|
Buckminster Fuller
Richard Buckminster Fuller (; July 12, 1895 – July 1, 1983) was an American architect, systems theorist, writer, designer, inventor, philosopher, and futurist. He styled his name as R. Buckminster Fuller in his writings, publishing more than 30 books and coining or popularizing such terms as " Spaceship Earth", "Dymaxion" (e.g., Dymaxion house, Dymaxion car, Dymaxion map), " ephemeralization", " synergetics", and " tensegrity". Fuller developed numerous inventions, mainly architectural designs, and popularized the widely known geodesic dome; carbon molecules known as fullerenes were later named by scientists for their structural and mathematical resemblance to geodesic spheres. He also served as the second World President of Mensa International from 1974 to 1983. Fuller was awarded 28 United States patents and many honorary doctorates. In 1960, he was awarded the Frank P. Brown Medal from The Franklin Institute. He was elected an honorary member of Phi Beta Kappa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milton, Massachusetts
Milton is a town in Norfolk County, Massachusetts, United States and an affluent suburb of Boston. The population was 28,630 at the 2020 census. Milton is the birthplace of former U.S. President George H. W. Bush, and architect Buckminster Fuller. Milton was ranked by Money as the 2nd, 7th, 8th, and 17th best place to live in the United States in 2011, 2009, 2019, 2021, and 2022 respectively. Milton is located in the relatively hilly area between the Neponset River and Blue Hills, bounded by Brush Hill to the west, Milton Hill to the east, Blue Hills to the south and the Neponset River to the north. It is also bordered by Boston's Dorchester and Mattapan neighborhoods to the north and its Hyde Park neighborhood to the west; Quincy to the southeast; Randolph to the south, and Canton to the west. History Indigenous peoples The area now known as Milton was inhabited for tens of thousands of years prior to European colonization. The Paleoamerican archaeological site Fowl Mead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Slave
An energy slave is that quantity of energy (ability to do work) which, when used to construct and drive non-human infrastructure (machines, roads, Electric power, power grids, fuel, draft animals, Windpump, wind-driven pumps, etc.) replaces a unit of Manual labor, human labor (actual work). An energy slave does the work of a person, through the energy consumption, consumption of energy in the non-human infrastructure. History In 1940, Richard Buckminster Fuller, Buckminster Fuller was the first to use the term "energy slave" in a map in Fortune (magazine), ''Fortune''. He calculated the yield of an energy slave by taking the energy from minerals and water consumed by industry and dividing it by the energy provided by a human being. For a world population of just over two billion people (2 125 000 000 exactly), Fuller estimates that there are thirty-six billion energy slaves at the time, representing 17 per capita. In 1940, these energy slaves were not equitably distributed arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constance Abernathy
Constance Abernathy (born Constance Davies, June 20, 1931 – June 18, 1994) was an American architect, jeweler, and associate of Buckminster Fuller. Architecture Abernathy worked on a special project studying with Buckminster Fuller to create the geodesic dome egg carton form of architecture, and functioned as Fuller's secretary maintaining sections of his files and archives. Between 1966 and 1971, she directed Fuller's New York office. Jewelry Beginning in 1977, Abernathy became a jeweler. In New York City she befriended and worked with many famous artists. Among her artist friends were many well known painters and sculptors like Larry Rivers, Peter Reginato, Peter Young, Ching Ho Cheng, Ronnie Landfield, and Dan Christensen. Ching Ho Cheng painted her portrait in 1977. In the 1980s her works started to include precious gems and cast parts she created. Her big bead necklaces were collected by Clarice Cosby and many others. Her works are in the collections of the Coop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William James Sidis
William James Sidis (; April 1, 1898 – July 17, 1944) was an American child prodigy with exceptional mathematical and linguistic skills. He is notable for his 1920 book ''The Animate and the Inanimate'', in which he speculates about the origin of life in the context of thermodynamics. Sidis was raised in a particular manner by his father, psychiatrist Boris Sidis, who wished his son to be gifted. Sidis first became famous for his precocity and later for his eccentricity and withdrawal from public life. Eventually, he avoided mathematics altogether, writing on other subjects under a number of pseudonyms. He entered Harvard at age 11 and, as an adult, was said to have an extremely high IQ, and to be conversant in about 25 languages and dialects. Some of these statements have not been verified, but many of his contemporaries, including Norbert Wiener, Daniel Frost Comstock and William James, agreed that he was extremely intelligent. Biography Parents and upbringing (1898–1908 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korzybski
Alfred Habdank Skarbek Korzybski (, ; July 3, 1879 – March 1, 1950) was a Polish-American independent scholar who developed a field called general semantics, which he viewed as both distinct from, and more encompassing than, the field of semantics. He argued that human knowledge of the world is limited both by the human nervous system and the languages humans have developed, and thus no one can have direct access to reality, given that the most we can know is that which is filtered through the brain's responses to reality. His best known dictum is " The map is not the territory". Early life and career Born in Warsaw, Vistula Country, which was then part of the Russian Empire, Korzybski belonged to an aristocratic Polish family whose members had worked as mathematicians, scientists, and engineers for generations. He learned the Polish language at home and the Russian language in schools, and having a French and German governess, he became fluent in four languages as a child. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Fröbel
Friedrich Wilhelm August Fröbel or Froebel (; 21 April 1782 – 21 June 1852) was a German pedagogue, a student of Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi, who laid the foundation for modern education based on the recognition that children have unique needs and capabilities. He created the concept of the ''kindergarten'' and coined the word, which soon entered the English language as well. He also developed the educational toys known as Froebel gifts. Biography Friedrich Fröbel was born at Oberweißbach in the Principality of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt in Thuringia. A cousin of his was the mother of Henriette Schrader-Breymann, and Henriette became a student of his. Fröbel's father, Johann Jacob Fröbel, who died in 1802, was the pastor of the orthodox Lutheran (alt-lutherisch) parish there. Fröbel's mother's name was Jacobine Eleonore Friederike (born Hoffmann). The church and Lutheran Christian faith were pillars in Fröbel's own early education. Oberweißbach was a wealthy village in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
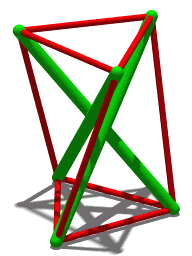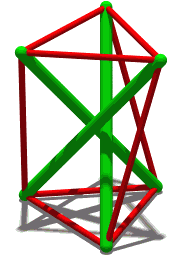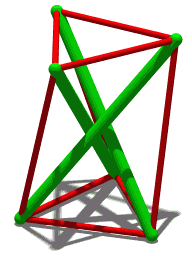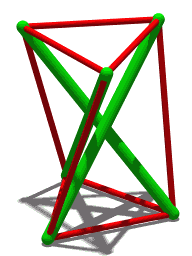
Tensegrity
Tensegrity, tensional integrity or floating compression is a structural principle based on a system of isolated components under compression inside a network of continuous tension, and arranged in such a way that the compressed members (usually bars or struts) do not touch each other while the prestressed tensioned members (usually cables or tendons) delineate the system spatially. The term was coined by Buckminster Fuller in the 1960s as a portmanteau of "tensional integrity". The other denomination of tensegrity, ''floating compression'', was used mainly by the constructivist artist Kenneth Snelson. Concept Tensegrity structures are based on the combination of a few simple design patterns: * members loaded in either pure compression or pure tension, which means that the structure will only fail if the cables yield or the rods buckle. This enables the material properties and cross-sectional geometry of each member to be optimized to the particular load it carries. * preload ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synergetics (Fuller)
Synergetics is the empirical study of systems in transformation, with an emphasis on whole system behaviors unpredicted by the behavior of any components in isolation. R. Buckminster Fuller (1895–1983) named and pioneered the field. His two-volume work ''Synergetics: Explorations in the Geometry of Thinking'', in collaboration with E. J. Applewhite, distills of a lifetime of research into book form. Since systems are identifiable at every scale, Synergetics is necessarily interdisciplinary, embracing a broad range of scientific and philosophical topics, especially in the area of geometry, wherein the tetrahedron features as Fuller's model of the simplest system. Despite mainstream endorsements such as the prologue by Arthur Loeb, and positive dust cover blurbs by U Thant and Arthur C. Clarke, along with the posthumous naming of the carbon allotrope "buckminsterfullerene", Synergetics remains an off-beat subject, ignored for decades by most traditional curricula and academic d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Frame
In architecture and structural engineering, a space frame or space structure ( 3D truss) is a rigid, lightweight, truss-like structure constructed from interlocking struts in a geometric pattern. Space frames can be used to span large areas with few interior supports. Like the truss, a space frame is strong because of the inherent rigidity of the triangle; flexing loads (bending moments) are transmitted as tension and compression loads along the length of each strut. History Alexander Graham Bell from 1898 to 1908 developed space frames based on tetrahedral geometry. Bell's interest was primarily in using them to make rigid frames for nautical and aeronautical engineering, with the tetrahedral truss being one of his inventions. Max Mengeringhausen developed the space grid system called MERO (acronym of ''MEngeringhausen ROhrbauweise'') in 1943 in Germany, thus initiating the use of space trusses in architecture. The commonly used method, still in use has individual tubular m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoscope
The Geoscope was a proposal by Buckminster Fuller around 1960 to create a globe that would be covered in colored lights so that it could function as a large spherical display. It was envisioned that the Geoscope would be connected to computers which would allow it to display both historical and current data, and enable people to visualize large scale patterns around the world. Several projects by his students to build a "miniature Earth", starting with a 20-foot version at Cornell University in 1952, were precursors of the Geoscope proposal. Before proposing the Geoscope, Fuller had invented the Dymaxion map, a novel map projection for the whole Earth. Many of Fuller's ideas for the functions of the Geoscope are now being realized by virtual globes. Fuller did not limit his use of the term "Geoscope" to the diameter globe proposed for installation near the United Nations in New York. He also used it to refer to smaller globes to be viewed from the inside outwards toward the stars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dymaxion Map
The Dymaxion map or Fuller map is a projection of a world map onto the surface of an icosahedron, which can be unfolded and flattened to two dimensions. The flat map is heavily interrupted in order to preserve shapes and sizes. The projection was invented by Buckminster Fuller. The March 1, 1943, edition of ''Life'' magazine included a photographic essay titled "Life Presents R. Buckminster Fuller's Dymaxion World". The article included several examples of its use together with a pull-out section that could be assembled as a "three-dimensional approximation of a globe or laid out as a flat map, with which the world may be fitted together and rearranged to illuminate special aspects of its geography." Fuller applied for a patent in the United States in February 1944, showing a projection onto a cuboctahedron, which he called "dymaxion". The patent was issued in January 1946. In 1954, Fuller and cartographer Shoji Sadao produced the Airocean World Map, a version of the Dymaxion ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |