Bouguer (Martian Crater) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bouguer Crater is an impact crater in the
 Some locations on the Red Planet show groups of layered rocks. Rock layers are present under the resistant caps of pedestal craters, on the floors of many large
Some locations on the Red Planet show groups of layered rocks. Rock layers are present under the resistant caps of pedestal craters, on the floors of many large
Wikibouguer.jpg, Bouguer (Martian crater), as seen by CTX camera (on
Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle
The Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. It is also referred to as MC-20 (Mars Chart-20).
The Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle cover ...
of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
, located at
18.7° S and 332.8° W It is 107 km in diameter and was named after Pierre Bouguer, French physicist-hydrographer (1698–1758).
When a comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ...
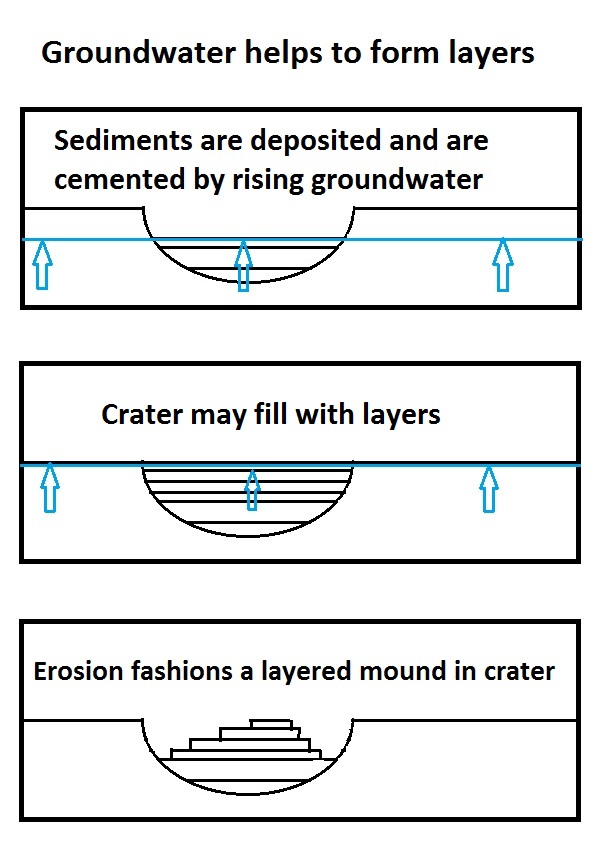
or asteroid collides at high speed interplanetary with the surface of Mars it creates an impact crater. Layers are visible in the crater with HiRISE; these can be seen in the HiRISE image below. Layers may be formed by a number of processes. On Earth rock layers are often formed under a lake or other body of water. However, on Mars many layers may be formed by the action of groundwater.
Layered terrain
 Some locations on the Red Planet show groups of layered rocks. Rock layers are present under the resistant caps of pedestal craters, on the floors of many large
Some locations on the Red Planet show groups of layered rocks. Rock layers are present under the resistant caps of pedestal craters, on the floors of many large impact craters
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters ...
, and in the area called Arabia. In some places the layers are arranged into regular patterns.
It has been suggested that the layers were put into place by volcanoes, the wind, or by being at the bottom of a lake or sea. Calculations and simulations show that groundwater carrying dissolved minerals would surface in the same locations that have abundant rock layers. According to these ideas, deep canyons and large craters would receive water coming from the ground. Many craters in the Arabia area of Mars contain groups of layers. Some of these layers may have resulted from climate changes. The tilt of the rotational axis of Mars has repeatedly changed in the past. Some changes are large. Because of these variations of climate, at times the atmosphere of Mars will be much thicker and contain more moisture. The amount of atmospheric dust also has increased and decreased. It is believed that these frequent changes helped to deposit material in craters and other low places. The rising of mineral-rich ground water cemented these materials. The model also predicts that after a crater is full of layered rocks; additional layers will be laid down in the area around the crater. So, the model predicts that layers may also have formed in intercrater regions; layers in these regions have been observed.
Layers can be hardened by the action of groundwater. Martian ground water probably moved hundreds of kilometers, and in the process it dissolved many minerals from the rock it passed through. When ground water surfaces in low areas containing sediments, water evaporates in the thin atmosphere and leaves behind minerals as deposits and/or cementing agents. Consequently, layers of dust could not later easily erode away since they were cemented together. On Earth, mineral-rich waters often evaporate forming large deposits of various types of salts
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively c ...
and other mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
s. Sometimes water flows through Earth's aquifers, and then evaporates at the surface just as is hypothesized for Mars. One location this occurs on Earth is the Great Artesian Basin
The Great Artesian Basin (GAB), located in Australia, is the largest and deepest artesian basin in the world, stretching over , with measured water temperatures ranging from . The basin provides the only source of fresh water through much ...
of Australia.Habermehl, M. A. (1980) The Great Artesian Basin, Australia. J. Austr. Geol. Geophys. 5, 9–38. On Earth the hardness of many sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
s, like sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
, is largely due to the cement that was put in place as water passed through.
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO) is a spacecraft designed to study the geology and climate of Mars, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth. It was launched on August 12, 2005, an ...
).
Image:Bouguercraterhirise.jpg, Close up of layers in eroded deposits on the floor of Bouguer Crater, as seen by HiRISE. This image is in a different part of the crater than the CTX image to the right.
See also
*Geology of Mars
The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geo ...
* Groundwater on Mars
During past ages, there was rain and snow on Mars; especially in the Noachian and early Hesperian epochs. Some moisture entered the ground and formed aquifers. That is, the water went into the ground, seeped down until it reached a formation tha ...
* HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the '' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction ...
* Impact crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact crater ...
* Impact event
* Lakes on Mars
In summer 1965, the first close-up images from Mars showed a cratered desert with no signs of water. However, over the decades, as more parts of the planet were imaged with better cameras on more sophisticated satellites, Mars showed evidence o ...
* Climate of Mars
The climate of Mars has been a topic of scientific curiosity for centuries, in part because it is the only terrestrial planet whose surface can be directly observed in detail from the Earth with help from a telescope.
Although Mars is smaller t ...
* List of craters on Mars
* Ore resources on Mars
Mars may contain ores that would be very useful to potential colonists. The abundance of volcanic features together with widespread cratering are strong evidence for a variety of ores. While nothing may be found on Mars that would justify the hi ...
* Planetary nomenclature
Planetary nomenclature, like terrestrial nomenclature, is a system of uniquely identifying features on the surface of a planet or natural satellite so that the features can be easily located, described, and discussed. Since the invention of the tel ...
References
Further reading
* Grotzinger, J. and R. Milliken (eds.). 2012. Sedimentary Geology of Mars. SEPM. {{Geography of Mars Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle Impact craters on Mars