|
Budapest Gambit
The Budapest Gambit (or Budapest Defence) is a chess opening that begins with the moves: :1. d4 Nf6 :2. c4 e5 Despite an early debut in 1896, the Budapest Gambit received attention from leading players only after a win as Black by Grandmaster Milan Vidmar over Akiba Rubinstein in 1918. It enjoyed a rise in popularity in the early 1920s, but nowadays is rarely played at the top level. It experiences a lower percentage of draws than other main lines, but also a lower overall performance for Black. After 3.dxe5 Black can try the ''Fajarowicz variation'' 3...Ne4 which concentrates on the rapid development of pieces, but the most common move is 3...Ng4 with three main possibilities for White. The ''Adler variation'' 4.Nf3 sees White seeking a in the with his pieces, notably the important d5-square. The ''Alekhine variation'' 4.e4 gives White an important spatial advantage and a strong . The ''Rubinstein variation'' 4.Bf4 leads to an important choice for White, after 4...Nc6 5. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Géza Maróczy
Géza Maróczy (; 3 March 1870 – 29 May 1951) was a Hungarian chess player, one of the leading players in the world in his time. He was one of the inaugural recipients of the title International Grandmaster from FIDE in 1950. Early career Géza Maróczy was born in Szeged, Hungary on 3 March 1870. He won the "minor" tournament at Hastings 1895, and over the next ten years he won several first prizes in international events. Between 1902 and 1908, he took part in thirteen tournaments and won five first prizes and five second prizes. Today the Maróczy Bind (see below) and the Maróczy Gambit bear his name. In 1906 he agreed to terms for a World Championship match with Emanuel Lasker, but the arrangements could not be finalised, and the match never took place. Retirement and return After 1908, Maróczy retired from international chess to devote more time to his profession as a clerk. He worked as an auditor and made a good career at the Center of Trade Unions and Social In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna
en, Viennese , iso_code = AT-9 , registration_plate = W , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = , timezone = CET , utc_offset = +1 , timezone_DST = CEST , utc_offset_DST = +2 , blank_name = Vehicle registration , blank_info = W , blank1_name = GDP , blank1_info = € 96.5 billion (2020) , blank2_name = GDP per capita , blank2_info = € 50,400 (2020) , blank_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank_info_sec1 = 0.947 · 1st of 9 , blank3_name = Seats in the Federal Council , blank3_info = , blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD , blank_info_sec2 = .wien , website = , footnotes = , image_blank_emblem = Wien logo.svg , blank_emblem_size = Vienna ( ; german: Wien ; ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semmering, Austria
Semmering is a town in the district of Neunkirchen in the Austrian state of Lower Austria. It is noted for its skiing, and has hosted the Alpine skiing World Cup The FIS Alpine Ski World Cup is the top international circuit of alpine skiing competitions, launched in 1966 by a group of ski racing friends and experts which included French journalist Serge Lang and the alpine ski team directors from France ( ... several times. When the Semmering Railway was completed in 1854, the town quickly became a popular tourist getaway in winter months. In 2011, the town had a permanent population of 571. Population Resort History of the resort At the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries, the better Viennese society discovered the Semmering as a nearby summer resort - destination. The place is mainly revived with the construction of the Semmering Railway, which opened 1854. Semmering - Südbahnhotel.JPG, Südbahnhotel, build 1882 Semmering - Kurhaus.JPG, Kurhotel, build 1909 Semm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hastings
Hastings () is a large seaside town and borough in East Sussex on the south coast of England, east to the county town of Lewes and south east of London. The town gives its name to the Battle of Hastings, which took place to the north-west at Senlac Hill in 1066. It later became one of the medieval Cinque Ports. In the 19th century, it was a popular seaside resort, as the railway allowed tourists and visitors to reach the town. Today, Hastings is a fishing port with the UK's largest beach-based fishing fleet. It has an estimated population of 92,855 as of 2018. History Early history The first mention of Hastings is found in the late 8th century in the form ''Hastingas''. This is derived from the Old English tribal name '' Hæstingas'', meaning 'the constituency (followers) of Hæsta'. Symeon of Durham records the victory of Offa in 771 over the ''Hestingorum gens'', that is, "the people of the Hastings tribe." Hastingleigh in Kent was named after that tribe. The place n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Seitz
Jakob Adolf Seitz (February 14, 1898, Meitingen, Germany – April 6, 1970, Switzerland) was a German–Argentine chess master and journalist. Career In 1920, he tied for 2-4th in Canterbury, took 10th in Berlin, and tied for 4-5th in Kulmbach. In 1921, he tied for 8-9th in Hamburg. In 1922, he tied for 2nd-3rd in London (Major Open). In 1922/23 he tied for 6-9th in Portsmouth/Southsea. In 1923, he tied for 6-7th in Triest. In 1923/24 he tied for 5-6th in Hastings (Max Euwe won). In 1924, he took 13th in Győr. 1924/25 he took 3rd in Hastings (Géza Maróczy won). In 1925, he tied for 6-10th in Debrecen. In 1925, he took 3rd in Bologna (Mario Monticelli won). In 1925/26 he tied for 3-4th in Hastings (Alexander Alekhine and Milan Vidmar won). In 1926, he tied for 6-7th in Milan, and tied for 3-4th in Scarborough. In 1927, he took 2nd, behind Stefano Rosselli del Turco, in Naples, and tied for 3-4th in London. In 1928, he tied for 3-4th in Cheltenham, tied for 4-5th in Dortmund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baden-Baden
Baden-Baden () is a spa town in the states of Germany, state of Baden-Württemberg, south-western Germany, at the north-western border of the Black Forest mountain range on the small river Oos (river), Oos, ten kilometres (six miles) east of the Rhine, the border with France, and forty kilometres (twenty-five miles) north-east of Strasbourg, France. In 2021, the town became part of the transnational World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site under the name "Great Spa Towns of Europe", because of its famous spas and architecture that exemplifies the popularity of spa towns in Europe in the 18th through 20th centuries. Name The springs at Baden-Baden were known to the Roman Empire, Romans as ("The Waters") and ("Aurelia (name), Aurelia-of-the-Waters") after M. Aurelius Severus Alexander Augustus. In modern German, ' is a noun meaning "bathing" but Baden, the original name of the town, derives from an earlier plural, plural form of ' (Bathing, "bath"). (Modern German uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilya Rabinovich
Ilya Leontievich Rabinovich (russian: Илья Леонтьевич Рабинович; 11 May 1891 – 23 April 1942) was a Russian and later Soviet chess player, among the best ones in his country for three decades, from 1910 to 1940. His best result was a shared first place in the 9th Soviet Championship of 1934-35. He was also a chess writer. Biography Rabinovich was born in Saint Petersburg. In 1911 he tied for first place with Platz in Saint Petersburg. In 1912 he tied for 4th-5th in Vilnius (''Hauptturnier''; Karel Hromádka won). Interned in Germany In July–August 1914 he played in Mannheim, Germany at the Mannheim 1914 chess tournament, 19th DSB Congress. When the chess congress had to be interrupted upon the outbreak of World War I, Rabinovich was tied for 2nd-3rd places in the ''Hauptturnier A''. After the declaration of war against Russia, eleven players from the Russian Empire (Alexander Alekhine, Efim Bogoljubov, Fedor Bogatyrchuk, Alexander Flamberg, N. Koppelma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Alekhine
Alexander Aleksandrovich Alekhine, ''Aleksándr Aleksándrovich Alékhin''; (March 24, 1946) was a Russian and French chess player and the fourth World Chess Champion, a title he held for two reigns. By the age of 22, Alekhine was already among the strongest chess players in the world. During the 1920s, he won most of the tournaments in which he played. In 1921, Alekhine left Soviet Russia and emigrated to France, which he represented after 1925. In 1927, he became the fourth World Chess Champion by defeating José Raúl Capablanca. In the early 1930s, Alekhine dominated tournament play and won two top-class tournaments by large margins. He also played first board for France in five Chess Olympiads, winning individual prizes in each (four medals and a brilliancy prize). Alekhine offered Capablanca a rematch on the same demanding terms that Capablanca had set for him, and negotiations dragged on for years without making much progress. Meanwhile, Alekhine defended his title wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegbert Tarrasch
Siegbert Tarrasch (; 5 March 1862 – 17 February 1934) was a German chess player, considered to have been among the strongest players and most influential theoreticians of the late 19th and early 20th century. Life Tarrasch was born in Breslau, in what was then Prussian Silesia and now is Poland. Having finished school in 1880, he left Breslau to study medicine in Berlin and then in Halle. With his family, he settled in Nuremberg, Bavaria, and later in Munich, setting up a successful medical practice. He had five children. Tarrasch was Jewish, converted to Christianity in 1909, and was a patriotic German who lost a son in World War I, yet he faced antisemitism in the early stages of the Third Reich. Chess career A medical doctor by profession, Tarrasch may have been the best player in the world in the early 1890s. He scored heavily against the ageing World Champion Wilhelm Steinitz in tournaments (+3−0=1) but refused an opportunity to challenge Steinitz for the world tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savielly Tartakower
Savielly Tartakower (also known as ''Xavier'' or ''Ksawery'' ''Tartakower'', less often ''Tartacover'' or ''Tartakover''; 21 February 1887 – 4 February 1956) was a Polish and French chess player. He was awarded the title of International Grandmaster in its inaugural year, 1950. Tartakower was also a leading chess journalist and author of the 1920s and 1930s. Early career Tartakower was born on 21 February 1887 in Rostov-on-Don, Russia, to Austrian citizens of Jewish origin. His father, a first-generation Christian, had him christened with the Latin form of his name, Sabelius.David Lovejoy (2008). ''Moral victories: the story of Savielly Tartakover'' (a historical novel), Echo Publications. ASIN: B0027P89DG. His parents were killed in a robbery in Rostov-on-Don in 1911. Tartakower stayed mainly in Austria. He graduated from the law faculties of universities in Geneva and Vienna. He spoke German and French. During his studies he became interested in chess and started attending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Mieses
Jacques Mieses (born Jacob Mieses; 27 February 1865 – 23 February 1954) was a German-born British chess player. He was one of the inaugural recipients of the title International Grandmaster from FIDE in 1950. He became a naturalized British citizen after World War II.p258 Chess career Born Jacob Mieses in Leipzig, Germany in 1865, his early successes as an adult chess player included a tie for second at Leipzig and third at Nuremberg in 1888. However, he was quickly eclipsed by two rising young superstars, Emanuel Lasker and Siegbert Tarrasch. Mieses attained maturity as a player in 1895, just after turning 30, when he contested the 9th Chess Congress in Leipzig, followed by an exhibition tour in Russia and then a match with David Janowski. His participation in the great Hastings tournament that year was important to his growth as a mature chess master despite a 20th-place finish. Mieses was a dangerous attacker with a number of famous victories to his credit, e.g. against Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
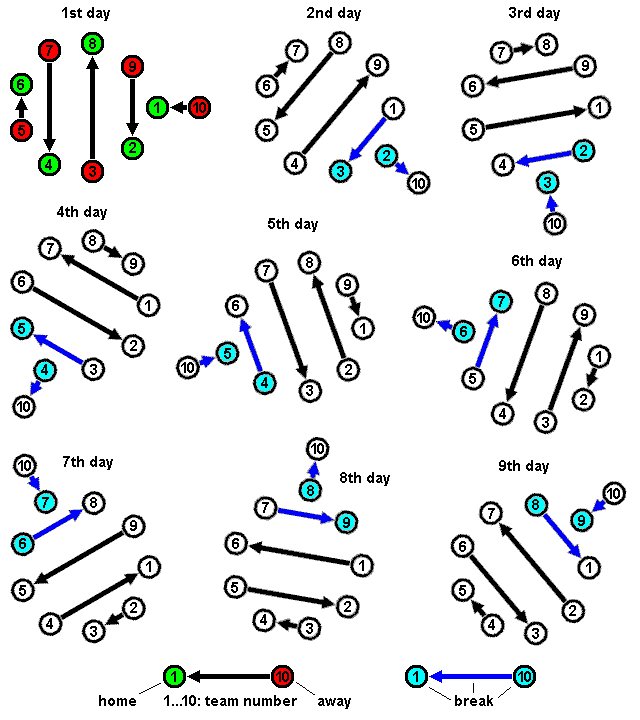
Round-robin Tournament
A round-robin tournament (or all-go-away-tournament) is a competition Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, indiv ... in which each contestant meets every other participant, usually in turn.''Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged'' (1971, G. & C. Merriam Co), p.1980. A round-robin contrasts with an elimination tournament, in which participants/teams are eliminated after a certain number of losses. Terminology The term ''round-robin'' is derived from the French term ''ruban'', meaning "ribbon". Over a long period of time, the term was Folk etymology, corrupted and idiomized to ''robin''. In a ''single round-robin'' schedule, each participant plays every other participant once. If each participant plays all others twice, this is freque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)