|
Budai Nagy Antal Revolt
The Transylvanian peasant revolt ( hu, erdélyi parasztfelkelés), also known as the peasant revolt of Bábolna or Bobâlna revolt ( ro, Răscoala de la Bobâlna), was a popular revolt in the eastern territories of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1437. The revolt broke out after George Lépes, bishop of Transylvania, had failed to collect the tithe for years because of a temporary debasement of the coinage, but then demanded the arrears in one sum when coins of higher value were again issued. Most commoners were unable to pay the demanded sum, but the bishop did not renounce his claim and applied interdict and other ecclesiastic penalties to enforce the payment. The Transylvanian peasants had already been outraged because of the increase of existing seigneurial duties and taxes and the introduction of new taxes during the first decades of the century. The bishop also tried to collect the tithe from the petty noblemen and from Orthodox Vlachs who had settled in parcels abandoned by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Apuseni Mountains. Broader definitions of Transylvania also include the western and northwestern Romanian regions of Crișana and Maramureș, and occasionally Banat. Transylvania is known for the scenery of its Carpathian landscape and its rich history. It also contains Romania's second-largest city, Cluj-Napoca, and other iconic cities and towns such as Brașov, Sibiu, Târgu Mureș, Alba Iulia and Sighișoara. It is also the home of some of Romania's List of World Heritage Sites in Romania, UNESCO World Heritage Sites such as the villages with fortified churches in Transylvania, Villages with fortified churches, the Historic Centre of Sighișoara, the Dacian Fortresses of the Orăștie Mountains and the Rosia Montana Mining Cultural Landsc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluj-Napoca
; hu, kincses város) , official_name=Cluj-Napoca , native_name= , image_skyline= , subdivision_type1 = Counties of Romania, County , subdivision_name1 = Cluj County , subdivision_type2 = Subdivisions of Romania, Status , subdivision_name2 = County seat , settlement_type = Municipiu, City , leader_title = Mayor , leader_name = Emil Boc , leader_party = National Liberal Party (Romania), PNL , leader_title1 = Deputy Mayor , leader_name1 = Dan Tarcea (PNL) , leader_title2 = Deputy Mayor , leader_name2 = Emese Oláh (Democratic Alliance of Hungarians in Romania, UDMR) , leader_title3 = City Manager , leader_name3 = Gheorghe Șurubaru (PNL) , established_title= Founded , established_date = 1213 (first official record as ''Clus'') , area_total_km2 = 179.5 , area_total_sq_mi = 69.3 , area_metro_km2 = 1537.5 , elevation_m = 340 , population_as_of = 2011 Romanian census, 2011 , population_total = 324,576 , population_foot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transylvanian Saxons
The Transylvanian Saxons (german: Siebenbürger Sachsen; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjer Såksen''; ro, Sași ardeleni, sași transilvăneni/transilvani; hu, Erdélyi szászok) are a people of German ethnicity who settled in Transylvania (german: Siebenbürgen) in waves starting from the mid- 12th century until the mid 19th century. The legal foundation of the settlement was laid down in the Diploma Andreanum issued by King Andrew II of Hungary that is known for providing the first territorial autonomy hitherto in the history. The Transylvanian "Saxons" originally came from Flanders, Hainaut, Brabant, Liège, Zeeland, Moselle, Lorraine, and Luxembourg, then situated in the north-western territories of the Holy Roman Empire around the 1140s. After 1918 and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, in the wake of the Treaty of Trianon, Transylvania united with the Kingdom of Romania. Consequently, the Transylvanian Saxons, together with other ethnic German sub-groups in newly e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Uralic language family. There are an estimated 15 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2–3 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia, and Austria. Significant groups of people with Hungarian ancestry live in various other parts of the world, most of them in the United States, Canada, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Chile, Brazil, Australia, and Argentina. Hungarians can be divided into several subgroups according to local linguistic and cultural characteristics; subgroups with distinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and the environment ( environmental geography). Geographic regions and sub-regions are mostly described by their imprecisely defined, and sometimes transitory boundaries, except in human geography, where jurisdiction areas such as national borders are defined in law. Apart from the global continental regions, there are also hydrospheric and atmospheric regions that cover the oceans, and discrete climates above the land and water masses of the planet. The land and water global regions are divided into subregions geographically bounded by large geological features that influence large-scale ecologies, such as plains and features. As a way of describing spatial areas, the concept of regions is important and widely used among the many branches o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
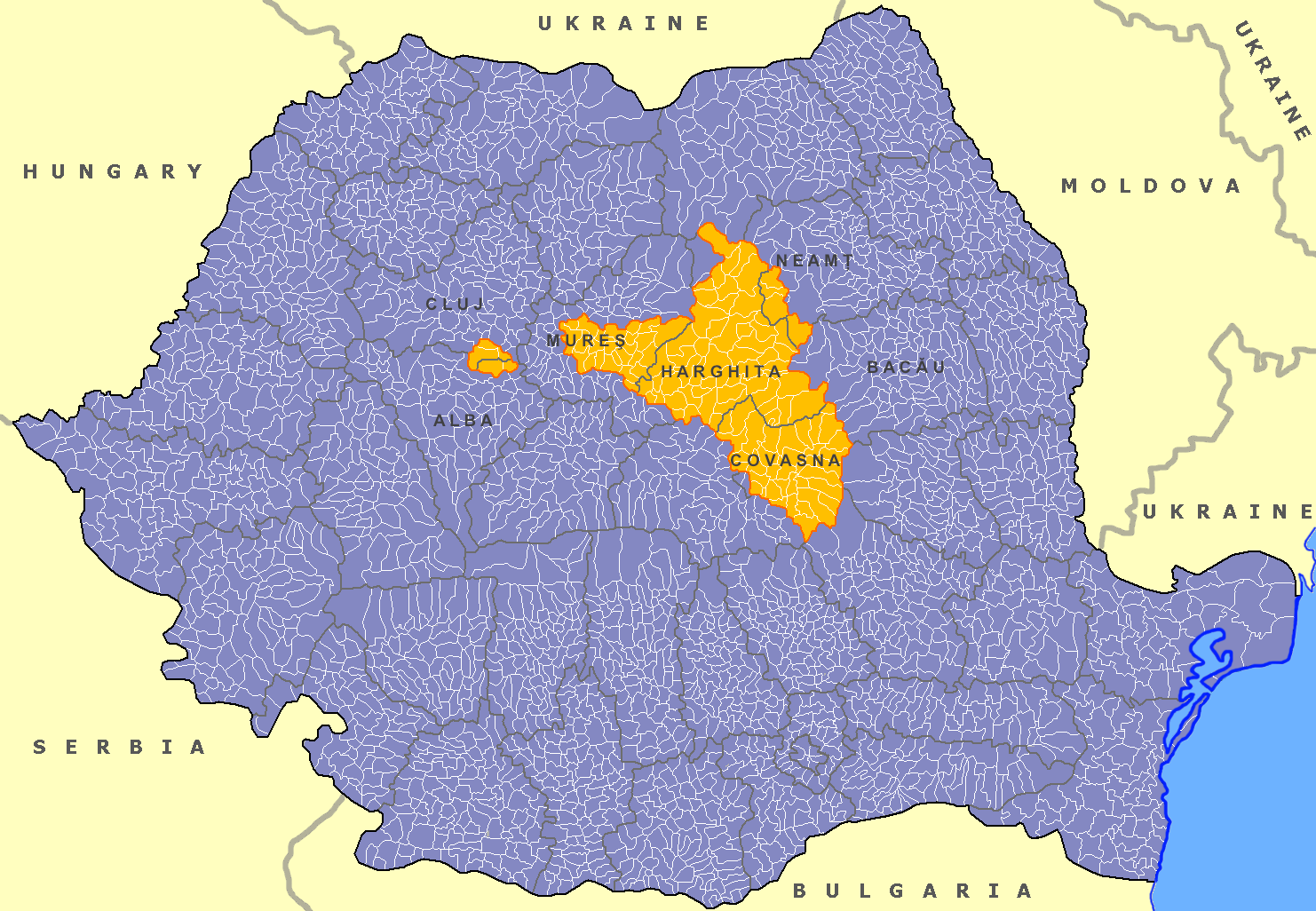
Székely Land
The Székely Land or Szeklerland ( hu, Székelyföld, ; ro, Ținutul Secuiesc and sometimes ; german: Szeklerland; la, Terra Siculorum) is a historic and ethnographic area in Romania, inhabited mainly by Székelys, a subgroup of Hungarians. Its cultural centre is the city of Târgu Mureș (Marosvásárhely), the largest settlement in the region. Székelys (or Szeklers) live in the valleys and hills of the Eastern Carpathian Mountains, corresponding mostly to the present-day Harghita, Covasna, and parts of Mureș counties in Romania. Originally, the name ''Székely Land'' denoted the territories of a number of autonomous Székely seats within Transylvania. The self-governing Székely seats had their own administrative system, and existed as legal entities from medieval times until the 1870s. The privileges of the Székely and Saxon seats were abolished and seats were replaced with counties in 1876. Along with Transylvania and eastern parts of Hungary proper, the Széke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Nations Of Transylvania
Unio Trium Nationum (Latin for "Union of the Three Nations") was a pact of mutual aid codified in 1438 by three Estates of Transylvania: the (largely Hungarian) nobility, the Saxon (German) patrician class, and the free military Székelys. The union was directed against the whole of the peasantry, regardless of ethnicity, in response to the Transylvanian peasant revolt. László Fosztó: ''Ritual Revitalisation After Socialism: Community, Personhood, and Conversion among Roma in a Transylvanian Village'', Halle-Wittenberg, 200 In this typical feudal estate parliament, the peasants (whether Hungarian, Saxon, Székely or Romanian in origin) were not represented, and they did not benefit from its acts, as the commoners were not considered to be members of these feudal "nations". Background Medieval administrative structure in Transylvania In medieval times, Transylvania was organised into two separate types of territorial units: the Noble Counties ( Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aiud
Aiud (; la, Brucla, hu, Nagyenyed, Hungarian pronunciation: ; german: Straßburg am Mieresch) is a city located in Alba County, Transylvania, Romania. The city's population is 22,876. It has the status of municipality and is the 2nd-largest city in the county, after county seat Alba Iulia. The city derives its name ultimately from Saint Giles (Aegidius), to whom the first church in the settlement was dedicated when built. Administration The municipality of Aiud is made up of the city proper and of ten villages. These are divided into four urban villages and six villages which are located outside the city proper but belong to the municipality. The four urban villages are: Aiudul de Sus, Gâmbaș, Măgina and Păgida. The rural villages are: Ciumbrud (0.81 km2), Sâncrai (0.65 km2), Gârbova de Jos (1.04 km2), Țifra (0.06 km2), Gârbova de Sus (0.52 km2) and Gârbovița (0.28 km2). Demographics , the total population is 26,296 (by gender: 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gâlgău
Gâlgău ( hu, Galgó) is a commune located in Sălaj County, Transylvania, Romania Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and .... It is composed of nine villages: Bârsău Mare (''Nagyborszó''), Căpâlna (''Csicsókápolna''), Chizeni (''Közfalu''), Dobrocina (''Döbörcsény''), Fodora (''Oláhfodorháza''), Frâncenii de Piatră (''Kőfrinkfalva''), Gâlgău, Glod (''Szamossósmező'') and Gura Vlădesei (''Vlegyászatanya''). Primăria Gâlgău In 2011 the total population was 2456. Sights * Wooden church of Gâlgău (constructed in 1658) * Wooden church of Bârsău Mare (constructed ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transylvania Saxons
The Transylvanian Saxons (german: Siebenbürger Sachsen; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjer Såksen''; ro, Sași ardeleni, sași transilvăneni/transilvani; hu, Erdélyi szászok) are a people of German ethnicity who settled in Transylvania (german: Siebenbürgen) in waves starting from the mid- 12th century until the mid 19th century. The legal foundation of the settlement was laid down in the Diploma Andreanum issued by King Andrew II of Hungary that is known for providing the first territorial autonomy hitherto in the history. The Transylvanian "Saxons" originally came from Flanders, Hainaut, Brabant, Liège, Zeeland, Moselle, Lorraine, and Luxembourg, then situated in the north-western territories of the Holy Roman Empire around the 1140s. After 1918 and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, in the wake of the Treaty of Trianon, Transylvania united with the Kingdom of Romania. Consequently, the Transylvanian Saxons, together with other ethnic German sub-groups in newly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolozsmonostor Abbey
The Kolozsmonostor Abbey was a Benedictine Christian monastery at Kolozsmonostor in Transylvania in the medieval Kingdom of Hungary (now Mănăștur in Cluj-Napoca in Romania). According to modern scholars' consensus, the monastery was established by Ladislaus I of Hungary before 1095. Establishment The Kolozsvár Abbey was the first Benedictine monastery in Transylvania, but medieval documents contain contradictory information about its foundation. According to a royal charter issued in 1341, Ladislaus I of Hungary established it. However, a late 14th-century forged version of a 1263 charter stated that Béla I of Hungary had set up the abbey, while an excerpt made around 1430 from the same charter named Stephen I of Hungary as its founder. The two latters document also recorded that Ladislaus I of Hungary had made a large grant to the monastery. Historian György Györffy says, both Stephen I and Béla I were most probably copied from the list of the benefactors of the bisho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Of The Székelys
The Count of the Székelys ( hu, székelyispán, la, comes Sicolorum) was the leader of the Hungarian-speaking Székelys in Transylvania, in the medieval Kingdom of Hungary. First mentioned in royal charters of the 13th century, the counts were the highest-ranking royal officials in Székely Land. From around 1320 to the second half of the 15th century, the counts' jurisdiction included four Transylvanian Saxon districts, in addition to the seven Székely seats (or administrative units). The counts also held important castles outside the territories under their administration, including their seat at Görgény (now Gurghiu in Romania). They were the supreme commanders of the Székely troops; their military campaigns against Bulgaria and the Golden Horde were mentioned in royal charters and medieval chronicles. The counts presided over the general assemblies of both the individual Székely seats and the entire Székely community. They also heard appeals of the decisions of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |