|
Brian (software)
Brian is an open source Python package for developing simulations of networks of spiking neurons. Details Brian is aimed at researchers developing models based on networks of spiking neurons. The general design is aimed at maximising flexibility, simplicity and users' development time.Goodman and Brette 2009 Users specify neuron models by giving their differential equations in standard mathematical form as strings, create groups of neurons and connect them via synapses. This is in contrast to the approach taken by many neural simulators in which users select from a predefined set of neuron models. Brian is written in Python. Computationally, it is based around the concept of code generation: users specify the model in Python but behind the scenes Brian generates, compiles and runs code in one of several languages (including Python, Cython and C++). In addition there is a "standalone" mode in which Brian generates an entire C++ source code tree with no dependency on Brian, all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level programming language, high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is type system#DYNAMIC, dynamically type-checked and garbage collection (computer science), garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured programming, structured (particularly procedural programming, procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC (programming language), ABC programming language, and he first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2.7.18, released in 2020, was the last release of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Biological Neuron Model
Biological neuron models, also known as spiking neuron models, are mathematical descriptions of the conduction of electrical signals in neurons. Neurons (or nerve cells) are electrically excitable cells within the nervous system, able to fire electric signals, called action potentials, across a neural network. These mathematical models describe the role of the biophysical and geometrical characteristics of neurons on the conduction of electrical activity. Central to these models is the description of how the membrane potential (that is, the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell) across the cell membrane changes over time. In an experimental setting, stimulating neurons with an electrical current generates an action potential (or spike), that propagates down the neuron's axon. This axon can branch out and connect to a large number of downstream neurons at sites called synapses. At these synapses, the spike can cause the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Scientific Simulation Software
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which study the physical world, and the social sciences, which study individuals and societies. While referred to as the formal sciences, the study of logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science are typically regarded as separate because they rely on deductive reasoning instead of the scientific method as their main methodology. Meanwhile, applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as engineering and medicine. The history of science spans the majority of the historical record, with the earliest identifiable predecessors to modern science dating to the Bronze Age in Egypt and Mesopotamia (). Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped the Greek nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computational Neuroscience
Computational neuroscience (also known as theoretical neuroscience or mathematical neuroscience) is a branch of neuroscience which employs mathematics, computer science, theoretical analysis and abstractions of the brain to understand the principles that govern the development, structure, physiology and cognitive abilities of the nervous system. Computational neuroscience employs computational simulations to validate and solve mathematical models, and so can be seen as a sub-field of theoretical neuroscience; however, the two fields are often synonymous. The term mathematical neuroscience is also used sometimes, to stress the quantitative nature of the field. Computational neuroscience focuses on the description of biologically plausible neurons (and neural systems) and their physiology and dynamics, and it is therefore not directly concerned with biologically unrealistic models used in connectionism, control theory, cybernetics, quantitative psychology, machine le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
NEST (software)
NEST is a simulation software for spiking neural network models, including large-scale neuronal networks. NEST was initially developed by Markus Diesmann and Marc-Oliver Gewaltig and is now developed and maintained by the NEST Initiative. Modeling philosophy A NEST simulation tries to follow the logic of an electrophysiological experiment that takes place inside a computer with the difference, that the neural system to be investigated must be defined by the experimenter. The neural system is defined by a possibly large number of neurons and their connections. In a NEST network, different neuron and synapse models can coexist. Any two neurons can have multiple connections with different properties. Thus, the connectivity can in general not be described by a weight or connectivity matrix but rather as an adjacency list. To manipulate or observe the network dynamics, the experimenter can define so-called devices which represent the various instruments (for measuring and stim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
GENESIS (software)
GENESIS (The ''General Neural Simulation System'') is a simulation environment for constructing realistic models of neurobiological systems at many levels of scale including: sub-cellular processes, individual neurons, networks of neurons, and neuronal systems. These simulations are “computer-based implementations of models whose primary objective is to capture what is known of the anatomical structure and physiological characteristics of the neural system of interest”. GENESIS is intended to quantify the physical framework of the nervous system in a way that allows for easy understanding of the physical structure of the nerves in question. “At present only GENESIS allows parallelized modeling of single neurons and networks on multiple-instruction-multiple-data parallel computers.” Development of GENESIS software spread from its home at Caltech to labs at the University of Texas at San Antonio, the University of Antwerp, the National Centre for Biological Sciences in Banga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neuron (software)
Neuron is a simulation environment for modeling individual and networks of neurons. It was primarily developed by Michael Hines, John W. Moore, and Ted Carnevale at Yale and Duke. Neuron models individual neurons via the use of sections that are automatically subdivided into individual compartments, instead of requiring the user to manually create compartments. The primary scripting language is hoc but a Python interface is also available. Programs can be written interactively in a shell, or loaded from a file. Neuron supports parallelization via the MPI protocol. Neuron is capable of handling diffusion-reaction models, and integrating diffusion functions into models of synapses and cellular networks. Parallelization is possible via internal multithreaded routines, for use on multi-core computers. The properties of the membrane channels of the neuron are simulated using compiled mechanisms written using the NMODL language or by compiled routines operating on internal data stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sample Raster Plot From Brian Neural Network Simulator
Sample or samples may refer to: * Sample (graphics), an intersection of a color channel and a pixel * Sample (material), a specimen or small quantity of something * Sample (signal), a digital discrete sample of a continuous analog signal * Sample (statistics), a subset of a population – complete data set People * Sample (surname) * Samples (surname) Places * Sample, Kentucky, unincorporated community, United States * Sampleville, Ohio, unincorporated community, United States * Hugh W. and Sarah Sample House, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Iowa, United States Music * Sample (music), to reuse a portion of a sound recording in another recording, or the portion reused * "Sample" (Sakanaction song) * "Sample", a song by No-Man from ''Flowermix'' * The Samples, a band from Boulder, Colorado Other uses * USS ''Sample'' (FF-1048), a frigate in the U.S. Navy * The Sample, a defunct department store in Buffalo, New York, U.S. * SAMPLE history, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Source Code
In computing, source code, or simply code or source, is a plain text computer program written in a programming language. A programmer writes the human readable source code to control the behavior of a computer. Since a computer, at base, only understands machine code, source code must be Translator (computing), translated before a computer can Execution (computing), execute it. The translation process can be implemented three ways. Source code can be converted into machine code by a compiler or an assembler (computing), assembler. The resulting executable is machine code ready for the computer. Alternatively, source code can be executed without conversion via an interpreter (computing), interpreter. An interpreter loads the source code into memory. It simultaneously translates and executes each statement (computer science), statement. A method that combines compilation and interpretation is to first produce bytecode. Bytecode is an intermediate representation of source code tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cross-platform
Within computing, cross-platform software (also called multi-platform software, platform-agnostic software, or platform-independent software) is computer software that is designed to work in several Computing platform, computing platforms. Some cross-platform software requires a separate build for each platform, but some can be directly run on any platform without special preparation, being written in an interpreted language or compiled to portable bytecode for which the Interpreter (computing), interpreters or run-time packages are common or standard components of all supported platforms. For example, a cross-platform application software, application may run on Linux, macOS and Microsoft Windows. Cross-platform software may run on many platforms, or as few as two. Some frameworks for cross-platform development are Codename One, ArkUI-X, Kivy (framework), Kivy, Qt (software), Qt, GTK, Flutter (software), Flutter, NativeScript, Xamarin, Apache Cordova, Ionic (mobile app framework ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
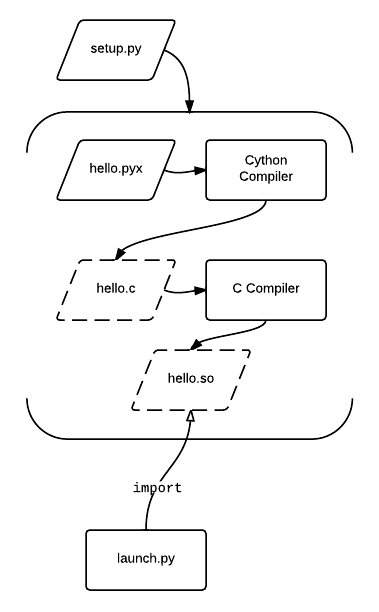
Cython
Cython () is a superset of the programming language Python, which allows developers to write Python code (with optional, C-inspired syntax extensions) that yields performance comparable to that of C. Cython is a compiled language that is typically used to generate CPython extension modules. Annotated Python-like code is compiled to C and then automatically wrapped in interface code, producing extension modules that can be loaded and used by regular Python code using the import statement, but with significantly less computational overhead at run time. Cython also facilitates wrapping independent C or C++ code into python-importable modules. Cython is written in Python and C and works on Windows, macOS, and Linux, producing C source files compatible with CPython 2.6, 2.7, and 3.3 and later versions. The Cython source code that Cython compiles (to C) can use both Python 2 and Python 3 syntax, defaulting to Python 2 syntax in Cython 0.x and Python 3 syntax in Cython 3.x. The d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that allows a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or a target effector cell. Synapses can be classified as either chemical or electrical, depending on the mechanism of signal transmission between neurons. In the case of electrical synapses, neurons are coupled bidirectionally with each other through gap junctions and have a connected cytoplasmic milieu. These types of synapses are known to produce synchronous network activity in the brain, but can also result in complicated, chaotic network level dynamics. Therefore, signal directionality cannot always be defined across electrical synapses. Chemical synapses, on the other hand, communicate through neurotransmitters released from the presynaptic neuron into the synaptic cleft. Upon release, these neurotransmitters bind to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, inducing an electrical or chemical response in the target neuron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |