|
Broom Hall Airfield
A broom (also known in some forms as a broomstick) is a cleaning tool consisting of usually stiff fibers (often made of materials such as plastic, hair, or corn husks) attached to, and roughly parallel to, a cylindrical handle, the broomstick. It is thus a variety of brush with a long handle. It is commonly used in combination with a dustpan. A distinction is made between a "hard broom" and a "soft broom" and a spectrum in between. Soft brooms are used in some cultures chiefly for sweeping walls of cobwebs and spiders, like a " feather duster", while hard brooms are for rougher tasks like sweeping dirt off sidewalks or concrete floors, or even smoothing and texturing wet concrete. The majority of brooms are somewhere in between, suitable for sweeping the floors of homes and businesses, soft enough to be flexible and to move even light dust, but stiff enough to achieve a firm sweeping action. The broom is also a symbolic object associated with witchcraft and ceremonial magic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorghum Bicolor
''Sorghum bicolor'', commonly called sorghum () and also known as great millet, broomcorn, guinea corn, durra, imphee, jowar, or milo, is a Poaceae, grass species cultivated for its grain, which is used for food for humans, animal feed, and ethanol production. Sorghum originated in Africa, and is now cultivated widely in tropical and subtropical regions. Sorghum is the world's fifth-most important cereal crop after rice, wheat, maize, and barley, with 59.34 million metric tons of annual global production in 2018. ''S. bicolor'' is typically an annual, but some cultivars are perennial. It grows in clumps that may reach over 4 m high. The grain is small, ranging from 2 to 4 mm in diameter. Sweet sorghums are sorghum cultivars that are primarily grown for forage, syrup production, and ethanol; they are taller than those grown for grain. ''Sorghum bicolor'' is the cultivated species of sorghum; its wild relatives make up the botanical genus ''Sorghum''. History The first archae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Qudamah
Ibn Qudāmah al-Maqdisī Muwaffaq al-Dīn Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd Allāh b. Aḥmad b. Muḥammad ( ar, ابن قدامة المقدسي موفق الدين ابو محمد عبد الله بن احمد بن محمد ; 1147 - 7 July 1223), often referred to as Ibn Qudamah or Ibn Qudama for short, was a Sunni Muslim ascetic, jurisconsult, Traditionalist theologian. Having authored many important treatises on Islamic jurisprudence and religious doctrine, including one of the standard works of Hanbali law, the revered ''al-Mug̲h̲nī'', Ibn Qudamah is highly regarded in Sunnism for being one of the most notable and influential thinkers of the Hanbali school of orthodox Sunni jurisprudence. Within that school, he is one of the few thinkers to be given the honorific epithet of '' Shaykh of Islam'', which is a prestigious title bestowed by Sunnis on some of the most important thinkers of their tradition. A proponent of the classical Sunni position of the "differences between the scholar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witch
Witchcraft traditionally means the use of Magic (supernatural), magic or supernatural powers to harm others. A practitioner is a witch. In Middle Ages, medieval and early modern Europe, where the term originated, accused witches were usually women who were believed to have used Black magic, malevolent magic against their own community, and often to have communed with evil beings. It was thought witchcraft could be thwarted by Apotropaic magic, protective magic or counter-magic, which could be provided by cunning folk or folk healers. Suspected witches were also intimidated, banished, attacked or killed. Often they would be formally prosecuted and punished, if found guilty or simply believed to be guilty. European witch-hunts and witch trials in the early modern period led to tens of thousands of executions. In some regions, many of those accused of witchcraft were folk healers or midwife, midwives. European belief in witchcraft gradually dwindled during and after the Age of Enl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goya - Caprichos (68)
Francisco José de Goya y Lucientes (; ; 30 March 174616 April 1828) was a Spanish romantic painter and printmaker. He is considered the most important Spanish artist of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. His paintings, drawings, and engravings reflected contemporary historical upheavals and influenced important 19th- and 20th-century painters. Goya is often referred to as the last of the Old Masters and the first of the moderns. Goya was born to a middle-class family in 1746, in Fuendetodos in Aragon. He studied painting from age 14 under José Luzán y Martinez and moved to Madrid to study with Anton Raphael Mengs. He married Josefa Bayeu in 1773. Their life was characterised by a series of pregnancies and miscarriages, and only one child, a son, survived into adulthood. Goya became a court painter to the Spanish Crown in 1786 and this early portion of his career is marked by portraits of the Spanish aristocracy and royalty, and Rococo-style tapestry cartoons design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Reno, Oklahoma
El Reno is a city in and county seat of Canadian County, Oklahoma, United States. As of the 2020 census, the city population was 16,989, marking a change of 1.55% from 16,729, recorded in the 2010 census. The city was begun shortly after the 1889 land rush and named for the nearby Fort Reno.Cynthia Savage, "El Reno." ''Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture''. Retrieved October 10, 2013. It is located in , about west of downtown Oklahoma City. History The land of Canadian County belonged to the historic |
Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the north, Missouri on the northeast, Arkansas on the east, New Mexico on the west, and Colorado on the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-most extensive and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw language, Choctaw words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its List of U.S. state and territory nicknames, nickname, "Sooners, The Sooner State", in reference to the settlers who staked their claims on land before the official op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagion began around September and led to the Wall Street stock market crash of October 24 (Black Thursday). It was the longest, deepest, and most widespread depression of the 20th century. Between 1929 and 1932, worldwide gross domestic product (GDP) fell by an estimated 15%. By comparison, worldwide GDP fell by less than 1% from 2008 to 2009 during the Great Recession. Some economies started to recover by the mid-1930s. However, in many countries, the negative effects of the Great Depression lasted until the beginning of World War II. Devastating effects were seen in both rich and poor countries with falling personal income, prices, tax revenues, and profits. International trade fell by more than 50%, unemployment in the U.S. rose to 23% and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern United States
The Eastern United States, commonly referred to as the American East, Eastern America, or simply the East, is the region of the United States to the east of the Mississippi River. In some cases the term may refer to a smaller area or the East Coast plus Illinois, Wisconsin, Indiana, Mississippi, and their border states. In 2011, the 26 states east of the Mississippi (in addition to Washington, D.C. but not including the small portions of Louisiana and Minnesota east of the river) had an estimated population of 179,948,346 or 58.28% of the total U.S. population of 331,745,358 (excluding Puerto Rico). New England New England is a region of the United States located in the northeastern corner of the country, bounded by the Atlantic Ocean, Canada and the state of New York, consisting of the modern states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut. In one of the earliest English settlements in the New World, English Pilgrims from Europe first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
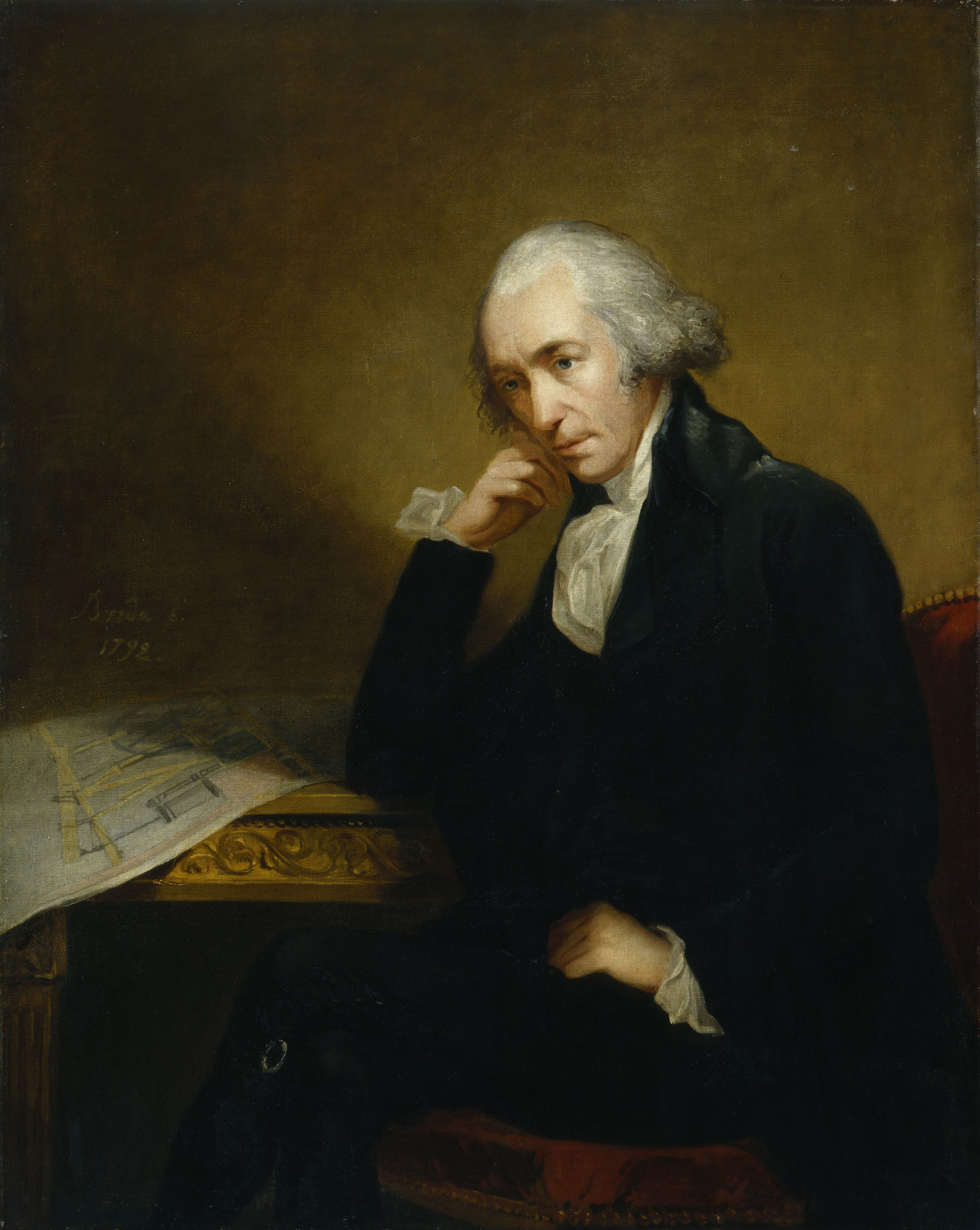
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going from hand production methods to machines, new chemical manufacturing and iron production processes, the increasing use of steam power and water power, the development of machine tools and the rise of the mechanized factory system. Output greatly increased, and a result was an unprecedented rise in population and in the rate of population growth. Textiles were the dominant industry of the Industrial Revolution in terms of employment, value of output and capital invested. The textile industry was also the first to use modern production methods. The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain, and many of the technological and architectural innovations were of British origin. By the mid-18th century, Britain was the world's leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorghum
''Sorghum'' () is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family (Poaceae). Some of these species are grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species is grown for grain, while many others are used as fodder plants, either cultivated in warm climates worldwide or naturalized in pasture lands. Taxonomy ''Sorghum'' is in the Poaceae (grass) subfamily Panicoideae and the tribe Andropogoneae (the same as maize, big bluestem and sugarcane). Species Accepted species recorded include: Distribution and habitat Seventeen of the 25 species are native to Australia, with the range of some extending to Africa, Asia, Mesoamerica, and certain islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Toxicity In the early stages of the plants' growth, some species of sorghum can contain levels of hydrogen cyanide, hordenine, and nitrates, which are lethal to grazing animals. Plants stressed by drought or heat can also contain toxic lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadley, Massachusetts
Hadley (, ) is a town in Hampshire County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 5,325 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Springfield, Massachusetts Metropolitan Statistical Area. The area around the Hampshire and Mountain Farms Malls along Route 9 is a major shopping destination for the surrounding communities. History Early Hadley was first settled in 1659 and was officially incorporated in 1661. The former Norwottuck was renamed for Hadleigh, Suffolk. Its settlers were primarily a discontented group of families from the Puritan colonies of Hartford and Wethersfield, Connecticut, who petitioned to start a new colony up north after some controversy over doctrine in the local church. The settlement was led by John Russell. The first settler inside of Hadley was Nathaniel Dickinson, who surveyed the streets of what is now Hadley, Hatfield, and Amherst. At the time, Hadley encompassed a wide radius of land on both sides of the Connecticut River (but mostly on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_p._p._sl32.jpg)