|
Bootstrapping (linguistics)
Bootstrapping is a term used in language acquisition in the field of linguistics. It refers to the idea that humans are born innately equipped with a mental faculty that forms the basis of language. It is this language faculty that allows children to effortlessly acquire language. As a process, bootstrapping can be divided into different domains, according to whether it involves semantic bootstrapping, syntactic bootstrapping, prosodic bootstrapping, or pragmatic bootstrapping. Background Etymology In literal terms, a bootstrap is the small strap on a boot that is used to help pull on the entire boot. Similarly in computer science, booting refers to the startup of an operation system by means of first initiating a smaller program. Therefore, bootstrapping refers to the leveraging of a small action into a more powerful and significant operation. Bootstrapping in linguistics was first introduced by Steven Pinker as a metaphor for the idea that children are innately equipped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Acquisition
Language acquisition is the process by which humans acquire the capacity to perceive and comprehend language. In other words, it is how human beings gain the ability to be aware of language, to understand it, and to produce and use words and sentence (linguistics), sentences to communicate. Language acquisition involves structures, rules, and representation. The capacity to successfully use language requires human beings to acquire a range of tools, including phonology, morphology (linguistics), morphology, syntax, semantics, and an extensive vocabulary. Language can be vocalized as in speech, or manual as in sign language, sign. Human language capacity is language processing in the brain, represented in the brain. Even though human language capacity is finite, one can say and understand an infinite number of sentences, which is based on a syntactic principle called recursion. Evidence suggests that every individual has three recursive Mechanisms of mindfulness meditation, mech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
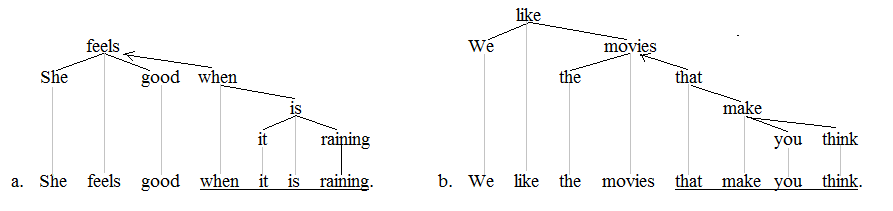
Prosodic Bootstrapping
Prosodic bootstrapping (also known as phonological bootstrapping) in linguistics refers to the hypothesis that learners of a primary language (L1) use prosodic features such as pitch, tempo, rhythm, amplitude, and other auditory aspects from the speech signal as a cue to identify other properties of grammar, such as syntactic structure. Acoustically signaled prosodic units in the stream of speech may provide critical perceptual cues by which infants initially discover syntactic phrases in their language. Although these features by themselves are not enough to help infants learn the entire syntax of their native language, they provide various cues about different grammatical properties of the language, such as identifying the ordering of heads and complements in the language using stress prominence, indicating the location of phrase boundaries, and word boundaries. It is argued that prosody of a language plays an initial role in the acquisition of the first language helping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intonation Pattern
In linguistics, a prosodic unit is a segment of speech that occurs with specific prosodic properties. These properties can be those of stress, Intonation (linguistics), intonation (a single Pitch contour, pitch and rhythm contour), or Tone (linguistics), tonal patterns. Prosodic units occur at a Phonological hierarchy, hierarchy of levels, from the syllable, the Foot (prosody), metrical foot and phonological word to the intonational unit (IU) and to a complete utterance. However, the term is often restricted to intermediate levels which do not have a dedicated terminology. Prosodic units do not generally correspond to syntactic units, such as phrases and clauses; it is thought that they reflect different aspects of how the brain processes speech, with prosodic units being generated through on-line interaction and processing, and with morphosyntactic units being more automated. Defining characteristics Prosodic units are characterized by several phonetic cues, such as pitch move ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentence (linguistics)
In linguistics and grammar, a sentence is a Expression (linguistics), linguistic expression, such as the English example "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog." In traditional grammar, it is typically defined as a string of words that expresses a complete thought, or as a unit consisting of a Subject (grammar), subject and Predicate (grammar), predicate. In non-functional linguistics it is typically defined as a maximal unit of syntactic structure such as a Constituent_(linguistics), constituent. In functional linguistics, it is defined as a unit of written texts delimited by writing, graphological features such as upper-case letters and markers such as periods, question marks, and exclamation marks. This notion contrasts with a curve, which is delimited by phonologic features such as pitch and loudness and markers such as pauses; and with a clause, which is a sequence of words that represents some process going on throughout time. A sentence can include words grouped meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clause
In language, a clause is a Constituent (linguistics), constituent or Phrase (grammar), phrase that comprises a semantic predicand (expressed or not) and a semantic Predicate (grammar), predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject (grammar), subject and a syntactic Predicate (grammar), predicate, the latter typically a verb phrase composed of a verb with or without any object (grammar), objects and other Grammatical modifier, modifiers. However, the subject is sometimes unexpressed if it is easily deducible from the context, especially in null-subject languages but also in other languages, including instances of the imperative mood in English grammar, English. A complete simple sentence contains a single clause with a finite verb. Complex sentences contain at least one clause subordinated (dependent clause, ''dependent'') to an ''independent clause'' (one that could stand alone as a simple sentence), which may be co-ordinated with other independents with or without dependents. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase
In grammar, a phrasecalled expression in some contextsis a group of words or singular word acting as a grammatical unit. For instance, the English language, English expression "the very happy squirrel" is a noun phrase which contains the adjective phrase "very happy". Phrases can consist of a single word or a complete sentence. In theoretical linguistics, phrases are often analyzed as units of syntactic structure such as a Constituent (linguistics), constituent. There is a difference between the common use of the term ''phrase'' and its technical use in linguistics. In common usage, a phrase is usually a group of words with some special idiomatic meaning or other significance, such as "all rights reserved", "economical with the truth", "kick the bucket", and the like. It may be a euphemism, a saying or proverb, a fixed expression, a figure of speech, etc.. In linguistics, these are known as phrasemes. In theories of syntax, a phrase is any group of words, or sometimes a single w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isochrony
Isochrony is a linguistic analysis or hypothesis assuming that any spoken language's utterances are divisible into equal rhythmic portions of some kind. Under this assumption, languages are proposed to broadly fall into one of two categories based on rhythm or timing: syllable-timed or stress-timed languages (or, in some analyses, a third category: mora-timed languages). However, empirical studies have been unable to directly or fully support the hypothesis, so the concept remains controversial in linguistics. History Rhythm is an aspect of prosody, others being intonation, stress, and tempo of speech. ''Isochrony'' refers to rhythmic division of time into equal portions by a language. The idea of was first expressed thus by Kenneth L. Pike in 1945, though the concept of language naturally occurring in chronologically and rhythmically equal measures is found at least as early as 1775 (in '' Prosodia Rationalis''). Soames (1889) attributed the idea to Curwen. This has impl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouthing
In sign language, mouthing is the production of visual syllables with the mouth while signing. That is, signers sometimes say or mouth a word in a spoken language at the same time as producing the sign for it. Mouthing is one of the many ways in which the face and mouth is used while signing. Although not present in all sign languages, and not in all signers, where it does occur it may be an essential (that is, phonemic) element of a sign, distinguishing signs which would otherwise be homophones; in other cases a sign may seem to be flat and incomplete without mouthing even if it is unambiguous. Other signs use a combination of mouth movements and hand movements to indicate the sign; for example, the ASL sign for includes a mouth gesture where the mouth is slightly open. Mouthing often originates from oralist education, where sign and speech are used together. Thus mouthing may preserve an often abbreviated rendition of the spoken translation of a sign. In educated Ugandan Sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facial Expression
Facial expression is the motion and positioning of the muscles beneath the skin of the face. These movements convey the emotional state of an individual to observers and are a form of nonverbal communication. They are a primary means of conveying social information between humans, but they also occur in most other mammals and some other animal species. Humans can adopt a facial expression voluntarily or involuntarily, and the neural mechanisms responsible for controlling the expression differ in each case. Voluntary facial expressions are often socially conditioned and follow a cortical route in the brain. Conversely, involuntary facial expressions are believed to be innate and follow a subcortical route in the brain. Facial recognition can be an emotional experience for the brain and the amygdala is highly involved in the recognition process. Beyond the accessory nature of facial expressions in spoken communication between people, they play a significant role in communication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign Language
Sign languages (also known as signed languages) are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with #Non-manual elements, non-manual markers. Sign languages are full-fledged natural languages with their own grammar and lexicon. Sign languages are not universal and are usually not mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible, although there are similarities among different sign languages. Linguists consider both spoken and signed communication to be types of natural language, meaning that both emerged through an abstract, protracted aging process and evolved over time without meticulous planning. This is supported by the fact that there is substantial overlap between the neural substrates of sign and spoken language processing, despite the obvious differences in modality. Sign language should not be confused with body language, a type of non verbal communicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accent (sociolinguistics)
In sociolinguistics, an accent is a way of pronouncing a language that is distinctive to a country, area, social class, or individual. An accent may be identified with the locality in which its speakers reside (a regional or geographical accent), the socioeconomic status of its speakers, their ethnicity (an ethnolect), their caste or social class (a social accent), or influence from their first language (a foreign accent). Accents typically differ in quality of voice, pronunciation and distinction of vowels and consonants, stress, and prosody. Although grammar, semantics, vocabulary, and other language characteristics often vary concurrently with accent, the word "accent" may refer specifically to the differences in pronunciation, whereas the word "dialect" encompasses the broader set of linguistic differences. "Accent" is often a subset of "dialect". History As human beings spread out into isolated communities, stresses and peculiarities develop. Over time, they can develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch Accent
A pitch-accent language is a type of language that, when spoken, has certain syllables in words or morphemes that are prominent, as indicated by a distinct contrasting pitch (music), pitch (tone (linguistics), linguistic tone) rather than by volume or length, as in some other languages like English language, English. Pitch-accent languages also contrast with fully tonal languages like Vietnamese language, Vietnamese, Thai language, Thai and Standard Chinese, in which practically every syllable can have an independent tone. Some scholars have claimed that the term "pitch accent" is not coherently defined and that pitch-accent languages are just a sub-category of tonal languages in general. Languages that have been described as pitch-accent languages include: most dialects of Serbo-Croatian, Slovene language, Slovene, Baltic languages, Ancient Greek, Vedic Sanskrit, Tlingit language, Tlingit, Turkish language, Turkish, Japanese language, Japanese, Limburgish, Norwegian language, No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |