|
Bouguer (Martian Crater)
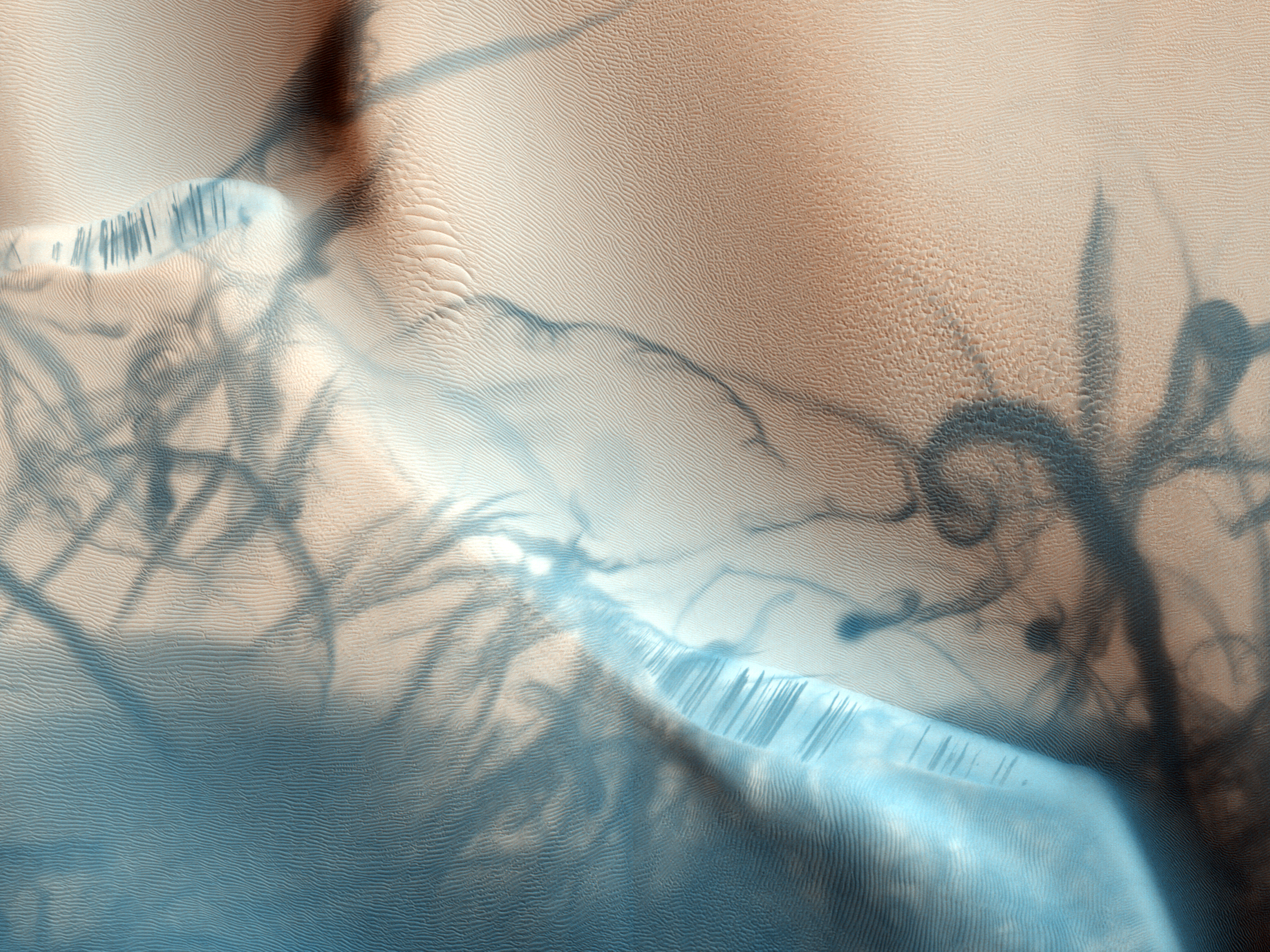
Bouguer Crater is an impact crater in the Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle of Mars, located at 18.7° S and 332.8° W It is 107 km in diameter and was named after Pierre Bouguer, French physicist-hydrographer (1698–1758). When a comet or asteroid collides at high speed interplanetary with the surface of Mars it creates an impact crater. Layers are visible in the crater with HiRISE; these can be seen in the HiRISE image below. Layers may be formed by a number of processes. On Earth rock layers are often formed under a lake or other body of water. However, on Mars many layers may be formed by the action of groundwater. Layered terrain Some locations on the Red Planet show groups of layered rocks. Rock layers are present under the resistant caps of pedestal craters, on the floors of many large impact craters, and in the area called Arabia. In some places the layers are arranged into regular patterns. It has been suggested that the layers were put into place by volcanoe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
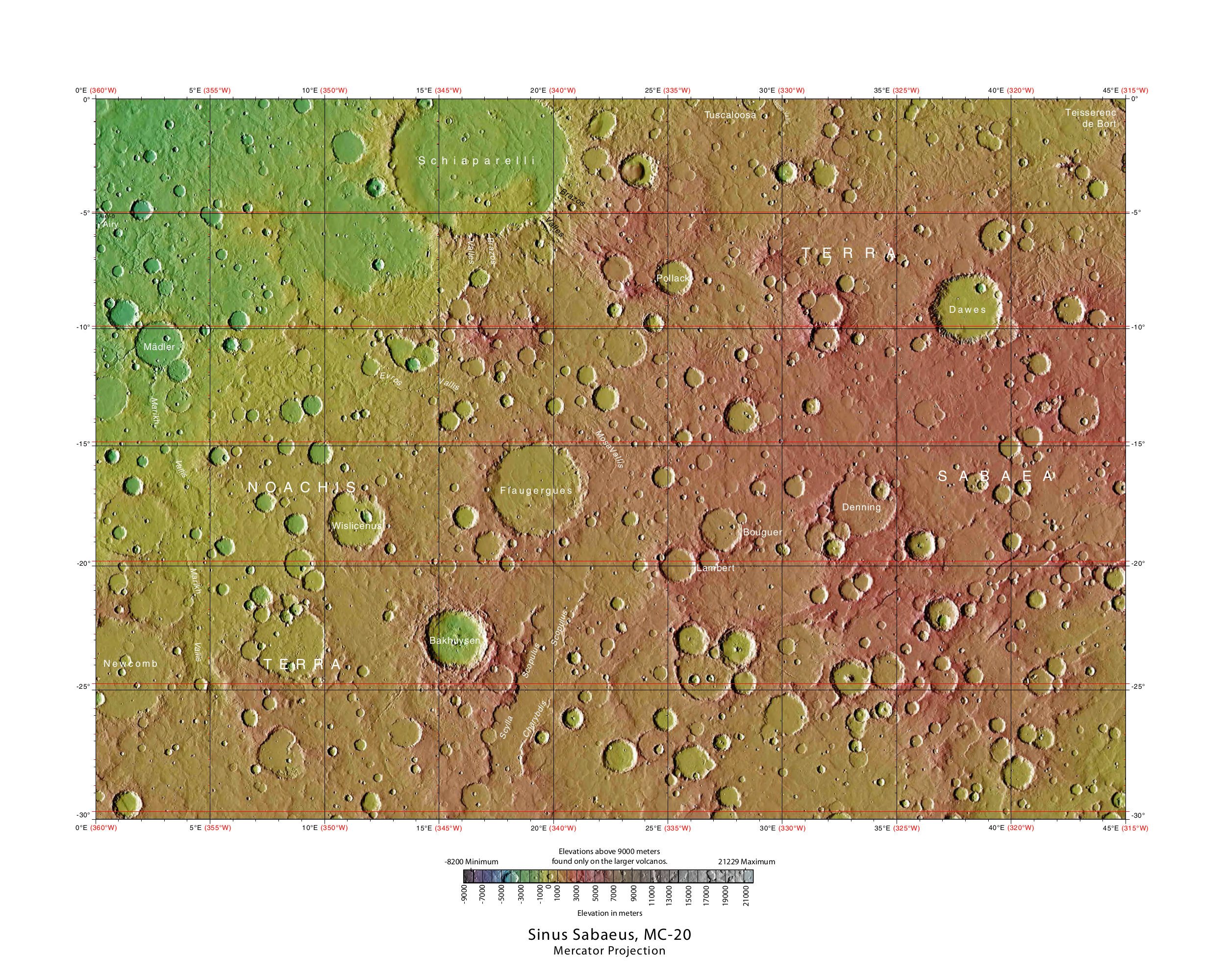
Sinus Sabaeus Quadrangle
The Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. It is also referred to as MC-20 (Mars Chart-20). The Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle covers the area from 315° to 360° west longitude and 0° to 30° degrees south latitude on Mars. It contains Schiaparelli, a large, easily visible crater that sits close to the equator. The Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle contains parts of Noachis Terra and Terra Sabaea. The name comes from an incense-rich location south of the Arabian peninsula (the Gulf of Aden). Layers Wislicenus Crater and the Schiaparelli basin crater contains layers, also called strata. Many places on Mars show rocks arranged in layers.Grotzinger, J. and R. Milliken (eds.) 2012. Sedimentary Geology of Mars. SEPM Sometimes the layers are of different colors. Light-toned rocks on Mars have been associated with hydrated minerals like sulfates. The Mars rover ''Opp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) because they are the most resistant minerals to weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be any color due to impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Since sandstone beds often form highly visible cliffs and other topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have been strongly identified with certain regions. Rock formations that are primarily composed of sandstone usually allow the percolation of water and other fluids and are porous enough to store large quantities, making them valuable aquifers and petroleum reservoirs. Quartz-bearing sandstone can be changed into quartzite through metamorphism, usually related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ore Resources On Mars
Mars may contain ores that would be very useful to colonization of Mars, potential colonists. The abundance of volcanic features together with widespread cratering are strong evidence for a variety of ores. While nothing may be found on Mars that would justify the high cost of transport to Earth, the more ores that future colonists can obtain from Mars, the easier it would be to build colonies there. How deposits are made Ore deposits are produced with the help of large amounts of heat. On Mars, heat can come from molten rock moving under the ground and from crater impacts. Liquid rock under the ground is called magma. When magma sits in underground chambers, slowly cooling over thousands of years, heavier elements sink. These elements, including copper, chromium, iron, and nickel become concentrated at the bottom. When magma is hot, many elements are free to move. As cooling proceeds, the elements bind with each other to form chemical compounds or minerals. Because some elemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Craters On Mars
__NOTOC__ This is a list of craters on Mars. Impact craters on Mars larger than exist by the hundreds of thousands, but only about one thousand of them have names. Names are assigned by the International Astronomical Union after petitioning by relevant scientists, and in general, only craters that have a significant research interest are given names. Martian craters are named after famous scientists and science fiction authors, or if less than in diameter, after towns on Earth. Craters cannot be named for living people, and names for small craters are rarely intended to commemorate a specific town. Latitude and longitude are given as planetographic coordinates with west longitude. Catalog of named craters The catalog is divided into three partial lists: * List of craters on Mars: A–G * List of craters on Mars: H–N * List of craters on Mars: O–Z Names are grouped into tables for each letter of the alphabet, containing the crater's name (linked if article exists), co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Of Mars
The climate of Mars has been a topic of scientific curiosity for centuries, in part because it is the only terrestrial planet whose surface can be directly observed in detail from the Earth with help from a telescope. Although Mars is smaller than the Earth, 11% of Earth's mass, and 50% farther from the Sun than the Earth, its climate has important similarities, such as the presence of polar ice caps, seasonal changes and observable weather patterns. It has attracted sustained study from planetologists and climatologists. While Mars' climate has similarities to Earth's, including periodic ice ages, there are also important differences, such as much lower thermal inertia. Mars' atmosphere has a scale height of approximately , 60% greater than that on Earth. The climate is of considerable relevance to the question of whether life is or ever has been present on the planet. The climate briefly received more interest in the news due to NASA measurements indicating increased sublima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakes On Mars
In summer 1965, the first close-up images from Mars showed a cratered desert with no signs of water. However, over the decades, as more parts of the planet were imaged with better cameras on more sophisticated satellites, Mars showed evidence of past river valleys, lakes and present ice in glaciers and in the ground. It was discovered that the climate of Mars displays huge changes over geologic time because its axis is not stabilized by a large moon, as Earth's is. Also, some researchers maintain that surface liquid water could have existed for periods of time due to geothermal effects, chemical composition or asteroid impacts. This article describes some of the places that could have held large lakes. Overview Besides seeing features that were signs of past surface water, researchers found other types of evidence for past water. Minerals detected in many locations needed water to form. An instrument in ''2001 Mars Odyssey'' orbiter mapped the distribution of water in the shal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Event
An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal effect. When large objects impact terrestrial planets such as the Earth, there can be significant physical and biospheric consequences, though atmospheres mitigate many surface impacts through atmospheric entry. Impact craters and Impact structure, structures are dominant landforms on many of the Solar System's solid objects and present the strongest empirical evidence for their frequency and scale. Impact events appear to have played a significant role in the Formation and evolution of the Solar System, evolution of the Solar System since its formation. Major impact events have significantly shaped History of the Earth, Earth's history, and have been implicated in the giant impact theory, formation of the Earth� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Lunar impact craters range from microscopic craters on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program and small, simple, bowl-shaped depressions in the lunar regolith to large, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth. Impact craters are the dominant geographic features on many solid Solar System objects including the Moon, Mercury, Callisto, Ganymede and most small moons and asteroids. On other planets and moons that experience more active surface geological processes, such as Earth, Venus, Europa, Io and Titan, visible impact craters are less common because they become eroded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction of the University of Arizona's Lunar and Planetary Laboratory by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. It consists of a 0.5m (19.7 in) aperture reflecting telescope, the largest so far of any deep space mission, which allows it to take pictures of Mars with resolutions of 0.3m/pixel (1ft/pixel), resolving objects below a meter across. HiRISE has imaged Mars exploration rovers on the surface, including the ''Opportunity'' rover and the ongoing ''Curiosity'' mission. History In the late 1980s, of Ball Aerospace & Technologies began planning the kind of high-resolution imaging needed to support sample return and surface exploration of Mars. In early 2001 he teamed up with Alfred McEwen of the University of Arizona to propose such a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
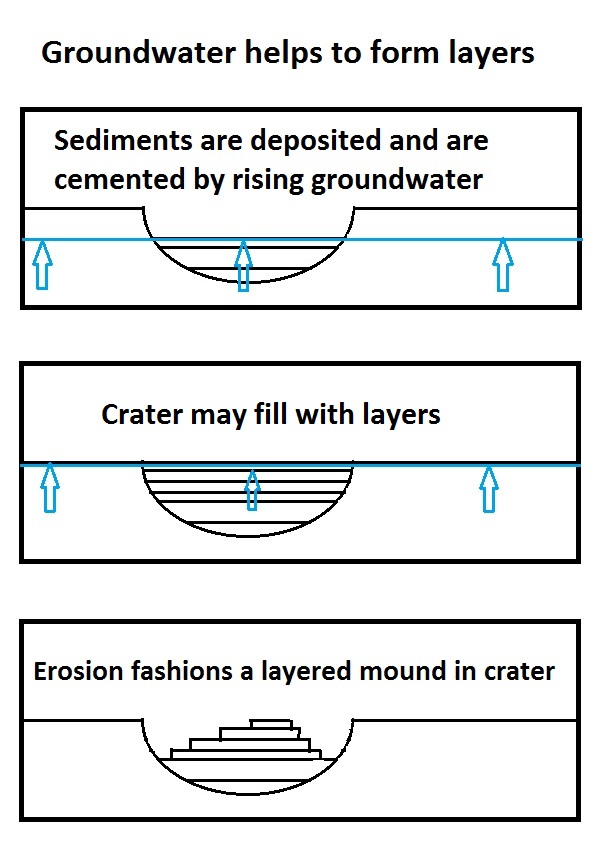
Groundwater On Mars
During past ages, there was rain and snow on Mars; especially in the Noachian and early Hesperian epochs. Some moisture entered the ground and formed aquifers. That is, the water went into the ground, seeped down until it reached a formation that would not allow it to penetrate further (such a layer is called impermeable). Water then accumulated forming a saturated layer. Deep aquifers may still exist. Overviews Researchers have found that Mars had a planet-wide groundwater system and several prominent features on the planet have been produced by the action of groundwater. When water rose to the surface or near the surface, various minerals were deposited and sediments became cemented together. Some of the minerals were sulfates that were probably produced when water dissolved sulfur from underground rocks, and then became oxidized when it came into contact with the air. While traveling through the aquifer, the water passed through igneous rock basalt, which would have contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
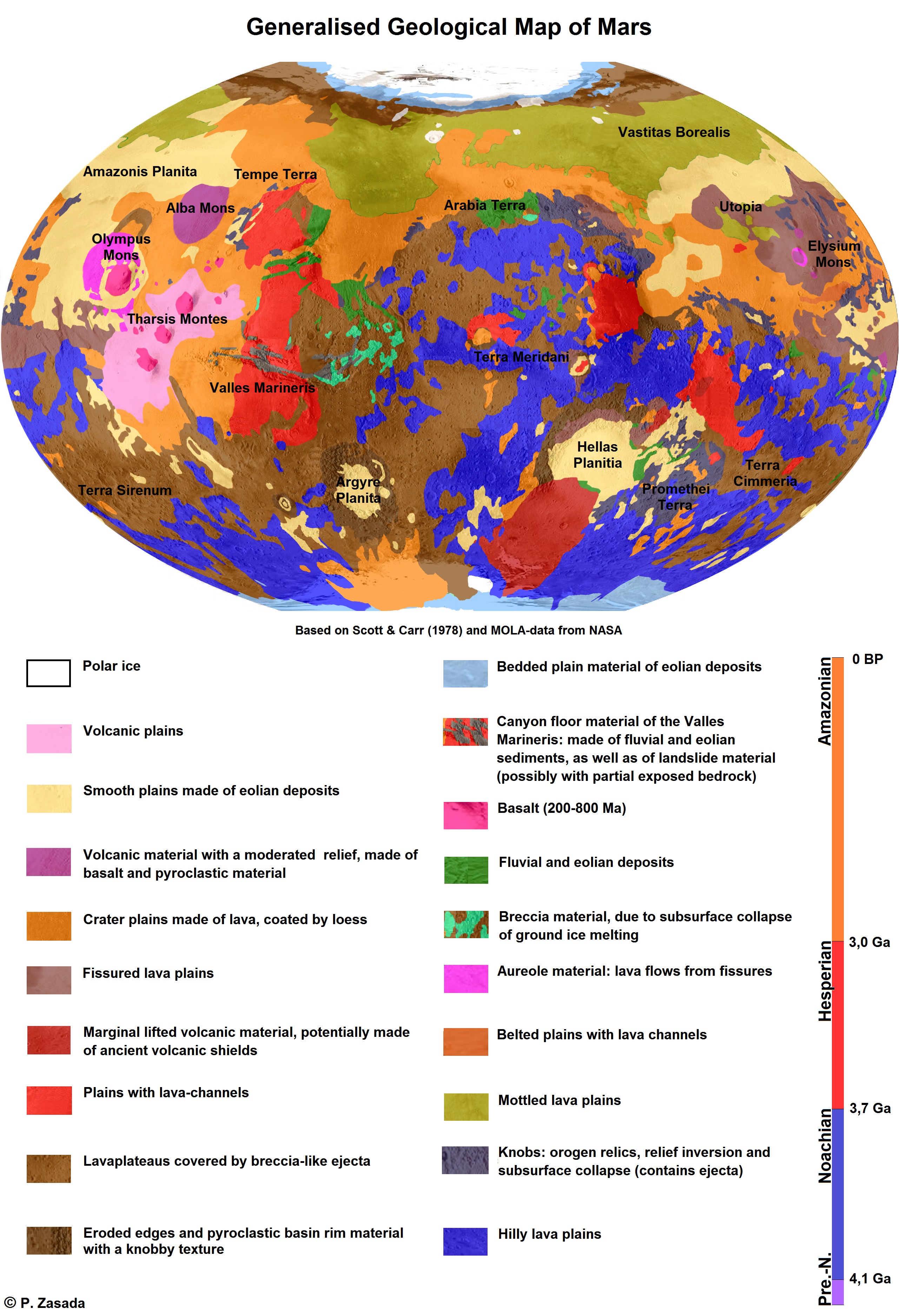
Geology Of Mars
The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term ''geology'' is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography. A neologism, areology, from the Greek word ''Arēs'' (Mars), sometimes appears as a synonym for Mars's geology in the popular media and works of science fiction (e.g. Kim Stanley Robinson, Kim Stanley Robinson's Mars trilogy). The term areology is also used by the Areological Society. Geological map of Mars (2014) File:Geologic Map of Mars figure2.pdf, Figure 2 for the geologic map of Mars Global Martian topography and large-scale features Composition of Mars Mars is a terrestrial planet, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO) is a spacecraft designed to study the geology and climate of Mars, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth. It was launched on August 12, 2005, and reached Mars on March 10, 2006. In November 2006, after five months of aerobraking, it entered its final science orbit and began its primary science phase. The cost to develop and operate MRO through the end of its prime mission in 2010 was . The spacecraft continues to operate at Mars, far beyond its intended design life. Due to its critical role as a high-speed data-relay for ground missions, NASA intends to continue the mission as long as possible, at least through the late 2020s. Pre-launch After the twin failures of the ''Mars Climate Orbiter'' and the Mars Polar Lander missions in 1999, NASA reorganized and replanned its Mars Exploration Program. In October 2000, NASA announced its reformulated Mars plans, which reduced the numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saunders_Quarry-1.jpg)