Geology Of New Hampshire on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 The geology of New Hampshire is similar to that of the rest of
The geology of New Hampshire is similar to that of the rest of
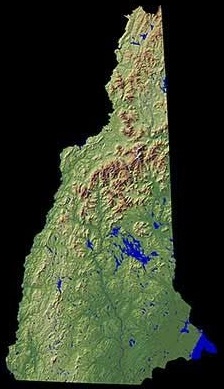 In the southwest corner of New Hampshire, the landmark
In the southwest corner of New Hampshire, the landmark


 The geology of New Hampshire is similar to that of the rest of
The geology of New Hampshire is similar to that of the rest of New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
in comprising a series of metamorphosed
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causin ...
sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic matter, organic particles at Earth#Surface, Earth's surface, followed by cementation (geology), cementation. Sedimentati ...
and volcanic rock
Volcanic rock (often shortened to volcanics in scientific contexts) is a rock formed from lava erupted from a volcano. In other words, it differs from other igneous rock by being of volcanic origin. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic r ...
s of Late Proterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago.
It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is prec ...
to Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, whe ...
age, intruded by many pluton
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and com ...
s and dikes
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes, ...
ranging in age from Late Proterozoic to early Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
. New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
is known as "the Granite State", but less than half is underlain by granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies undergro ...
; much of it is schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock showing pronounced schistosity. This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes o ...
or gneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures an ...
, both of which are metamorphic rocks.
Geological structure
The state straddles three compositetectonostratigraphic In geology, tectonostratigraphy is stratigraphy that refers either to rock sequences in which large-scale layering is caused by the stacking of thrust sheets, or nappes, in areas of thrust tectonics or to the effects of tectonics on lithostratigraph ...
terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its own ...
s. The larger part of the state lies on the Central Maine composite terrane, comprising the Central Maine trough in the east and the Bronson Hill mantled gneiss domes in the west. A small area of the first composite terrane belongs to the Hurricane Mountain belt and olistostrome
An olistostrome is a sedimentary deposit composed of a chaotic mass of heterogeneous material, such as blocks and mud, known as olistoliths, that accumulates as a semifluid body by submarine gravity sliding or slumping of the unconsolidated sedi ...
belt. The northernmost corner of the state lies in the Connecticut Valley trough of the Boundary Mountains composite terrane. In the coastal region in the southeast is the Merrimack–Orrington Belt of the Nashoba–Casco–Miramichi composite terrane.
Geography
The state is bounded byQuebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
, Canada, to the north and northwest; Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and north ...
and the Atlantic Ocean to the east; Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
to the south; and Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
to the west. New Hampshire's major regions are the Great North Woods, the White Mountains, the Lakes Region, the Seacoast, the Merrimack Valley
The Merrimack Valley is a bi-state region along the Merrimack River in the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Massachusetts. The Merrimack is one of the larger waterways in New England and has helped to define the livelihood and culture of those l ...
, the Monadnock Region
The Monadnock Region is a region in southwestern New Hampshire. It is named after Mount Monadnock, a 3,165 foot isolated mountain, which is the dominant geographic landmark in the region. Although it has no specific borders, the Monadnock Region i ...
, and the Dartmouth-Lake Sunapee area. New Hampshire has the shortest ocean coastline of any U.S. coastal state, with a length of , sometimes measured as only . New Hampshire was home to the rock formation called the Old Man of the Mountain
The Old Man of the Mountain, also called the Great Stone Face and the Profile, was a series of five granite cliff ledges on Cannon Mountain in Franconia, New Hampshire, United States, that appeared to be the jagged profile of a human face when v ...
, a face-like profile in Franconia Notch
Franconia Notch (elev. ) is a major mountain pass through the White Mountains of New Hampshire. Dominated by Cannon Mountain to the west and Mount Lafayette to the east, it lies principally within Franconia Notch State Park and is traversed by ...
, until the formation disintegrated in May 2003.
The White Mountains in New Hampshire span the north-central portion of the state, with the summit of Mount Washington
Mount Washington is the highest peak in the Northeastern United States at and the most topographically prominent mountain east of the Mississippi River.
The mountain is notorious for its erratic weather. On the afternoon of April 12, 1934, ...
the highest point in the northeastern United States.
 In the southwest corner of New Hampshire, the landmark
In the southwest corner of New Hampshire, the landmark Mount Monadnock
Mount Monadnock, or Grand Monadnock, is a mountain in the towns of Jaffrey and Dublin, New Hampshire. It is the most prominent mountain peak in southern New Hampshire and is the highest point in Cheshire County. It lies southwest of Concord a ...
has given its name to a class of earth-forms – a ''monadnock
An inselberg or monadnock () is an isolated rock hill, knob, ridge, or small mountain that rises abruptly from a gently sloping or virtually level surrounding plain.
In Southern Africa a similar formation of granite is known as a koppie, a ...
'' – signifying, in geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or n ...
, any isolated resistant peak rising from a less resistant eroded plain.
Major rivers include the Merrimack River
The Merrimack River (or Merrimac River, an occasional earlier spelling) is a river in the northeastern United States. It rises at the confluence of the Pemigewasset and Winnipesaukee rivers in Franklin, New Hampshire, flows southward into Mas ...
, which bisects the lower half of the state north-south and reaches the Atlantic Ocean in Newburyport, Massachusetts
Newburyport is a coastal city in Essex County, Massachusetts, United States, northeast of Boston. The population was 18,289 at the 2020 census. A historic seaport with vibrant tourism industry, Newburyport includes part of Plum Island. The mo ...
. Its New Hampshire tributaries include the Contoocook River
The Contoocook River () is a river in New Hampshire. It flows from Contoocook Lake on the Jaffrey/ Rindge border to Penacook (just north of Concord), where it empties into the Merrimack River. It is one of only a few rivers in New Hampshire that ...
, Pemigewasset River
The Pemigewasset River , known locally as "The Pemi", is a river in the state of New Hampshire, the United States. It is in length and (with its tributaries) drains approximately . The name "Pemigewasset" comes from the Abenaki word ''bemijijoase ...
, and Winnipesaukee River
The Winnipesaukee River is a river that connects Lake Winnipesaukee with the Pemigewasset and Merrimack rivers in Franklin, New Hampshire. The river is in the Lakes Region of central New Hampshire. The river's drainage area is approximately .
...
. The Connecticut River
The Connecticut River is the longest river in the New England region of the United States, flowing roughly southward for through four states. It rises 300 yards (270 m) south of the U.S. border with Quebec, Canada, and discharges at Long Island ...
, which starts at New Hampshire's Connecticut Lakes
The Connecticut Lakes are a group of lakes in Coos County, northern New Hampshire, United States, situated along the headwaters of the Connecticut River. They are accessed via the northernmost segment of U.S. Route 3, between the village of Pitt ...
and flows south to Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its cap ...
, defines the western border with Vermont. The state border is not in the center of that river, as is usually the case, but at the low-water mark on the Vermont side; meaning that the entire river along the Vermont border (save for areas where the water level has been raised by a dam) lies within New Hampshire. Only one town – Pittsburg – shares a land border with the state of Vermont. The "northwesternmost headwaters" of the Connecticut, now known as Halls Stream
Halls Stream or Rivière Hall is a tributary of the Connecticut River in eastern North America. For most of its length, it forms the Canada–United States border, with the province of Quebec (Canada) to its west and the state of New Hampshire ...
, define Canada's border with New Hampshire.
The Piscataqua River
The Piscataqua River (Abenaki: ''Pskehtekwis'') is a tidal river forming the boundary of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine from its origin at the confluence of the Salmon Falls River and Cochecho River. The drainage basin of the river ...
forms the state's only significant ocean port where it flows into the Atlantic at Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
. The Salmon Falls River
The Salmon Falls River is a tributary of the Piscataqua River in the U.S. states of Maine and New Hampshire. It rises at Great East Lake, Newichawannock Canal, and Horn Pond and flows south-southeast for approximately , forming the border between ...
and the Piscataqua define the southern portion of the border with Maine. The largest of New Hampshire's lakes is Lake Winnipesaukee
Lake Winnipesaukee () is the largest lake in the U.S. state of New Hampshire, located in the Lakes Region at the foothills of the White Mountains. It is approximately long (northwest-southeast) and from wide (northeast-southwest), covering & ...
, which covers in the east-central part of New Hampshire. Umbagog Lake
Umbagog Lake is a wilderness lake located in Coös County, New Hampshire, and Oxford County, Maine. It is one of the most pristine lakes in the state of New Hampshire. It lies in the towns of Errol, New Hampshire, and Upton, Maine, as well as the t ...
along the Maine border, approximately , is a distant second. Squam Lake
Squam Lake is a lake located in the Lakes Region of central New Hampshire, United States, south of the White Mountains, straddling the borders of Grafton, Carroll, and Belknap counties. The largest town center on the lake is Holderness. The l ...
is the second largest lake entirely in New Hampshire.
New Hampshire has the shortest ocean coastline of any state in the United States, approximately long. About offshore are the Isles of Shoals
The Isles of Shoals are a group of small islands and tidal ledges situated approximately off the east coast of the United States, straddling the border of the states of Maine and New Hampshire.
They have been occupied for more than 400 years, fi ...
, nine small islands (four in New Hampshire and five in Maine).
Earthquakes
While New Hampshire, along with the rest ofNew England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
, does not frequently experience earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
s, it has experienced several in history and has been affected by some of the larger events that were centered in the Saint Lawrence rift system
The Saint Lawrence rift system is a seismically active zone paralleling the Saint Lawrence River. The rift system trends northeast and southwest and forms a half-graben that links the Ottawa-Bonnechere and the Saguenay grabens. The rift system e ...
in Canada. One of these was the 1663 Charlevoix earthquake
The 1663 Charlevoix earthquake occurred on February 5 in New France (now the Canadian province of Quebec), and was assessed to have a moment magnitude of between 7.3 and 7.9. The earthquake occurred at 5:30 p.m. local time and was estimated ...
that was centered near the Quebec–Maine border, the magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
of which has since been estimated at 7.3 to 7.9. In 1727, Newbury, Massachusetts
Newbury is a town in Essex County, Massachusetts, USA. The population was 6,716 at the 2020 census. Newbury includes the villages of Old Town (Newbury Center), Plum Island and Byfield. Each village is a precinct with its own voting district, ...
, experienced a damaging earthquake that shook New Hampshire also. The 1755 Cape Ann earthquake
The 1755 Cape Ann earthquake took place off the coast of the British Province of Massachusetts Bay (present-day Massachusetts) on November 18. At between 6.0 and 6.3 on the Richter scale, it remains the largest earthquake in the history of Massac ...
, estimated magnitude 5.5–6.0, also shook most or all of New Hampshire. On November 9, 1810, Exeter
Exeter () is a city in Devon, South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter was established as the base of Legio II Augusta under the personal comm ...
experienced an estimated intensity VI (''Strong'') tremor. It was accompanied by an unusual noise like an explosion, and broke windows in Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
. Concord
Concord may refer to:
Meaning "agreement"
* Pact or treaty, frequently between nations (indicating a condition of harmony)
* Harmony, in music
* Agreement (linguistics), a change in the form of a word depending on grammatical features of other ...
, the capital, experienced a series of shocks between 1872 and 1891. One earthquake was felt in late 1872, lasting ten seconds in Concord, and was felt in Laconia
Laconia or Lakonia ( el, Λακωνία, , ) is a historical and administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparta. The word ''laconic''—to speak in a blunt, c ...
and other towns to the north. Ten years later, another tremor was strongest in Concord, although Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone ...
and Pittsfield
Pittsfield is the largest city and the county seat of Berkshire County, Massachusetts, United States. It is the principal city of the Pittsfield, Massachusetts Metropolitan Statistical Area which encompasses all of Berkshire County. Pittsfield� ...
reportedly had buildings shaken. On November 23, 1884, a light shock was followed fifteen minutes later by a severe earthquake in Concord. The second shock was felt in Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
, Connecticut, and eastern New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
. Concord's last tremor in that period was mild and was reported in Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
and Melrose, Massachusetts
Melrose is a city located in the Greater Boston metropolitan area in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. Its population, per the 2020 United States Census, is 29,817. It is a suburb located approximately seven miles north of Boston. I ...
.
Southeastern New Hampshire and Maine experienced an earthquake in 1925. Dishes and goods were jostled from shelves in Ossipee
Ossipee is a town in Carroll County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 4,372 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Carroll County. Ossipee, which includes several villages, is a resort area and home to part of Pine River S ...
, Tuftonboro, and Effingham Falls. In 1929 the Grand Banks of Newfoundland
The Grand Banks of Newfoundland are a series of underwater plateaus south-east of the island of Newfoundland on the North American continental shelf. The Grand Banks are one of the world's richest fishing grounds, supporting Atlantic cod, swordf ...
( to the east) experienced a magnitude 7.2 earthquake, and New Hampshire felt minor effects. In 1935, a 6.25 earthquake centered in Timiskaming, Ontario, away, was felt in an area of over , and some places in New Hampshire experienced Mercalli intensities as high as V (''Moderate''). Ossipee Lake
Ossipee Lake is located in Carroll County in eastern New Hampshire, in the communities of Ossipee and Freedom. At , it is the sixth-largest lake located entirely in New Hampshire. The lake is fed by the West Branch (entering from the north), the ...
was the site of two moderate earthquakes in December 1940. The quakes were felt in all six New England states, as well as parts of New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
. In the epicentral area, a large number of aftershock
In seismology, an aftershock is a smaller earthquake that follows a larger earthquake, in the same area of the main shock, caused as the displaced crust adjusts to the effects of the main shock. Large earthquakes can have hundreds to thousand ...
s happened. One observer counted over 120 aftershocks through January 31, 1941.
See also
*Geology of New England
New England is a region in the North Eastern United States consisting of the states Rhode Island, Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Vermont, and Maine. Most of New England consists geologically of volcanic island arcs that accreted onto ...
References
{{Geology of the United States by political divisionNew Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
Natural history of New Hampshire