|
Bouqras
Bouqras is a large, oval shaped, prehistoric, Neolithic Tell, about in size, located around from Deir ez-Zor in Syria. Excavation The tell was discovered in 1960 by Dutch geomorphologist, Willem van Liere. It was excavated between 1960 and 1965 by Henri de Contenson and van Liere and later between 1976 and 1978 by Peter Akkermans, Maurits van Loon, J. J. Roodenberg and H. T. Waterbolk. Construction The mound was found to be approximately deep and showed evidence of 11 periods of occupation spread over at least 1000 years between ca. 7400 and 6200 BC. The earliest levels, 11 to 8, showed early Neolithic aceramic occupation developing on to stages with pottery in levels 7 to 1, from which over 7000 sherds were recovered. Material from later levels was visible on the surface when first discovered. The layout and arrangement of houses seems to have been well ordered with similar arrangements of rooms, entrances, hearths and other features. Houses were made of mud bricks and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tjalling Waterbolk
Harm Tjalling "Tjalling" Waterbolk (18 May 1924 – 27 September 2020) was a Dutch archaeologist. He was a professor of archaeology and director of the Biological-Archaeological Institute at the University of Groningen between 1954 and 1987. Waterbolk was known for his interdisciplinary approach and combined his work in archaeology with insights in nature and landscapes. He worked in a wide variety of countries, but had special interest in the Northern part of the Netherlands and especially his home province of Drenthe. Early life Waterbolk was born on 18 May 1924 in Havelte. His father Albert was the municipal clerk ''(Dutch: gemeentesecretaris)'' of Havelte. From an early age Waterbolk had an interest in nature, with this interest being supported by his parents, teachers and townspeople of Havelte. In 1942 he became a member of the during his youth, which further strengthened his interest in nature. Waterbolk attended the University of Groningen to study biology and later bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deir Ez-Zor Museum
The Deir ez-Zor Museum ( ar, متحف دير الزور) is a museum devoted to the archaeology and history of northeastern Syria, an area more commonly known as the Jezirah, or Upper Mesopotamia. The museum is located in Deir ez-Zor, the capital of Deir ez-Zor Governorate, Syria. It was founded in 1974 and housed in a gallery of a shopping mall. Between 1983 and 1996, it was located in an old law court built in 1930. In 1996, the museum moved to its current location in a building that had been especially designed for the museum. The exhibition halls cover an area of and are arranged around a courtyard. The construction of the new museum was a joint Syrian–German operation. When the museum was founded in 1974, its collection consisted of only 140 objects, donated by the National Museum of Damascus and the National Museum of Aleppo. The current collection consists of some 25,000 objects, including the majority of the clay tablets found at Mari. The museum also holds many objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is also called a ''pottery'' (plural "potteries"). The definition of ''pottery'', used by the ASTM International, is "all fired ceramic wares that contain clay when formed, except technical, structural, and refractory products". In art history and archaeology, especially of ancient and prehistoric periods, "pottery" often means vessels only, and sculpted figurines of the same material are called "terracottas". Pottery is one of the oldest human inventions, originating before the Neolithic period, with ceramic objects like the Gravettian culture Venus of Dolní Věstonice figurine discovered in the Czech Republic dating back to 29,000–25,000 BC, and pottery vessels that were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PPNB
Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) is part of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, a Neolithic culture centered in upper Mesopotamia and the Levant, dating to years ago, that is, 8800–6500 BC. It was typed by British archaeologist Kathleen Kenyon during her archaeological excavations at Jericho in the West Bank. Like the earlier PPNA people, the PPNB culture developed from the Mesolithic Natufian culture. However, it shows evidence of a northerly origin, possibly indicating an influx from the region of northeastern Anatolia. Lifestyle Cultural tendencies of this period differ from that of the earlier Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA) period in that people living during this period began to depend more heavily upon domesticated animals to supplement their earlier mixed agrarian and hunter-gatherer diet. In addition, the flint tool kit of the period is new and quite disparate from that of the earlier period. One of its major elements is the naviform core. This is the first period in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
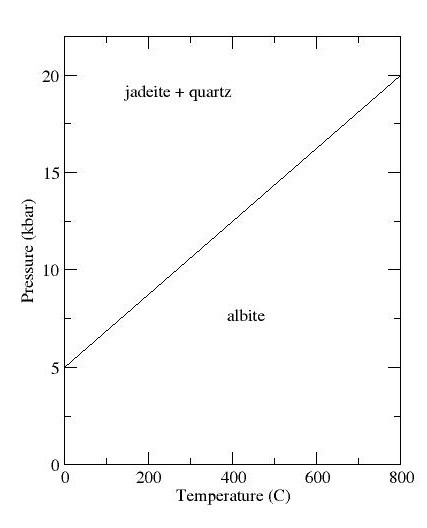
Jadeite
Jadeite is a pyroxene mineral with composition sodium, Naaluminium, Alsilicon, Si2oxygen, O6. It is hard (Mohs hardness of about 6.5 to 7.0), very tough, and dense, with a specific gravity of about 3.4. It is found in a wide range of colors, but is most often found in shades of green or white. Jadeite is formed only in subduction zones on continental margins, where rock undergoes metamorphism at high pressure but relatively low temperature. Jadeite is the principal mineral making up the most valuable form of jade, a precious stone particularly prized in China. Most gem-quality jadeite jade comes from northern Myanmar. Jade tools and implements have been found at Stone Age sites, showing that the mineral has been prized by humans since before the beginning of written history. Name The name ''jadeite'' is derived (via french: jade and la, ilia) from the Spanish language, Spanish phrase "piedra de ijada" which means "stone of the side". The Latin version of the name, ''lapis neph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusc Shell
The mollusc (or molluskOften spelled mollusk shell in the USA; the spelling "mollusc" are preferred by ) shell is typically a calcareous exoskeleton which encloses, supports and protects the soft parts of an animal in the phylum Mollusca, which includes snails, clams, tusk shells, and several other classes. Not all shelled molluscs live in the sea; many live on the land and in freshwater. The ancestral mollusc is thought to have had a shell, but this has subsequently been lost or reduced on some families, such as the squid, octopus, and some smaller groups such as the caudofoveata and solenogastres. Today, over 100,000 living species bear a shell; there is some dispute as to whether these shell-bearing molluscs form a monophyletic group (conchifera) or whether shell-less molluscs are interleaved into their family tree. Malacology, the scientific study of molluscs as living organisms, has a branch devoted to the study of shells, and this is called conchology—although these te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnelian
Carnelian (also spelled cornelian) is a brownish-red mineral commonly used as a semi-precious gemstone. Similar to carnelian is sard, which is generally harder and darker (the difference is not rigidly defined, and the two names are often used interchangeably). Both carnelian and sard are varieties of the silica mineral chalcedony colored by impurities of iron oxide. The color can vary greatly, ranging from pale orange to an intense almost-black coloration. Significant localities include Yanacodo (Peru); Ratnapura (Sri Lanka); and Thailand. It has been found in Indonesia, Brazil, India, Russia (Siberia), and Germany. History upPolish signet ring in light-orange carnelian intaglio showing Korwin coat of arms The red variety of chalcedony has been known to be used as beads since the Early Neolithic in Bulgaria. The first faceted (with constant 16+16=32 facets on each side of the bead) carnelian beads are described from the Varna Chalcolithic necropolis (middle of the 5th m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentalium (anthropology)
The word dentalium, as commonly used by Native American artists and anthropologists, refers to tooth shells or tusk shells used in indigenous jewelry, adornment, and commerce in western Canada and the United States. These tusk shells are a kind of seashell, specifically the shells of scaphopod mollusks. The name "dentalium" is based on the scientific name for the genus '' Dentalium'', but because the taxonomy has changed over time, not all of the species used are still placed in that genus; however, all of the species are certainly in the family Dentaliidae. Dentalium shells were used by Inuit, First Nations, and Native Americans as an international trade item. This usage is found along the western coast of Canada and along the Pacific Ocean coast of the northwest United States extending southward to Southern California. Traditionally, the shells of '' Antalis pretiosa'' (previously known as ''Dentalium pretiosum'', the precious dentalium (a species which occurs from Alaska to Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deir Ez-Zor
, population_urban = , population_density_urban_km2 = , population_density_urban_sq_mi = , population_blank1_title = Ethnicities , population_blank1 = , population_blank2_title = Religions , population_blank2 = , population_density_blank1_km2 = , population_density_blank1_sq_mi = , timezone = EET , utc_offset = +2 , timezone_DST = EEST , utc_offset_DST = +3 , coordinates = , elevation_footnotes = , elevation_m = 210 , elevation_ft = , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code = Country code: 963 City code: 051 , geocode = C5086 , blank_name = Climate , blank_info = BWh , blank_name_sec2 = International airport , blank_info_sec2 = Deir ez-Zor Airport , blank1_name = , blank1_info = , website ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byblos Point
Byblos ( ; gr, Βύβλος), also known as Jbeil or Jubayl ( ar, جُبَيْل, Jubayl, locally ; phn, 𐤂𐤁𐤋, , probably ), is a city in the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon. It is believed to have been first occupied between 8800 and 7000BC and continuously inhabited since 5000BC, making it one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. During its history, Byblos was part of numerous civilizations, including Egyptian, Phoenician, Assyrian, Persian, Hellenistic, Roman, Fatimid, Genoese, Mamluk and Ottoman. The city is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It was in ancient Byblos that the Phoenician alphabet, likely the ancestor of the Greek, Latin and all other Western alphabets, was developed. Etymology Byblos appears as ''Kebny'' in Egyptian hieroglyphic records going back to the 4th-dynasty pharaoh Sneferu (BC) and as () in the Akkadian cuneiform Amarna letters to the 18th-dynasty pharaohs and IV. In the 1stmillenniumBC, its name appeare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amuq Point
The Amik Valley ( tr, Amik Ovası; ar, ٱلْأَعْمَاق, al-ʾAʿmāq) is located in the Hatay Province, close to the city of Antakya (Antioch on the Orontes River) in the southern part of Turkey. Along with Dabiq in northwestern Syria, it is believed to be one of two possible sites of the battle of Armageddon according to Islamic eschatology. Archaeological significance It is notable for a series of archaeological sites in the "plain of Antioch". The primary sites of the series are Tell al-Judaidah, Çatalhöyük (not to be confused with Çatalhöyük in Anatolia), Tell Tayinat, Tell Kurdu, Alalakh, and Tell Dhahab. Tell Judaidah was surveyed by Robert Braidwood and excavated by C. MacEwan of the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago in the 1930s. Lake Amik was an ancient lake in the area, that was located in the centre of Amik Plain. There is also archaeological evidence for Caspian tigers in this valley (Ellerman and Morrison-Scott, 1951; Vallino and Guazzo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |