|
Bones Of Skeletal System
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions. Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the uncountable sense of that word, is hard tissue, a type of specialized connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are involved in the formation and mineralization of bone; osteoclasts are involved in the resorption of bone tissue. Modified (flattened) osteoblasts become the lining cells that form a protective layer on the bone surface. The mineralized matrix o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoblast
Osteoblasts (from the Greek language, Greek combining forms for "bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cell (biology), cells with a single Cell nucleus, nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the process of bone formation, osteoblasts function in groups of connected cells. Individual cells cannot make bone. A group of organized osteoblasts together with the bone made by a unit of cells is usually called the osteon. Osteoblasts are specialized, terminally differentiated products of mesenchymal stem cells. They synthesize dense, crosslinked collagen and specialized proteins in much smaller quantities, including osteocalcin and osteopontin, which compose the organic matrix of bone. In organized groups of disconnected cells, osteoblasts produce hydroxylapatite, the bone mineral, that is deposited in a highly regulated manner, into the organic matrix forming a strong and dense mineralized tissues, mineralized tissue, the mineralized mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon, within the nerve, is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Finally, the entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called neurons) are f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periosteum
The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. Endosteum lines the inner surface of the medullary cavity of all long bones. Structure The periosteum consists of an outer fibrous layer, and an inner cambium layer (or osteogenic layer). The fibrous layer is of dense irregular connective tissue, containing fibroblasts, while the cambium layer is highly cellular containing progenitor cells that develop into osteoblasts. These osteoblasts are responsible for increasing the width of a long bone and the overall size of the other bone types. After a bone fracture, the progenitor cells develop into osteoblasts and chondroblasts, which are essential to the healing process. The outer fibrous layer and the inner cambium layer is differentiated under electron micrography. As opposed to osseous tissue, the periosteum has nociceptors, sensory neurons that make it very sensitive to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endosteum
The endosteum (plural endostea) is a thin vascular membrane of connective tissue that lines the inner surface of the bony tissue that forms the medullary cavity of long bones. This endosteal surface is usually resorbed during long periods of malnutrition, resulting in less cortical thickness. The outer surface of a bone is lined by a thin layer of connective tissue that is very similar in morphology and function to endosteum. It is called the periosteum, or the periosteal surface. During bone growth, the width of the bone increases as osteoblasts lay new bone tissue at the periosteum. To prevent the bone from becoming unnecessarily thick, osteoclasts An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated prote ... resorb the bone from the endosteal side. Additional images File:Illu long bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
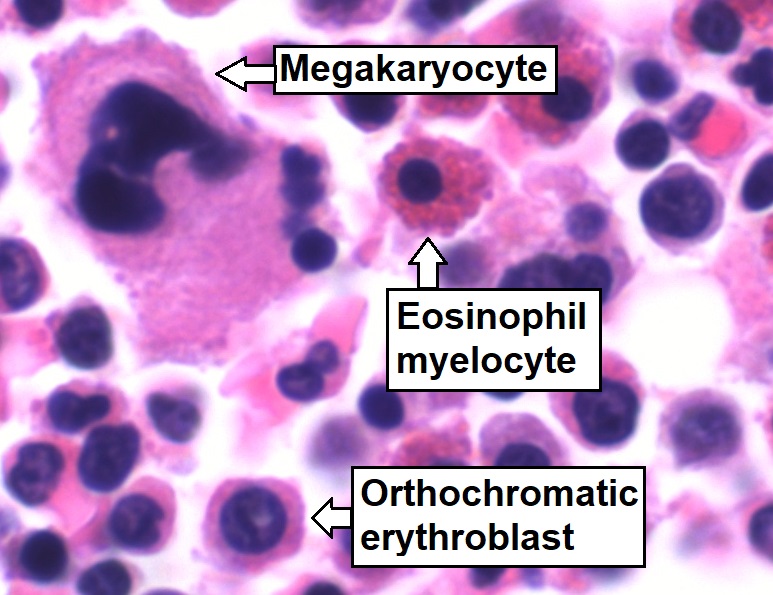
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a man weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of hematopoietic cells, including both myeloid and lymphoid lineages, are created in bone marrow; however, lymphoid cells must migrate to other lymphoid organs (e.g. thymus) in order to complete maturation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as biological organisms, minerals and chemicals. Abstract structures include data structures in computer science and musical form. Types of structure include a hierarchy (a cascade of one-to-many relationships), a network featuring many-to-many links, or a lattice featuring connections between components that are neighbors in space. Load-bearing Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of load-bearing structures. The results of construction are divided into buildings and non-building structures, and make up the infrastructure of a human society. Built structures are broadly divided by their varying design approaches and standards, into categories including building structures, arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineralized Tissues
Mineralized tissues are biological tissues that incorporate minerals into soft matrices. Typically these tissues form a protective shield or structural support. Bone, mollusc shells, deep sea sponge ''Euplectella'' species, radiolarians, diatoms, antler bone, tendon, cartilage, tooth enamel and dentin are some examples of mineralized tissues. These tissues have been finely tuned to enhance their mechanical capabilities over millions of years of evolution. Thus, mineralized tissues have been the subject of many studies since there is a lot to learn from nature as seen from the growing field of biomimetics. The remarkable structural organization and engineering properties makes these tissues desirable candidates for duplication by artificial means. Mineralized tissues inspire miniaturization, adaptability and multifunctionality. While natural materials are made up of a limited number of components, a larger variety of material chemistries can be used to simulate the same propertie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Mineral
Bone mineral (also called inorganic bone phase, bone salt, or bone apatite) is the inorganic component of bone tissue. It gives bones their compressive strength. Bone mineral is formed predominantly from carbonated hydroxyapatite with lower crystallinity. Bone mineral is formed from globular and plate structures distributed among the collagen fibrils of bone and forming yet a larger structure. The bone salt and collagen fibers together constitute the extracellular matrix of bone tissue. Often the plural form "bone salts" is used; it reflects the notion of various salts that, on the level of molecular metabolism, can go into the formation of the hydroxyapatite. Bone mineral is dynamic in living animals; it is continually being resorbed and built anew in the bone remodeling process. In fact, the bones function as a bank or storehouse in which calcium can be continually withdrawn for use or deposited for storage, as dictated by homeostasis, which maintains the concentration of calci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossein
Ossein is the organic extracellular matrix of bone, which is made of 95% collagen. It can be isolated by treating bones with hydrochloric acid, which dissolves the inorganic matrix (calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate). This substance is used in industry for the production of gelatin and bone glue. In the early 20th century, bones were found to consist of three types of proteins: ossein (collagens), osseomucoid (proteoglycans) and osseoalbuminoid (elastin). Advances in molecular biology rendered these terms obsolete. Applications When processed industrially, 1,000 kg of bones yield 300 kg of ossein, which can be rapidly degraded and partially denatured by the prolonged action of slightly acidic boiling water, yielding gelatin. The product is specifically known as ossein gelatin in contrast to skin gelatin, which is generated from animal hides. Depending on the method of extraction, there are various types of ossein gelatin (acid ossein gelatin, limed ossein gelatin, etc.). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content. Collagen consists of amino acids bound together to form a triple helix of elongated fibril known as a collagen helix. It is mostly found in connective tissue such as cartilage, bones, tendons, ligaments, and skin. Depending upon the degree of mineralization, collagen tissues may be rigid (bone) or compliant (tendon) or have a gradient from rigid to compliant (cartilage). Collagen is also abundant in corneas, blood vessels, the gut, intervertebral discs, and the dentin in teeth. In muscle tissue, it serves as a major component of the endomysium. Collagen constitutes one to two percent of muscle tissue and accounts for 6% of the weight of the skeletal muscle tissue. The fibroblast is the most common cell that crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Resorption
Bone resorption is resorption of bone tissue, that is, the process by which osteoclasts break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood. The osteoclasts are multi-nucleated cells that contain numerous mitochondria and lysosomes. These are the cells responsible for the resorption of bone. Osteoblasts are generally present on the outer layer of bone, just beneath the periosteum. Attachment of the osteoclast to the osteon begins the process. The osteoclast then induces an infolding of its cell membrane and secretes collagenase and other enzymes important in the resorption process. High levels of calcium, magnesium, phosphate and products of collagen will be released into the extracellular fluid as the osteoclasts tunnel into the mineralized bone. Osteoclasts are prominent in the tissue destruction found in psoriatic arthritis and rheumatological disorders. The human body is in a constant state of bone remod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |