|
Buddleja Nivea
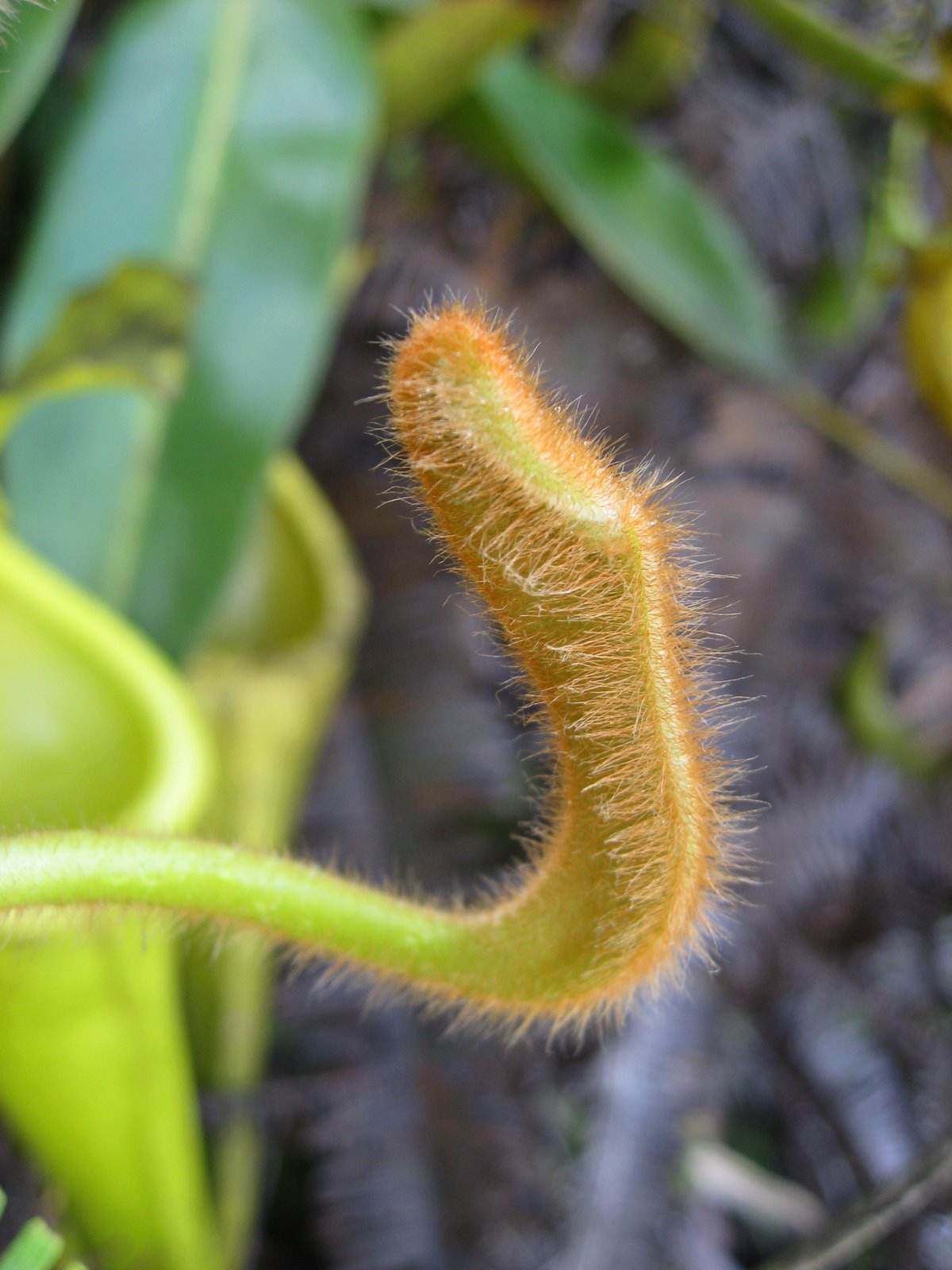
''Buddleja nivea'' is a vigorous shrub endemic to western China, evergreen in the wild, but deciduous in cultivation in the UK. The plant was discovered by Wilson in the Yangtze basin at altitudes of 700 – 3,600 m. Introduced to cultivation in 1901, it was named by Duthie in 1905.Bean, W. J. (1970). ''Trees & Shrubs Hardy in the British Isles, 8th ed., Vol. 1.'' (2nd impression 1976) LondonStuart, D. (2006). ''Buddlejas''. RHS Plant Collector Guide. Timber Press, Oregon, USA. Several plants similar to the species but originally treated as species and varieties in their own right have now been sunk as ''B. nivea'' (see synonyms). Li, P. T. & Leeuwenberg, A. J. M. (1996). Loganiaceae, in Wu, Z. & Raven, P. (eds) ''Flora of China'', Vol. 15. Science Press, Beijing, and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis, USA. vol. 15 (1996)online at www.efloras.org/ref> Description ''Buddleja nivea'' reaches 1 – 3 m high, and is chiefly distinguished by the dense wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Firminger Duthie
John Firminger Duthie (1845–1922) was an English botanist and explorer Exploration refers to the historical practice of discovering remote lands. It is studied by geographers and historians. Two major eras of exploration occurred in human history: one of convergence, and one of divergence. The first, covering most .... From 1875 to 1903 he was the Superintendent of Saharanpur Botanical Gardens. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Duthie, John Firminger 1845 births 1922 deaths English botanists Place of birth missing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budd
Budd may refer to: People * Budd (given name) * Budd (surname) Places * Budd Coast, Wilkes Land, Antarctica * Budd Creek, California * Budd Peak (Enderby Land), Antarctica * Budd Peak (Heard Island), Indian Ocean ** Budd Pass * Budd Inlet, a southern arm of Puget Sound, Washington * Budd Lake (other) * Budd, Manitoba, Canada; see Budd station Other uses * Budd (shirtmakers), a high-end London tailor * Budd Company, a metal fabricator and major supplier of body components to the automobile industry * ''Budd'' (EP), by Rapeman * Budd Rail Diesel Car See also * Budd–Chiari syndrome, the clinical picture caused by occlusion of the hepatic vein or inferior vena cava * East Budd Island, Mac. Robertson Land, Antarctica * West Budd Island West Budd Island is the western of two larger islands at the north end of the Flat Islands, Holme Bay. Mapped by Norwegian cartographers from air photos taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition, 1936–37. They named the northern isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the United States federal executive departments, federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and production, works to assure food safety, protects natural resources, fosters rural communities and works to end hunger in the United States and internationally. It is headed by the United States Secretary of Agriculture, Secretary of Agriculture, who reports directly to the President of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet of the United States, Cabinet. The current secretary is Tom Vilsack, who has served since February 24, 2021. Approximately 80% of the USDA's $141 billion budget goes to the Food and Nutrition Service (FNS) program. The largest component of the FNS budget is the Supplementa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
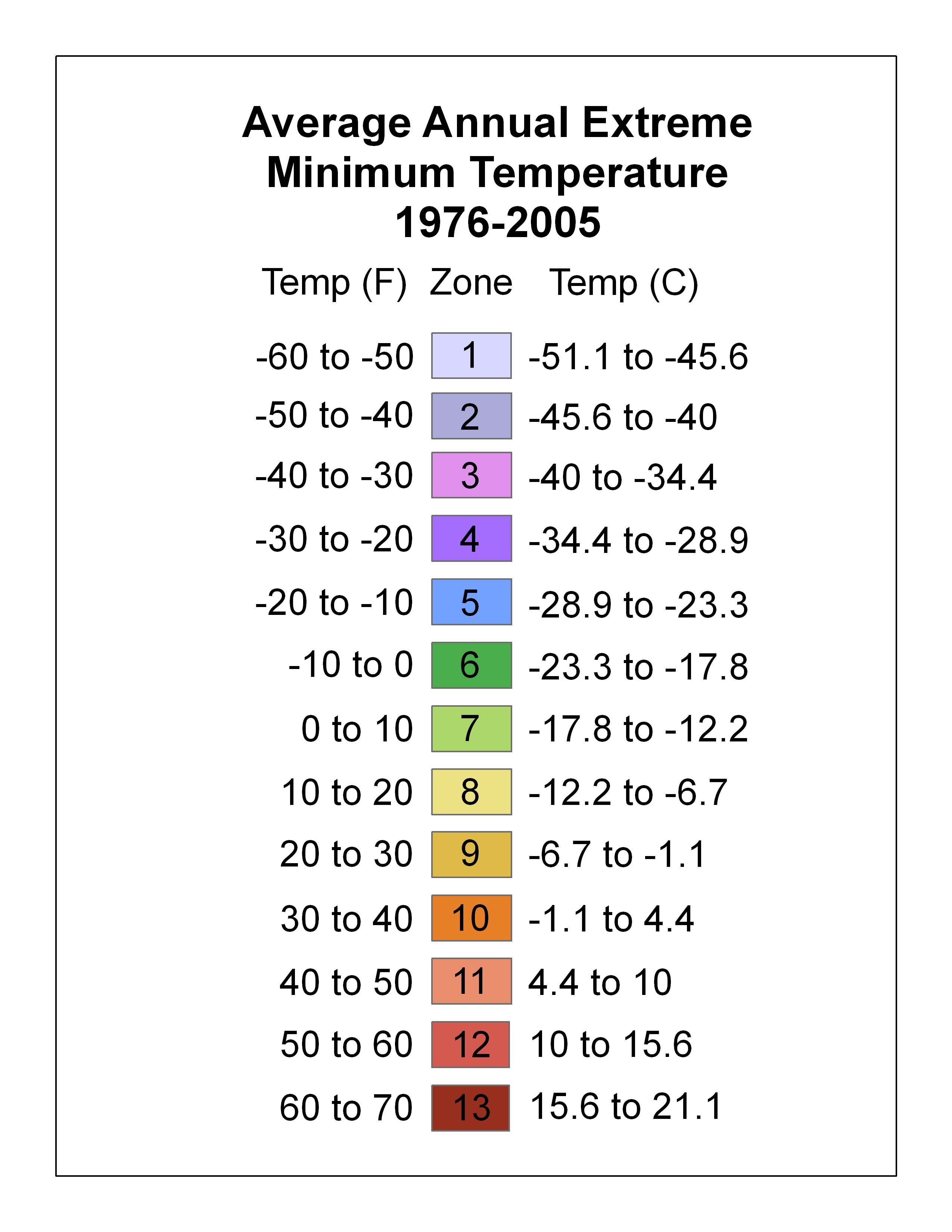
Hardiness Zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely used system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a rough guide for landscaping and gardening, defines 13 zones by long-term average annual extreme minimum temperatures. It has been adapted by and to other countries (such as Canada) in various forms. Unless otherwise specified, in American contexts "hardiness zone" or simply "zone" usually refers to the USDA scale. For example, a plant may be described as "hardy to zone 10": this means that the plant can withstand a minimum temperature of 30 °F (−1.1 °C) to 40 °F (4.4 °C). Other hardiness rating schemes have been developed as well, such as the UK Royal Horticultural Society and US Sunset Western Garden Book systems. A heat zone (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire is the 9th-most populous county in England. The county town of Hampshire is Winchester, located in the north of the county. The county is bordered by Dorset to the south-west, Wiltshire to the north-west, Berkshire to the north, Surrey to the north-east, and West Sussex to the south east. The county is geographically diverse, with upland rising to and mostly south-flowing rivers. There are areas of downland and marsh, and two national parks: the New Forest National Park, New Forest and part of the South Downs National Park, South Downs, which together cover 45 per cent of Hampshire. Settled about 14,000 years ago, Hampshire's recorded history dates to Roman Britain, when its chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stockbridge, Hampshire
Stockbridge is a small town and civil parish in the Test Valley district of Hampshire, England. It is one of the smallest towns in the United Kingdom with a population of 592 at the 2011 census. It sits astride the River Test and at the foot of Stockbridge Down. Description The town is situated on the A30 road, which once carried most of the traffic from London to Dorset, south Somerset, Devon and Cornwall in the South West, though today this route is less important than the A303 dual carriageway to the north. The bridge over the Test led to the town's name, a local legend suggested a coach stop stocked provisions, but it derives from an earlier bridge that was made of 'stocks' (tree trunks). Salisbury is by road; Winchester is by the B3049 road that joins the A30 nearby. The town's long high street was thus on a useful route between the two medieval cathedral cities. The town's civil parish has an area of . The town's street crosses the River Test, marking the border of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longstock Park
Longstock Park is in the civil parish of Longstock in the Test Valley district of Hampshire, England, and forms part of the Leckford Estate (1520 ha.), wholly owned by the John Lewis Partnership. Description Formerly Longstock Manor, of medieval origins, the park was purchased by Sir Joshua East in 1849. On his death, the park passed to his sons Alfred and Arthur. In 1914, the park became the home of the Beddington family until 1945, when it was sold to John Spedan Lewis, founder of the John Lewis Partnership. Lewis lived at Longstock House throughout his retirement until his death in 1963, after which the house became a retreat for the company's executives. The park is today home to a retail horticultural emporium, the Longstock Park Nursery, and also accommodates an arboretum, woodland gardens and water gardens. Longstock border.jpg, Part of the herbaceous border at Longstock Park Longstock pinetum 2.jpg, The Pinetum, Longstock Park Nursery and walled garden The nurse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NCCPG
Plant Heritage, formerly known as the National Council for the Conservation of Plants and Gardens (NCCPG), is a botanical conservation organisation in the United Kingdom and a registered charity. It was founded in 1978 to combine the talents of botanists, horticulturalists and conservationists with the dedication of keen amateur and professional gardeners. The mission statement of the organisation declares that "The NCCPG seeks to conserve, document, promote and make available Britain and Ireland's rich biodiversity of garden plants for the benefit of everyone through horticulture, education and science." Specifically, the aims of the organisation are to: * encourage the propagation and conservation of endangered garden plants in the British Isles, both species and cultivars; * encourage and conduct research into cultivated plants, their origins, their historical and cultural importance and their environments; and * encourage the education of the public in garden plant conserv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corolla (flower)
Petals are modified leaves that surround the reproductive parts of flowers. They are often brightly colored or unusually shaped to attract pollinators. All of the petals of a flower are collectively known as the ''corolla''. Petals are usually accompanied by another set of modified leaves called sepals, that collectively form the ''calyx'' and lie just beneath the corolla. The calyx and the corolla together make up the perianth, the non-reproductive portion of a flower. When the petals and sepals of a flower are difficult to distinguish, they are collectively called tepals. Examples of plants in which the term ''tepal'' is appropriate include genera such as '' Aloe'' and ''Tulipa''. Conversely, genera such as ''Rosa'' and '' Phaseolus'' have well-distinguished sepals and petals. When the undifferentiated tepals resemble petals, they are referred to as "petaloid", as in petaloid monocots, orders of monocots with brightly colored tepals. Since they include Liliales, an alternative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaf Shape
The following is a list of terms which are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple (a single leaf blade or lamina) or compound (with several leaflets). The edge of the leaf may be regular or irregular, may be smooth or bearing hair, bristles or spines. For more terms describing other aspects of leaves besides their overall morphology see the leaf article. The terms listed here all are supported by technical and professional usage, but they cannot be represented as mandatory or undebatable; readers must use their judgement. Authors often use terms arbitrarily, or coin them to taste, possibly in ignorance of established terms, and it is not always clear whether because of ignorance, or personal preference, or because usages change with time or context, or because of variation between specimens, even specimens from the same plant. For example, whether to call leaves on the same tree "acuminate", "lanceolate", or "linear" could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calyx (botany)
A sepal () is a part of the flower of angiosperms (flowering plants). Usually green, sepals typically function as protection for the flower in bud, and often as support for the petals when in bloom., p. 106 The term ''sepalum'' was coined by Noël Martin Joseph de Necker in 1790, and derived . Collectively the sepals are called the calyx (plural calyces), the outermost whorl of parts that form a flower. The word ''calyx'' was adopted from the Latin ,Jackson, Benjamin, Daydon; A Glossary of Botanic Terms with their Derivation and Accent; Published by Gerald Duckworth & Co. London, 4th ed 1928 not to be confused with 'cup, goblet'. ''Calyx'' is derived from Greek 'bud, calyx, husk, wrapping' ( Sanskrit 'bud'), while is derived from Greek 'cup, goblet', and the words have been used interchangeably in botanical Latin. After flowering, most plants have no more use for the calyx which withers or becomes vestigial. Some plants retain a thorny calyx, either dried or live, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indumentum
In biology, an indumentum (Latin, literally: "garment") is a covering of trichomes (fine "hairs") on a plant Davis, Peter Hadland and Heywood, Vernon Hilton (1963) ''Principles of angiosperm taxonomy'' Van Nostrandpage, Princeton, New Jersey, page 154, or of bristles (rarely scales) of an insect. In plants, indumentum types include: *pubescent *hirsute *pilose *lanate *villous *tomentose *stellate *scabrous *scurfy The indumentum on plants can have a wide variety of functions, including as anchorage in climbing plants (e.g., ''Galium aparine''), in transpiration control, in water absorption (''Tillandsia''), the reflection of solar radiation, increasing water-repellency (e.g., in the aquatic fern ''Salvinia''), in protection against insect predation, and in the trapping of insects (''Drosera'', ''Nepenthes'', ''Stylosanthes''). The use of an indumentum on insects can also be pollen-related, as on bees, sensory like whiskers, or for varied other uses including adhesion an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |