|
Bowin P3
The Bowin P3 is a monocoque racing car that was produced in 1968 by Bowin. The P3 was designed for the Australian National Formula and the Australian 1½ Litre Formula. After the capacity limit for Australian Formula 2 was increased from 1100cc to 1600cc at the beginning of 1969, the P3 found a new home in that class. The car was designed by John Joyce, founder of Bowin and assisted by Ray Parson, better known as a mechanic. This was the only Bowin car type to come out of the Joyce-Parsons association. The project took just over 12 weeks to complete. Three P3s were built.Pedr Davis, The Macquarie Dictionary of Motoring, 1986, page 54 The first was for Queensland racing driver Glyn Scott, who fitted the car with a "spare" 1600cc Cosworth FVA engine he bought from Piers Courage after the 1968 Tasman Series. A Formula 2 version was built for Ian Ferguson and a Holden powered hillclimb car was produced for Barry Garner. Design Concept There were two major points about th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowin Cars
Bowin Cars was an Australia, Australian designer and manufacturer of motor racing cars from 1968 to 1976. The company was founded by John Joyce (car designer), John Vincent Joyce (1938–2002), a successful designer and builder of racing cars and in later years gas appliances incorporating LO-NOx burner, Low NOx Technology. History Approximately ten racing cars were sold for export to Canada, New Zealand and South East Asia. Bowin Cars have raced successfully in these countries as well as Europe. Models All Bowin Cars started with the letter P, which simply stood for project. Earlier Models In fact, two Formula Juniors were designed and built by John Joyce prior to the formation of Bowin Cars. * (P1) - A Cooper-based car in 1959 * (P2) - The Koala in 1962. Bowin Models * Bowin P3 - 1967-1968 P3 Australian National Formula Car * Bowin P4 - 1970-1974 P4 Formula Ford Car * Bowin P6 - 1972-1974 P6 Formula Ford & Formula 2 Car * Bowin P7 - 1973-1975 P7 ? * Bowin P8 - 1973-1975 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indianapolis
Indianapolis (), colloquially known as Indy, is the state capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Indiana and the seat of Marion County. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the consolidated population of Indianapolis and Marion County was 977,203 in 2020. The "balance" population, which excludes semi-autonomous municipalities in Marion County, was 887,642. It is the 15th most populous city in the U.S., the third-most populous city in the Midwest, after Chicago and Columbus, Ohio, and the fourth-most populous state capital after Phoenix, Arizona, Austin, Texas, and Columbus. The Indianapolis metropolitan area is the 33rd most populous metropolitan statistical area in the U.S., with 2,111,040 residents. Its combined statistical area ranks 28th, with a population of 2,431,361. Indianapolis covers , making it the 18th largest city by land area in the U.S. Indigenous peoples inhabited the area dating to as early as 10,000 BC. In 1818, the Lenape relinquished their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disc Brakes
A disc brake is a type of brake that uses the calipers to squeeze pairs of pads against a disc or a "rotor" to create friction. This action slows the rotation of a shaft, such as a vehicle axle, either to reduce its rotational speed or to hold it stationary. The energy of motion is converted into waste heat which must be dispersed. Hydraulically actuated disc brakes are the most commonly used form of brake for motor vehicles, but the principles of a disc brake are applicable to almost any rotating shaft. The components include the disc, master cylinder, and caliper (which contains a cylinder and two brake pads) on both sides of the disc. Design The development of disc-type brakes began in England in the 1890s. In 1902, the Lanchester Motor Company designed brakes that looked and operated in a similar way to a modern disc-brake system even though the disc was thin and a cable activated the brake pad. Other designs were not practical or widely available in cars for another 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camber Angle
Camber angle is one of the angles made by the wheels of a vehicle; specifically, it is the angle between the vertical axis of a wheel and the vertical axis of the vehicle when viewed from the front or rear. It is used in the design of steering and suspension. If the top of the wheel is farther out than the bottom (that is, tilted away from the axle), it is called positive camber; if the bottom of the wheel is farther out than the top, it is called negative camber. Effect on handling Camber angle alters the handling qualities of some suspension designs; in particular, negative camber improves grip in corners especially with a short long arms suspension. This is because it places the tire at a better angle to the road, transmitting the centrifugal forces through the vertical plane of the tire rather than through a shear force across it. The centrifugal (outwards) force is compensated for by applying negative camber, which turns the contact surface of the tire outwards to match ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casting
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a ''casting'', which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process. Casting materials are usually metals or various ''time setting'' materials that cure after mixing two or more components together; examples are epoxy, concrete, plaster and clay. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be otherwise difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods. Heavy equipment like machine tool beds, ships' propellers, etc. can be cast easily in the required size, rather than fabricating by joining several small pieces. Casting is a 7,000-year-old process. The oldest surviving casting is a copper frog from 3200 BC. History Throughout history, metal casting has been used to make tools, weapons, and religious objects. Metal casting history and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic table) it occurs naturally only in combination with other elements and it almost always has an oxidation state of +2. It reacts readily with air to form a thin passivation coating of magnesium oxide that inhibits further corrosion of the metal. The free metal burns with a brilliant-white light. The metal is obtained mainly by electrolysis of magnesium salts obtained from brine. It is less dense than aluminium and is used primarily as a component in strong and lightweight alloys that contain aluminium. In the cosmos, magnesium is produced in large, aging stars by the sequential addition of three helium nuclei to a carbon nucleus. When such stars explode as supernovas, much of the magnesium is expelled into the interstellar medium where it ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
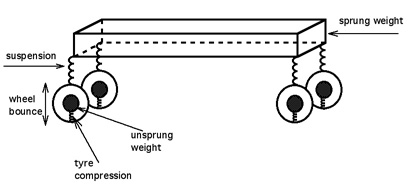
Unsprung Weight
The unsprung mass (colloquially unsprung weight) of a vehicle is the mass of the suspension, wheels or tracks (as applicable), and other components directly connected to them. This contrasts with the sprung mass (or weight) supported by the suspension, which includes the body and other components within or attached to it. Components of the unsprung mass include the wheel axles, wheel bearings, wheel hubs, tires, and a portion of the weight of driveshafts, springs, shock absorbers, and suspension links. Brakes that are mounted inboard (i.e. as on the drive shaft, and not part of the wheel or its hub) are part of a vehicle's sprung mass. Effects The unsprung mass of a typical wheel/tire combination represents a trade-off between the pair's bump-absorbing/road-tracking ability and vibration isolation. Bumps and surface imperfections in the road cause tire compression, inducing a force on the unsprung mass. The unsprung mass then reacts to this force with movement of its o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drive Shaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power (physics), power and torque and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them. As torque carriers, drive shafts are subject to torsion (mechanics), torsion and shear stress, equivalent to the difference between the input torque and the load. They must therefore be strong enough to bear the stress, while avoiding too much additional weight as that would in turn increase their inertia. To allow for variations in the alignment and distance between the driving and driven components, drive shafts frequently incorporate one or more universal joints, jaw couplings, or rag joints, and sometimes a Rotating spline, splined joint or prismatic joint. History The term ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock Absorbers
A shock absorber or damper is a mechanical or hydraulic device designed to absorb and damp shock impulses. It does this by converting the kinetic energy of the shock into another form of energy (typically heat) which is then dissipated. Most shock absorbers are a form of dashpot (a damper which resists motion via viscous friction). Description Pneumatic and hydraulic shock absorbers are used in conjunction with cushions and springs. An automobile shock absorber contains spring-loaded check valves and orifices to control the flow of oil through an internal piston (see below). One design consideration, when designing or choosing a shock absorber, is where that energy will go. In most shock absorbers, energy is converted to heat inside the viscous fluid. In hydraulic cylinders, the hydraulic fluid heats up, while in air cylinders, the hot air is usually exhausted to the atmosphere. In other types of shock absorbers, such as electromagnetic types, the dissipated energy can be s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coil Spring
A selection of conical coil springs The most common type of spring is the coil spring, which is made out of a long piece of metal that is wound around itself. Coil springs were in use in Roman times, evidence of this can be found in bronze Fibulae - the clasps worn by Roman soldiers among others. These are quite commonly found in Roman archeological digs. Coil springs can be either compression springs, tension springs or torsion springs, depending on how they are wound. A coil spring is a mechanical device which is typically used to store energy and subsequently release it, to absorb shock, or to maintain a force between contacting surfaces. They are made of an elastic material formed into the shape of a helix which returns to its natural length when unloaded. They are commonly used in mattresses, automotive suspensions, and residential plumbing. Coil springs come in a variety of sizes and shapes and can be used for a variety of applications. Small coil springs are often us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-roll Bar
An anti-roll bar (roll bar, anti-sway bar, sway bar, stabilizer bar) is a part of many automobile suspensions that helps reduce the body roll of a vehicle during fast cornering or over road irregularities. It connects opposite (left/right) wheels together through short lever arms linked by a torsion spring. A sway bar increases the suspension's roll stiffness—its resistance to roll in turns—independent of its spring rate in the vertical direction. The first stabilizer bar patent was awarded to Canadian inventor Stephen Coleman of Fredericton, New Brunswick on April 22, 1919. Anti-roll bars were unusual on pre-WW2 cars due to the generally much stiffer suspension and acceptance of body roll. From the 1950s on, however, production cars were more commonly fitted with anti-roll bars, especially those vehicles with softer coil spring suspension. Purpose and operation An anti-sway or anti-roll bar is intended to force each side of the vehicle to lower, or rise, to similar heig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
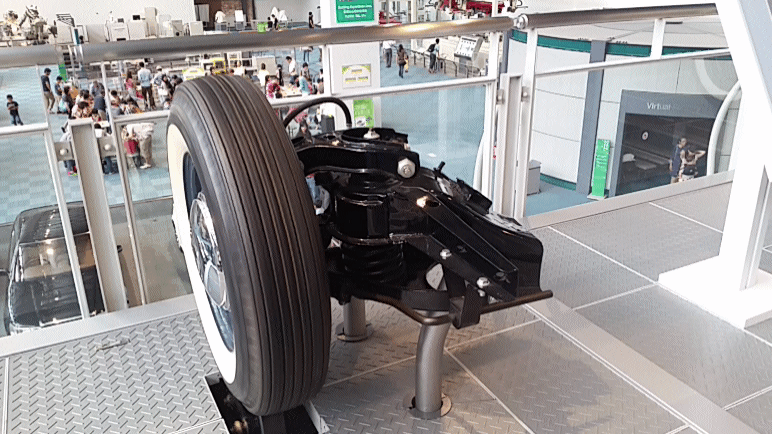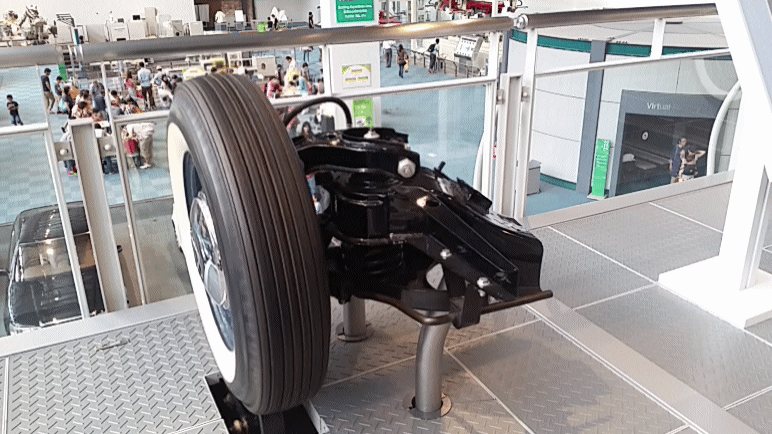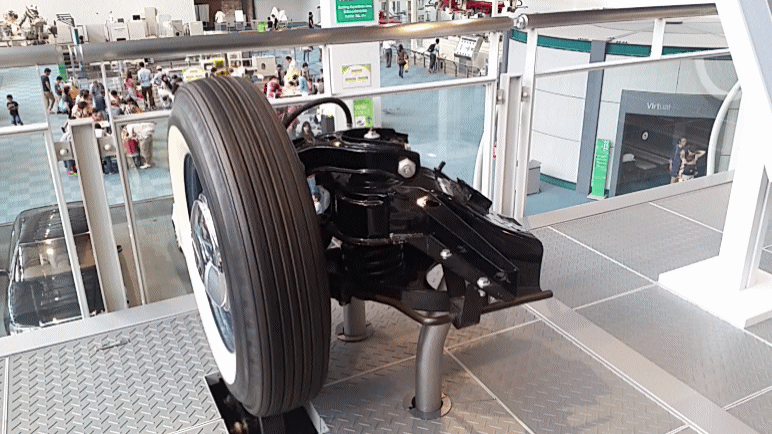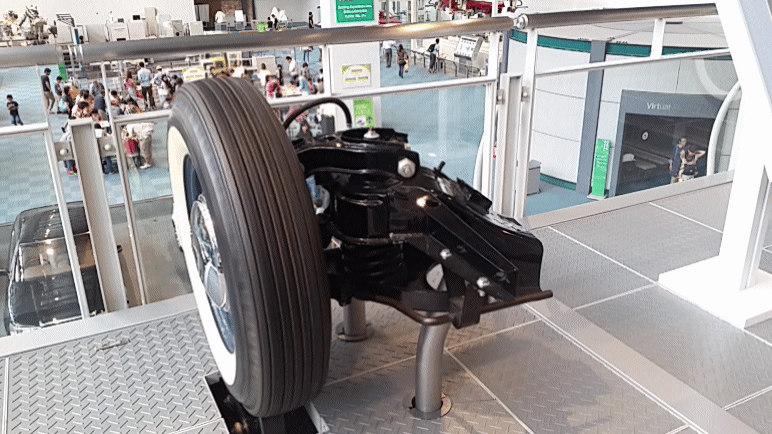
Double Wishbone
A double wishbone suspension is an independent suspension design for automobiles using two (occasionally parallel) wishbone-shaped arms to locate the wheel. Each wishbone or arm has two mounting points to the chassis and one joint at the knuckle. The shock absorber and coil spring mount to the wishbones to control vertical movement. Double wishbone designs allow the engineer to carefully control the motion of the wheel throughout suspension travel, controlling such parameters as camber angle, caster angle, toe pattern, roll center height, scrub radius, scuff and more. Implementation The double-wishbone suspension can also be referred to as "double A-arms", though the arms themselves can be A-shaped, L-shaped, or even a single bar linkage. A single wishbone or A-arm can also be used in various other suspension types, such as variations of the MacPherson strut. The upper arm is usually shorter to induce negative camber as the suspension jounces (rises), and often this arrangement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)