|
Bronson Hill Arc
The Bronson Hill Arc is a bimodal volcanic arc and associated sediments that formed over a west (?) dipping subduction zone during the Ordovician period (c. 475 - 450 million years ago (Ma)) as part of the Taconic Orogeny. These rocks are presently well exposed along the Connecticut River Valley of Vermont and New Hampshire. The arc is evidenced by plutonism and extrusive volcanicsm, including the Ammonoosuc Volcanics (c. 461 Ma from U/Pb zircon Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of the r ... dates) and the overlying Partridge Formation (c. 457 Ma from graptolites in the formation). It is related to the slightly older Shelburne Falls arc that sits to the west. These rocks were metamorphosed and deformed during the Acadian Orogeny and the Alleghenian Orogeny. References * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bimodal Volcanism
Bimodal volcanism is the eruption of both mafic and felsic lavas from a single volcanic centre with little or no lavas of intermediate composition. This type of volcanism is normally associated with areas of extensional tectonics, particularly rifts. Occurrence Most occurrences of bimodal volcanism are associated with thinning of the crust and the presence of such rocks in metamorphic sequences has been used to provide evidence for past rifting events. Most examples come from areas of active continental rifting such as the Basin and Range Province. Bimodal volcanism has also been described from areas of transtension, the early phases of back-arc basin formation and in the products of both continental and oceanic hotspots (e.g. Yellowstone, Anahim and the Canary Islands). Mechanism of formation Bimodal volcanism is normally explained as a result of partial melting of the crust, creating granitic magma Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium–lead Dating
Uranium–lead dating, abbreviated U–Pb dating, is one of the oldest and most refined of the radiometric dating schemes. It can be used to date rocks that formed and crystallised from about 1 million years to over 4.5 billion years ago with routine precisions in the 0.1–1 percent range. The method is usually applied to zircon. This mineral incorporates uranium and thorium atoms into its crystal structure, but strongly rejects lead when forming. As a result, newly-formed zircon deposits will contain no lead, meaning that any lead found in the mineral is radiogenic. Since the exact rate at which uranium decays into lead is known, the current ratio of lead to uranium in a sample of the mineral can be used to reliably determine its age. The method relies on two separate decay chains, the uranium series from 238U to 206Pb, with a half-life of 4.47 billion years and the actinium series from 235U to 207Pb, with a half-life of 710 million years. Decay routes Uranium decays to lead via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of New Hampshire
The geology of New Hampshire is similar to that of the rest of New England in comprising a series of metamorphosed sedimentary and volcanic rocks of Late Proterozoic to Devonian age, intruded by many plutons and dikes ranging in age from Late Proterozoic to early Cretaceous. New Hampshire is known as "the Granite State", but less than half is underlain by granite; much of it is schist or gneiss, both of which are metamorphic rocks. Geological structure The state straddles three composite tectonostratigraphic terranes. The larger part of the state lies on the Central Maine composite terrane, comprising the Central Maine trough in the east and the Bronson Hill mantled gneiss domes in the west. A small area of the first composite terrane belongs to the Hurricane Mountain belt and olistostrome belt. The northernmost corner of the state lies in the Connecticut Valley trough of the Boundary Mountains composite terrane. In the coastal region in the southeast is the Merrimack–Orringt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alleghenian Orogeny
The Alleghanian orogeny or Appalachian orogeny is one of the geological mountain-forming events that formed the Appalachian Mountains and Allegheny Mountains. The term and spelling Alleghany orogeny was originally proposed by H.P. Woodward in 1957. The Alleghanian orogeny occurred approximately 325 million to 260 million years ago over at least five deformation events in the Carboniferous to Permian period. The orogeny was caused by Africa's collision with North America. At the time, these continents did not exist in their current forms: North America was part of the Euramerica super-continent, while Africa was part of Gondwana. This collision formed the super-continent Pangaea, which contained all major continental land masses. The collision provoked the orogeny: it exerted massive stress on what is today the Eastern Seaboard of North America, forming a wide and high mountain chain. Evidence for the Alleghanian orogeny stretches for many hundreds of miles on the surface from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface. Various forms of metamorphism exist, including regional, contact, hydrothermal, shock, and dynamic metamorphism. These differ in the characteristic temperatures, pressures, and rate at which they take place and in the extent to which reactive fluids are involved. Metamorphism occurring at increasing pressure and temperature conditions is known as ''prograde metamorphism'', while decreasing temperature and pressure characterize ''retrograde metamorphism''. Metamorphic petrology is the study of metamorphism. Metamorphic petrologists re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graptolite
Graptolites are a group of colonial animals, members of the subclass Graptolithina within the class Pterobranchia. These filter-feeding Filter feeders are a sub-group of suspension feeding animals that feed by straining suspended matter and food particles from water, typically by passing the water over a specialized filtering structure. Some animals that use this method of feedin ... organisms are known chiefly from fossils found from the Middle Cambrian (Miaolingian, Wuliuan) through the Lower Carboniferous (Mississippian (geology), Mississippian). A possible early graptolite, ''Chaunograptus'', is known from the Middle Cambrian. Recent analyses have favored the idea that the living pterobranch ''Rhabdopleura'' represents an extant graptolite which diverged from the rest of the group in the Cambrian. Fossil graptolites and ''Rhabdopleura'' share a colony structure of interconnected zooids housed in organic tubes (theca) which have a basic structure of stacked half-rings (fuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of the range of substitution in zircon is (Zr1–y, REEy)(SiO4)1–x(OH)4x–y. Zircon precipitates from silicate melts and has relatively high concentrations of high field strength incompatible elements. For example, hafnium is almost always present in quantities ranging from 1 to 4%. The crystal structure of zircon is tetragonal crystal system. The natural color of zircon varies between colorless, yellow-golden, red, brown, blue, and green. The name derives from the Persian ''zargun'', meaning "gold-hued". This word is corrupted into "jargoon", a term applied to light-colored zircons. The English word "zircon" is derived from ''Zirkon'', which is the German adaptation of this word. Yellow, orange, and red zircon is also known as "hyacinth", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonoosuc Volcanics
The Ammonoosuc Volcanics is a rock unit in parts of New Hampshire and Vermont in the United States. This unit is named for the Ammonoosuc River that runs through the portion of New Hampshire that houses the Ammonoosuc Volcanics. Setting The Ammonoosuc Volcanics are a component of the Bronson Hill Arc, which is approximately long and reaches from the Quebec border down to southern Connecticut. The Bronson Hill arc is made up of both volcanic and plutonic sequences of felsic and mafic rocks, whose ages range from the Cambrian into the Lower Devonian. The Bronson Hill Arc is also a part of the New Hampshire sequence and is sometimes referred to as the Bronson Hill anticlinorium. The Ammonoosuc Volcanics are stratigraphically situated in the New Hampshire sequence on top of the Albee Formation and below the Partridge Formation. The contacts between these units are usually quite sharp but could grade into one another over a few meters in some localities. The geographical setting o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction Zone
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the dens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
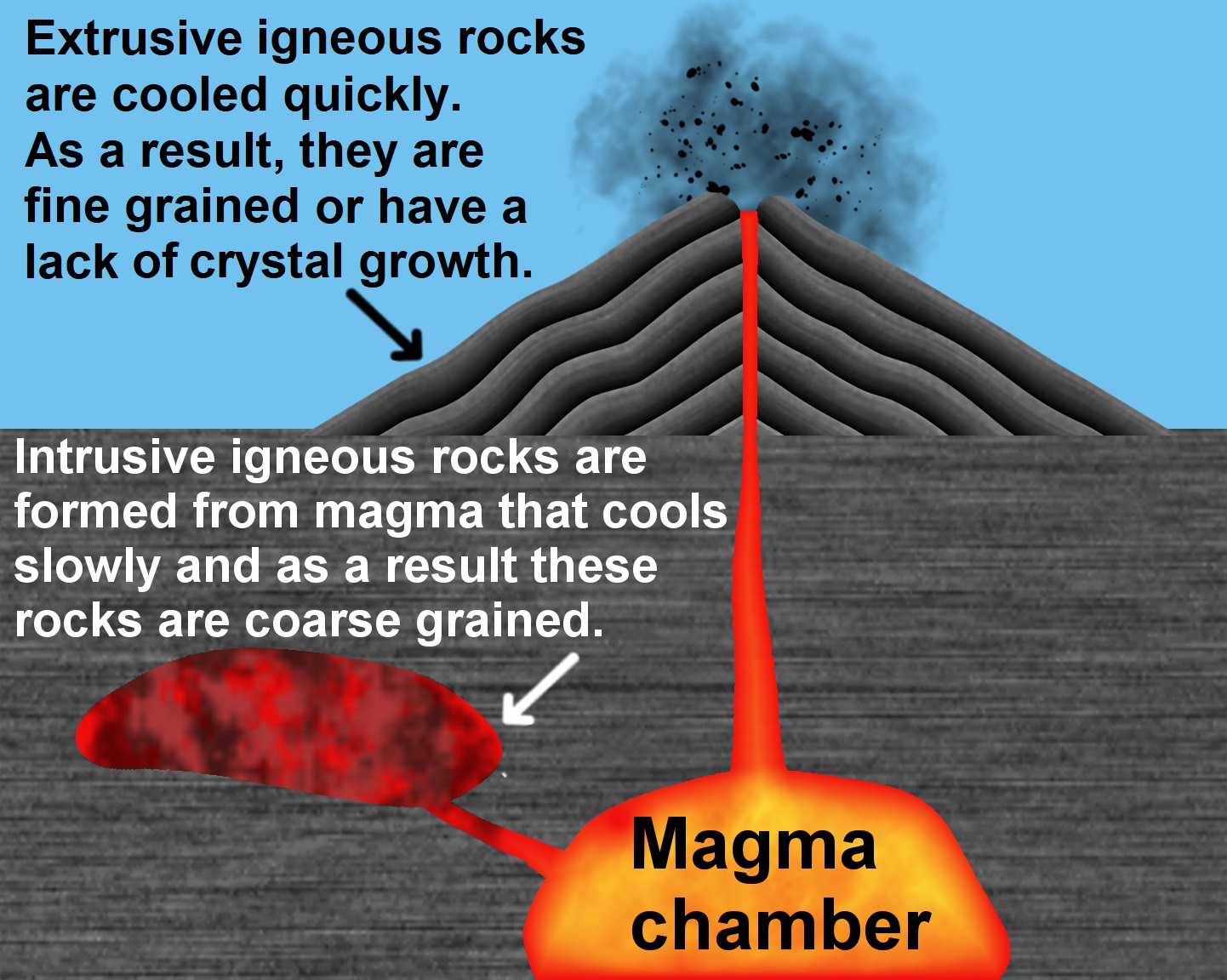
Extrusive
Extrusive rock refers to the mode of igneous volcanic rock formation in which hot magma from inside the Earth flows out (extrudes) onto the surface as lava or explodes violently into the atmosphere to fall back as pyroclastics or tuff. In contrast, intrusive rock refers to rocks formed by magma which cools below the surface.Jain, Sreepat (2014). ''Fundamentals of Physical Geology''. New Delhi, India: Springer. . The main effect of extrusion is that the magma can cool much more quickly in the open air or under seawater, and there is little time for the growth of crystals. Sometimes, a residual portion of the matrix fails to crystallize at all, instead becoming a natural glass or obsidian. If the magma contains abundant volatile components which are released as free gas, then it may cool with large or small vesicles (bubble-shaped cavities) such as in pumice, scoria, or vesicular basalt. Other examples of extrusive rocks are rhyolite and andesite. Texture The texture of ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutonism
Plutonism is the geologic theory that the igneous rocks forming the Earth originated from intrusive magmatic activity, with a continuing gradual process of weathering and erosion wearing away rocks, which were then deposited on the sea bed, re-formed into layers of sedimentary rock by heat and pressure, and raised again. It proposes that basalt is solidified molten magma. The theory lead to plutonic (intrinsic) rock classification, which includes intrinsic igneous rocks such as gabbro, diorite, granite and pegmatite. The name ''plutonism'' references Pluto, the classical ruler of the underworld and the Roman god of wealth. A main reason Pluto was incorporated into the classification was due to the plutonic rocks commonly being present in gold and silver ore deposits (veins). The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces use of the word "plutonists" to 1799, and the appearance of the word ''plutonism'' to 1842. Abbé Anton Moro, who had studied volcanic islands, first proposed the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |