fjords in Ireland. Geography and ecology Located on the Fanad Peninsula, in County Donegal, the northern extremities of the lough are marked by Fanad, Fanad Head with its lighthouse and Dunaff Head. Towns situated on the lough include Buncrana on Inishowen and Rathmullan on the western side. At the southern end of the lough lies Letterkenny. In the south of the lough a number of islands (Burt, Inch Island, Inch, Coney, Big Isle) were poldered and the land reclaimed during the 19th century for agriculture and the Londonderry and Lough Swilly Railway constructed embankments on the line from Derry to Letterkenny. These reclaimed lands are now wetlands associated with wildlife conservation and birdwatching, and support over 4,000 whooper s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O'Doherty Family
The O’Doherty family ( ga, Clann Ua DochartaigNorthern Uí Néill) is an Irish clan based in County Donegal in the north of the island of Ireland. Like clans in other cultures, Irish clans such as the O’Dohertys are divided into many septs and regional families. In the modern day, there are over 250 variations in spelling of the name Ó Dochartaigh, of which Doherty (with or without the "Ó") is the most common anglicisation. Naming conventions Origins The O’Dohertys are named after Dochartach (fl. 10th century), a member of the Cenél Conaill dynasty which in medieval Irish genealogy traced itself to Niall of the Nine Hostages (see Uí Néill). Their coat of arms is a gules rampant stag in an argent field, vert chief with three stars. The clan motto is ''Ár nDuthchas'' (English: Our heritage). In Munster O'Doherty is often a different surname, Ó Dubhartaigh, which has sometimes been anglicized as Doorty in Co. Clare. The O’Doherty clan and family name is on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derry
Derry, officially Londonderry (), is the second-largest city in Northern Ireland and the fifth-largest city on the island of Ireland. The name ''Derry'' is an anglicisation of the Old Irish name (modern Irish: ) meaning 'oak grove'. The old walled city lies on the west bank of the River Foyle, which is spanned by two road bridges and one footbridge. The city now covers both banks (Cityside on the west and Waterside on the east). The population of the city was 83,652 at the 2001 Census, while the Derry Urban Area had a population of 90,736. The district administered by Derry City and Strabane District Council contains both Londonderry Port and City of Derry Airport. Derry is close to the border with County Donegal, with which it has had a close link for many centuries. The person traditionally seen as the founder of the original Derry is Saint , a holy man from , the old name for almost all of modern County Donegal, of which the west bank of the Foyle was a part before 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eircode
A "postal address" in Ireland is a place of delivery defined by Irish Standard (IS) EN 14142-1:2011 ("Postal services. Address databases") and serviced by the universal service provider, '' An Post''. Its addressing guides comply with the guidelines of the Universal Postal Union (UPU), the United Nations-affiliated body responsible for promoting standards in the postal industry, across the world. In Ireland, 35% of Irish premises (over 600,000) have non-unique addresses due to an absence of house numbers or names. Before the introduction of a national postcode system (Eircode) in 2015, this required postal workers to remember which family names corresponded to which house in smaller towns, and many townlands,. As of 2021, An Post encourages customers to use Eircode because it ensures that their post person can pinpoint the exact location. Ireland was the last country in the OECD to create a postcode system. In July 2015 all 2.2 million residential and business addresses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Numbers In The Republic Of Ireland
Numbers on the Irish telephone numbering plan are regulated and assigned to operators by ComReg. Overview Telephone numbers in Ireland are part of an open numbering plan that allows variations in number length. The Irish format is similar to systems used in many parts of Europe, notably the Netherlands, Sweden, Germany, Belgium and France, where geographical numbers are organised using a logic of large regional prefixes, which are then further subdivided into smaller regions. It differs from UK numbering, which originated as alphanumeric codes based on town names. Irish Mobile and non–geographic numbers are fixed length and do not support local dialling. The trunk prefix 0 is used to access numbers outside the local area and for all mobile calls. This is followed by an area code, referred to as a National Dialling Code (NDC), the first digit of which indicates the geographical area or type of service (e.g. mobile). Calls made from mobile phones and some VoIP systems always ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donegal (Dáil Constituency)
Donegal is a parliamentary constituency which has been represented in Dáil Éireann, the lower house of the Irish parliament or Oireachtas, since the 2016 general election. The constituency elects 5 deputies ( Teachtaí Dála, commonly known as TDs) on the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote (PR-STV). It covers County Donegal with the exception of nine southern electoral divisions which are part of the neighbouring Sligo–Leitrim constituency. History and boundaries 1921 to 1937 The Donegal constituency was first created in 1921 under the Government of Ireland Act 1920, for the 1921 election to the House of Commons of Southern Ireland, whose members formed the Second Dáil. It elected 6 deputies in 1921, and again at the 1922 general election. It covered the whole territory of County Donegal in north-west Ireland. Under the Electoral Act 1923, the constituency's boundaries remained unchanged, and were defined simply as "the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cahir O'Doherty
Sir Cahir O'Doherty ( ga, Cathaoir Ó Dochartaigh or ga, label=none, Caṫaoir Ó Doċartaiġ; 1587–5 July 1608) was the last Gaelic Chief of the Name of Clan O'Doherty and Lord of Inishowen, in what is now County Donegal. O'Doherty was a noted loyalist during Tyrone's Rebellion and became known as the Queen's O'Doherty for his service on the Crown's side during the fighting. After the war O'Doherty had ambitions to become a courtier and applied for a position in the household of Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales, but he increasingly came into dispute with Irish-based officials such as the Viceroy Sir Arthur Chichester and the Governor of Derry Sir George Paulet. In 1608 he launched a rebellion, seizing Derry from Paulet and burning it to the ground. O'Doherty was subsequently killed in a battle at Kilmacrennan, and the rebellion swiftly collapsed. Early life Cahir was the son of Sir John O'Doherty, the head of the O'Dohertys and effective ruler of Inishowen. One of Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
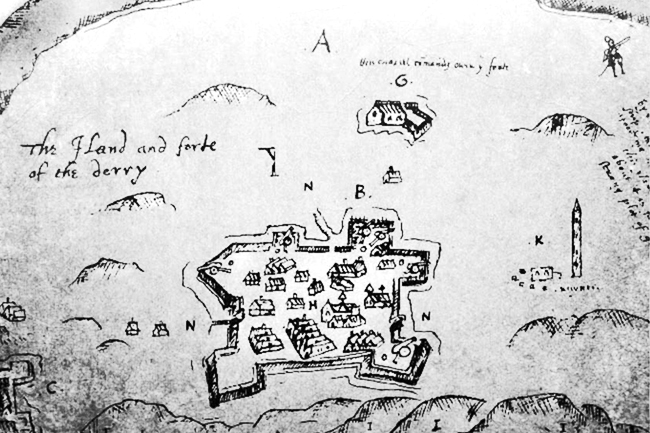
Burning Of Derry
The Burning of Derry took place on 19 April 1608 during O'Doherty's Rebellion when Sir Cahir O'Doherty led a force of rebels to storm Derry in Ulster. He launched his rebellion with an attack on the garrison town of Derry, which was taken thanks to the element of surprise. The town was then almost entirely destroyed by fire. Background O'Doherty was the Gaelic Lord of Inishowen. He had been allied with the government during the Nine Years' War (1594-1603), and has been described as "a youthful war hero on the side of the crown". During the conflict, he fought alongside Sir Henry Docwra's troops from the key base of Derry. O'Doherty, along with other pro-English Irish lords, was unhappy when the Treaty of Mellifont restored the leading rebels, Hugh O'Neill, Earl of Tyrone and Rory O'Donnell, 1st Earl of Tyrconnell, to land which had been promised to them. O'Doherty was further unsettled when his friend and ally Docwra was replaced as Governor of Derry by Sir George Paulet. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |