|
Bourbonnais Creole
Bourbonnais Creole is the group of French-based creole languages spoken in the western Indian Ocean. The close relation of the languages is from the similar historical and cultural backgrounds of the islands. The name is derived from the former name of Réunion Island: Bourbon Island before 1793. Another name is Mascarene Creole, as the predominant island group is called the Mascarenes. There are six languages in this group: * Agalega Creole * Chagossian Creole * Mauritian Creole * Réunion Creole * Rodriguan Creole * Seychellois Creole Seychellois Creole (), also known as kreol, is the French-based creole language spoken by the Seychelles Creole people of the Seychelles. It shares national language status with English and French (in contrast to Mauritian and Réunion Creo ... Bibliography *Chaudenson, Robert (1974). ''Le Lexique du parler créole de la Réunion''. Paris: Champion, tomes I-II. *Baker, Philip & Chris Corne (1982). ''Isle de France Creole: Affinities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bourbonnais Dialect
The Bourbonnais dialects are spoken in the historic region of Bourbonnais, located in central France and including the department of Allier the area surrounding Saint-Amand-Montrond, in southeastern Cher. This linguistic zone is located between those home to the languages of Oïl, Occitan, and Franco-Provençal. Bourbonnais, an ambiguous term There are two indigenous languages in Bourbonnais: * An Oïl language is spoken in two thirds of Allier, north of the line Montluçon (Occitan) – Saint-Pourçain-sur-Sioule (Oïl) – Lapalisse (Oïl), and in the Bourbonnais part of Cher. The dialect has its origins in the Moulins, Allier area, Bourbon-l'Archambault, and Souvigny. * Occitan languages are spoken south of Montluçon and near Gannat and Vichy. These are dialects of the Occitan langage of the Croissant (linguistic) in southern Bourbonnais and northern Limousin. They are on their way to be integrated into the French language. The scientific term for these idioms i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' ( Atlantic) before the Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Chinese explorers in the Indian Ocean during the 15th century called it the Western Oceans. In Anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French-based Creole Languages
A French creole, or French-based creole language, is a creole for which French is the lexifier. Most often this lexifier is not modern French but rather a 17th- or 18th-century koiné of French from Paris, the French Atlantic harbors, and the nascent French colonies. This article also contains information on French pidgin languages, contact languages that lack native speakers. These contact languages are not to be confused with non-creole varieties of French outside of Europe that date to colonial times, such as Acadian, Louisiana, New England or Quebec French. There are over 15.5 million speakers of some form of based French based creole languages. Haitian Creole is the most spoken creole language in the world, with over 12 million speakers. History Throughout the 17th century, French Creoles became established as a unique ethnicity originating from the mix of French, Indian, and African cultures. These French Creoles held a distinct ethno-cultural identity, a shared an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Réunion Island
Réunion (; french: La Réunion, ; previously ''Île Bourbon''; rcf, label= Reunionese Creole, La Rényon) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas department and region of France. It is located approximately east of the island of Madagascar and southwest of the island of Mauritius. , it had a population of 868,846. Like the other four overseas departments, Réunion also holds the status of a region of France, and is an integral part of the French Republic. Réunion is an outermost region of the European Union and is part of the eurozone. Réunion and the fellow French overseas department of Mayotte are the only eurozone regions located in the Southern Hemisphere. As in the rest of France, the official language of Réunion is French. In addition, a majority of the region's population speaks Réunion Creole. Toponymy When France took possession of the island in the seventeenth century, it was named Bourbon, after the dynasty that then ruled France. To break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Group
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands. Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archipelago, the Aleutian Islands, the Lakshadweep Islands, the Galápagos Islands, the Japanese archipelago, the Philippine Archipelago, the Maldives, the Balearic Islands, the Åland Islands, The Bahamas, the Aegean Islands, the Hawaiian Islands, the Canary Islands, Malta, the Azores, the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, the British Isles, the islands of the Archipelago Sea, and Shetland. Archipelagos are sometimes defined by political boundaries. For example, while they are geopolitically divided, the San Juan Islands and Gulf Islands geologically form part of a larger Gulf Archipelago. Etymology The word ''archipelago'' is derived from the Ancient Greek ἄρχι-(''arkhi-'', "chief") and πέλαγος (''pélagos'', "sea") through the Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mascarene
The Mascarene Islands (, ) or Mascarenes or Mascarenhas Archipelago is a group of islands in the Indian Ocean east of Madagascar consisting of the islands belonging to the Republic of Mauritius as well as the French department of Réunion. Their name derives from the Portuguese navigator Pedro Mascarenhas, who first visited them in April 1512. The islands share a common geologic origin in the volcanism of the Réunion hotspot beneath the Mascarene Plateau and form a distinct ecoregion with a unique flora and fauna. Geography The archipelago comprises three large islands, Mauritius, Réunion, and Rodrigues, plus a number of volcanic remnants in the tropics of the southwestern Indian Ocean, generally between 700 and 1500 kilometres east of Madagascar. The terrain includes a variety of reefs, atolls, and small islands. They present various topographical and edaphic regions. On the largest islands these gave rise to unusual biodiversity. The climate is oceanic and tropical. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauritian Creole
Mauritian Creole or Morisien (formerly Morisyen) ( mfe, kreol morisien, links=no ) is a French-based creole language spoken in Mauritius. English words are included in the standardized version of the language. In addition, the slaves and indentured servants from cultures in Africa and Asia left a diverse legacy of language in the country. The words spoken by these groups are also incorporated into contemporary Morisien. Mauritian Creole is the '' lingua franca'' of the Republic of Mauritius, which gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1968. Both English and French are used as alternatives to Mauritian Creole. English is spoken primarily for administration and educational purposes and French is used by the media and as a second language. Mauritians tend to speak Mauritian Creole at home and French in the workplace. French and English are taught in schools. Though Mauritians are of numerous ethnic origins (including Indian, African, European, and Chinese) Mauritian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Réunion Creole
Réunion Creole, or Reunionese Creole ( rcf, kréol rénioné; french: créole réunionnais), is a French-based creole language spoken on Réunion. It is derived mainly from French and includes terms from Malagasy, Hindi, Portuguese, Gujarati and Tamil. In recent years, there has been an effort to develop a spelling dictionary and grammar rules. Partly because of the lack of an official orthography but also because schools are taught in French, Réunion Creole is rarely written. Notably, two translations of the French comic ''Asterix'' have been published. Réunion Creole is the main vernacular of the island and is used in most colloquial and familiar settings. It is, however, in a state of diglossia In linguistics, diglossia () is a situation in which two dialects or languages are used (in fairly strict compartmentalization) by a single language community. In addition to the community's everyday or vernacular language variety (labeled " ... with French as the hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
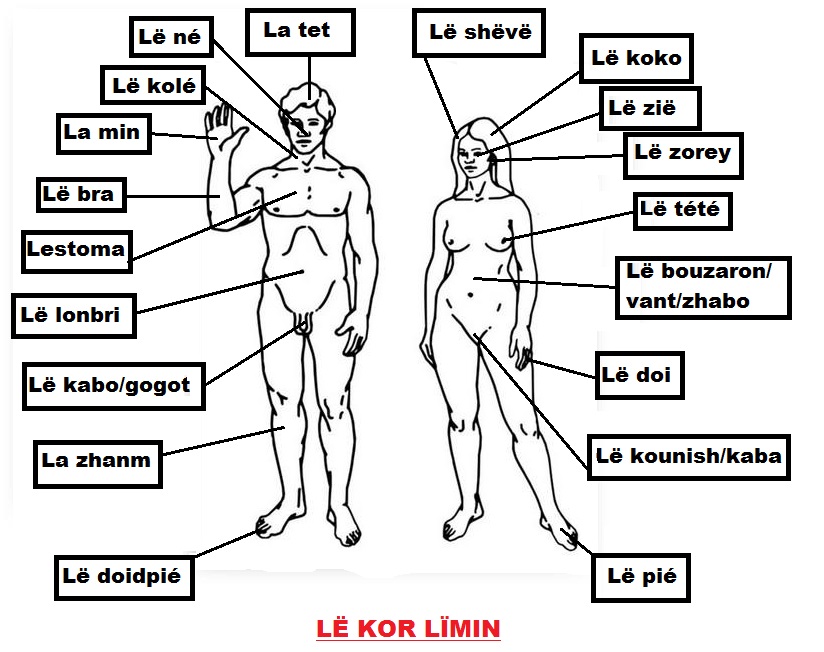
Seychellois Creole
Seychellois Creole (), also known as kreol, is the French-based creole language spoken by the Seychelles Creole people of the Seychelles. It shares national language status with English and French (in contrast to Mauritian and Réunion Creole, which lack official status in Mauritius and France). Description Since its independence in 1976, the government of the Seychelles has sought to develop the language, with its own orthography and codified grammar, establishing ''Lenstiti Kreol'' (the Creole Institute) for this purpose. In several Seychellois Creole words derived from French, the French definite article (''le'', ''la'' and ''les'') has become part of the word; for example, 'future' is ''lavenir'' (French ''l'avenir''). The possessive is the same as the pronoun, so that 'our future' is ''nou lavenir''. Similarly in the plural, ''les Îles Éloignées Seychelles'' in French ('the Outer Seychelles Islands') has become ''Zil Elwanyen Sesel'' in Creole. Note the ''z'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |