|
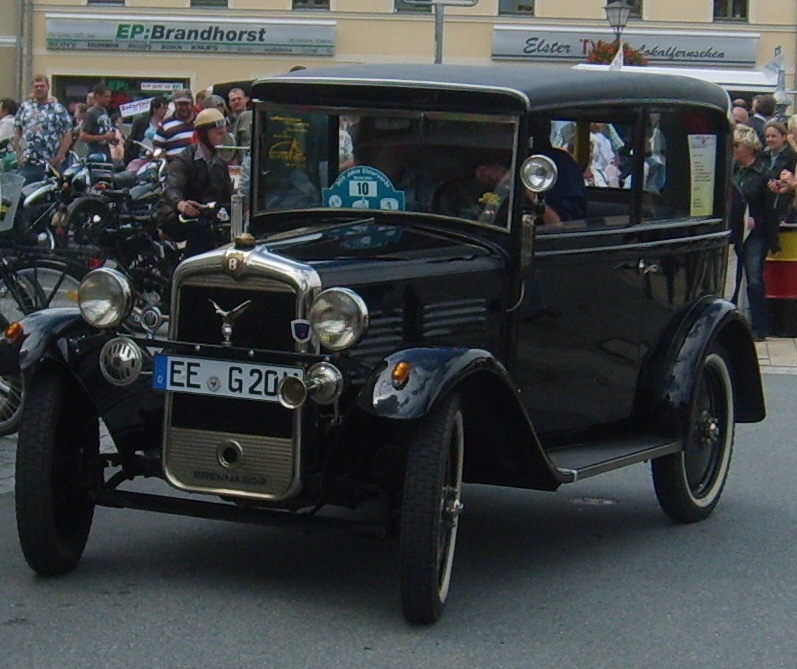
Brennabor Typ D
The 1 Litre Brennabor Typ C is a small car introduced by Brennabor in 1931. In the wake of a sustained period of economic difficulties it represented a belated extension of the company’s range into the "small car" sector which hitherto Brennabor had ignored. In 1933 the car was upgraded and became the short-lived Brennabor Typ D The Typ C was powered by a newly developed 4-cylinder 1 litre side-valve engine of 3.4 litres, mounted ahead of the driver and delivering 20 hp at 2,800 rpm. Power was delivered to the rear wheels through a single plate dry clutch and a three-speed gear box controlled using a centrally positioned floor-mounted gear stick. The car sat on a U-profile pressed steel chassis with rigid axles and semi-elliptical leaf springing. It was offered as a two-door sedan/saloon, a two-door cabriolet or a two-day roadster, in every case with a 2+2 seating configuration. The mechanically linked foot brake operated directly on all four wheels, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brennabor Elsterwerda
Brennabor-Werke AG (previously Brennabor-Werke Gebr. Reichstein) was a German manufacturer of infant buggies, bicycles, motorcycles and, for two decades, of powered motor vehicles. It was based in Brandenburg an der Havel and operated between 1871 and 1945. History The company was set up in 1871 by three brothers named Adolf, Carl and Hermann Reichstein. The brothers had already been producing basket-work child buggies and children's two-wheelers in 1870, and in 1881 had moved into the booming mainstream bicycle business. From 1892 the bicycles were branded with the Brennabor name. By the 1930s the company had grown to become Europe's largest produced of infant buggies and was also a leading bicycle producer. Volume production of motor bikes began in 1901, and from 1903 the company was producing, at this stage only to special order, three- and four-wheeled powered vehicles. 1908 saw the beginning of series production of cars, and this was also the year that the comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
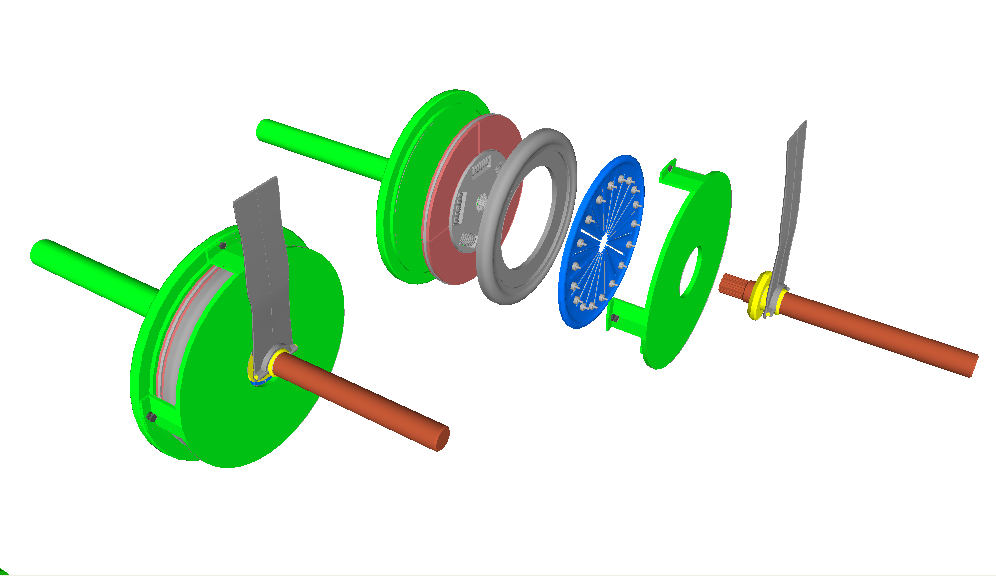
Brennabor D 1933
Brennabor-Werke AG (previously Brennabor-Werke Gebr. Reichstein) was a German manufacturer of infant buggies, bicycles, motorcycles and, for two decades, of powered motor vehicles. It was based in Brandenburg an der Havel and operated between 1871 and 1945. History The company was set up in 1871 by three brothers named Adolf, Carl and Hermann Reichstein. The brothers had already been producing basket-work child buggies and children's two-wheelers in 1870, and in 1881 had moved into the booming mainstream bicycle business. From 1892 the bicycles were branded with the Brennabor name. By the 1930s the company had grown to become Europe's largest produced of infant buggies and was also a leading bicycle producer. Volume production of motor bikes began in 1901, and from 1903 the company was producing, at this stage only to special order, three- and four-wheeled powered vehicles. 1908 saw the beginning of series production of cars, and this was also the year that the comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brennabor
Brennabor-Werke AG (previously Brennabor-Werke Gebr. Reichstein) was a German manufacturer of infant buggies, bicycles, motorcycles and, for two decades, of powered motor vehicles. It was based in Brandenburg an der Havel and operated between 1871 and 1945. History The company was set up in 1871 by three brothers named Adolf, Carl and Hermann Reichstein. The brothers had already been producing basket-work child buggies and children's two-wheelers in 1870, and in 1881 had moved into the booming mainstream bicycle business. From 1892 the bicycles were branded with the Brennabor name. By the 1930s the company had grown to become Europe's largest produced of infant buggies and was also a leading bicycle producer. Volume production of motor bikes began in 1901, and from 1903 the company was producing, at this stage only to special order, three- and four-wheeled powered vehicles. 1908 saw the beginning of series production of cars, and this was also the year that the company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Side-valve Engine
A flathead engine, also known as a sidevalve engine''American Rodder'', 6/94, pp.45 & 93. or valve-in-block engine is an internal combustion engine with its poppet valves contained within the Cam-in-block, engine block, instead of in the cylinder head, as in an overhead valve engine. Flatheads were widely used internationally by automobile manufacturers from the late 1890s until the mid-1950s but were replaced by more efficient overhead valve and Overhead camshaft engine, overhead camshaft engines. They are currently experiencing a revival in low-revving aviation engine, aero-engines such as the D-Motor. The side-valve design The valve gear comprises a camshaft sited low in the cylinder block which operates the poppet valve, poppet valves via tappets and short pushrods (or sometimes with no pushrods at all). The flathead system obviates the need for further valvetrain components such as lengthy pushrods, rocker arms, overhead valves or overhead camshafts. The sidevalves are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission, especially from a drive shaft to a driven shaft. In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts). In these devices, one shaft is typically attached to an engine or other power unit (the driving member), while the other shaft (the driven member) provides output power for work. Typically the motions involved are rotary, but linear clutches also exist. In a motor vehicle, the clutch acts as a mechanical linkage between the engine and transmission, and briefly disconnects, or separates the engine from the transmission system. This disconnects the drive wheels whenever the clutch pedal is depressed, allowing the driver to smoothly change gears. In a torque-controlled drill, for instance, one shaft is driven by a motor, and the other drives a drill chuck. The clutch connects the two shafts so they may be locked together and spin at the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gear Box
Propulsion transmission is the mode of transmitting and controlling propulsion power of a machine. The term ''transmission'' properly refers to the whole drivetrain, including clutch, gearbox, prop shaft (for rear-wheel drive vehicles), differential, and final drive shafts. In the United States the term is sometimes used in casual speech to refer more specifically to the gearbox alone, and detailed usage differs. The transmission reduces the higher engine speed to the slower wheel speed, increasing torque in the process. Transmissions are also used on pedal bicycles, fixed machines, and where different rotational speeds and torques are adapted. Often, a transmission has multiple gear ratios (or simply "gears") with the ability to switch between them as the speed varies. This switching may be done manually (by the operator) or automatically (by a control unit). Directional (forward and reverse) control may also be provided. Single-ratio transmissions also exist, which simply chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaf Spring
A leaf spring is a simple form of spring commonly used for the suspension in wheeled vehicles. Originally called a ''laminated'' or ''carriage spring'', and sometimes referred to as a semi-elliptical spring, elliptical spring, or cart spring, it is one of the oldest forms of vehicle suspension. A leaf spring is one or more narrow, arc-shaped, thin plates which are attached to the axle and chassis in a way that allows the leaf spring to flex vertically in response to irregularities in the road surface. Lateral leaf springs are the most commonly used arrangement, running the length of the vehicle and mounted perpendicular to the wheel axle, but numerous examples of transverse leaf springs exist as well. Leaf springs can serve multiple suspension functions: location, springing, and to some extent damping as well, through interleaf friction. However, this friction is not well controlled, resulting in stiction and irregular suspension motions. For this reason, some manufacturers have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabriolet
A convertible or cabriolet () is a passenger car that can be driven with or without a roof in place. The methods of retracting and storing the roof vary among eras and manufacturers. A convertible car's design allows an open-air driving experience, with the ability to provide a roof when required. A potential drawback of convertibles is their reduced structural rigidity (requiring significant engineering and modification to counteract the effects of removing a car's roof). The majority of convertible roofs are of a folding construction framework with the actual top made from cloth or other fabric. Other types of convertible roofs include retractable hardtops (often constructed from metal or plastic) and detachable hardtops (where a metal or plastic roof is manually removed and often stored in the trunk). Terminology Other terms for convertibles include cabriolet, cabrio, drop top, drophead coupé, open two-seater, open top, rag top, soft top, spider, and spyder. Consistenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brennabor Typ D
The 1 Litre Brennabor Typ C is a small car introduced by Brennabor in 1931. In the wake of a sustained period of economic difficulties it represented a belated extension of the company’s range into the "small car" sector which hitherto Brennabor had ignored. In 1933 the car was upgraded and became the short-lived Brennabor Typ D The Typ C was powered by a newly developed 4-cylinder 1 litre side-valve engine of 3.4 litres, mounted ahead of the driver and delivering 20 hp at 2,800 rpm. Power was delivered to the rear wheels through a single plate dry clutch and a three-speed gear box controlled using a centrally positioned floor-mounted gear stick. The car sat on a U-profile pressed steel chassis with rigid axles and semi-elliptical leaf springing. It was offered as a two-door sedan/saloon, a two-door cabriolet or a two-day roadster, in every case with a 2+2 seating configuration. The mechanically linked foot brake operated directly on all four wheels, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compression Ratio
The compression ratio is the ratio between the volume of the cylinder and combustion chamber in an internal combustion engine at their maximum and minimum values. A fundamental specification for such engines, it is measured two ways: the static compression ratio, calculated based on the relative volumes of the combustion chamber and the cylinder when the piston is at the bottom of its stroke, and the volume of the combustion chamber when the piston is at the top of its stroke. The dynamic compression ratio is a more advanced calculation which also takes into account gasses entering and exiting the cylinder during the compression phase. Effect and typical ratios A high compression ratio is desirable because it allows an engine to extract more mechanical energy from a given mass of air–fuel mixture due to its higher thermal efficiency. This occurs because internal combustion engines are heat engines, and higher compression ratios permit the same combustion temperature to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with Wheel, wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, people instead of cargo, goods. The year 1886 is regarded as the birth year of the car, when German inventor Carl Benz patented his Benz Patent-Motorwagen. Cars became widely available during the 20th century. One of the first cars affordable by the masses was the 1908 Ford Model T, Model T, an American car manufactured by the Ford Motor Company. Cars were rapidly adopted in the US, where they replaced Draft animal, animal-drawn carriages and carts. In Europe and other parts of the world, demand for automobiles did not increase until after World War II. The car is considered an essential part of the Developed country, developed economy. Cars have controls for driving, parking, passenger comfort, and a variety of lights. Over the decades, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

.jpg)


