|
Bombing Of Padua In World War II
The bombing of Padua was a series of attacks by the United States Army Air Force and the Royal Air Force on the Italian city of Padua, Veneto, during World War II. These raids were aimed at disabling Padua's marshalling yard, but also resulted in heavy damage to the city and civilian casualties. Chronology of main air raids 16 December 1943 First air raid on Padua. In two attacks, the first one at ten in the morning and the second one at 1:00 P.M., seventy-two bombers of the 15th Air Force attacked the marshalling yard, but many of the 200 tons of bombs dropped in these attacks fell on the city, and especially on the Arcella district (hit by over 400 bombs); the Temple of Peace and the churches of San Carlo, Dimesse and Santissima Trinità suffered damage, as did the University and the Da Monte Sanatorium. A passenger train that had just arrived from Venice was hit by several bombs, causing dozens of victims. Another raid was carried out during the following night, hitting a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
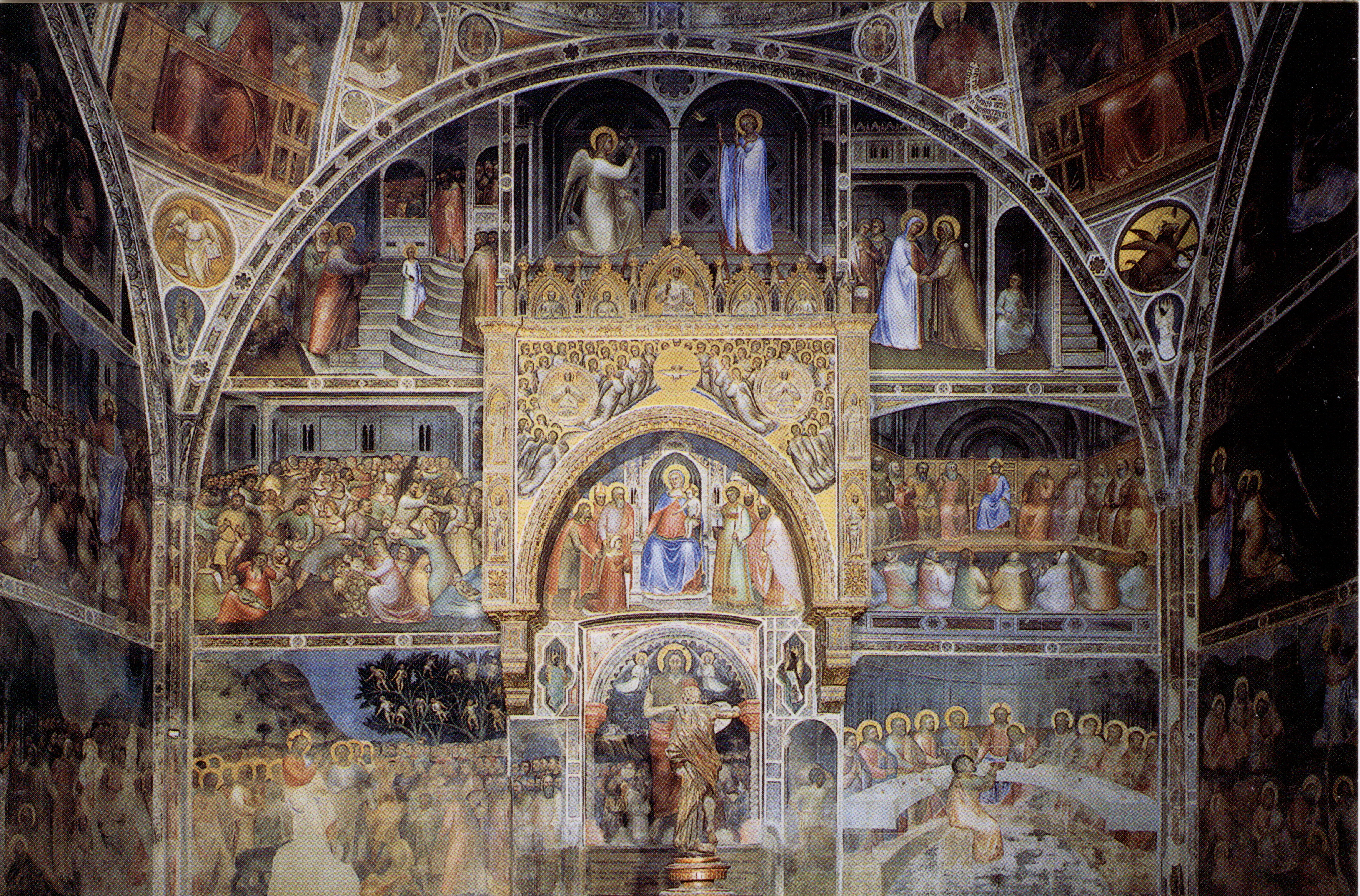
Fresco
Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaster, the painting becomes an integral part of the wall. The word ''fresco'' ( it, affresco) is derived from the Italian adjective ''fresco'' meaning "fresh", and may thus be contrasted with fresco-secco or secco mural painting techniques, which are applied to dried plaster, to supplement painting in fresco. The fresco technique has been employed since antiquity and is closely associated with Italian Renaissance painting. The word ''fresco'' is commonly and inaccurately used in English to refer to any wall painting regardless of the plaster technology or binding medium. This, in part, contributes to a misconception that the most geographically and temporally common wall painting technology was the painting into wet lime plaster. Even in appar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walls Of Padua
The Walls of Padua (Italian: ''cinta muraria di Padova'') are a complex of defensive works around the Italy, Italian city of Padua, designed to defend it from hostile attack. It was built in 4 phases. Phases Roman Of the walls built during the ancient Roman era, the only traces to survive are those incorporated into the foundations of certain palazzi. The route of this wall corresponded to a meander of the river Medoacus (now the Brenta River) in which developed Padua's first urban centre. 13th century The ''Mura Duecentesche'' ("13th century walls"; also known as the ''mura comunali'' or ''mura medievali'') were built at the start of the 13th century by the Comune of Padua. Their route was delimited by the two branches of the Bacchiglione, the Tronco Maestro and the Naviglio Interno, which came to be used as defensive ditches. There are several remains of them around the Castello and near Porta Molino. More minor remains are to be found in the Riviera Tito Livio and Riviera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually something that is otherwise difficult or impossible to cross. There are many different designs of bridges, each serving a particular purpose and applicable to different situations. Designs of bridges vary depending on factors such as the function of the bridge, the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored, and the material used to make it, and the funds available to build it. The earliest bridges were likely made with fallen trees and stepping stones. The Neolithic people built boardwalk bridges across marshland. The Arkadiko Bridge (dating from the 13th century BC, in the Peloponnese) is one of the oldest arch bridges still in existence and use. Etymology The '' Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Francis Of Sales
Francis de Sales (french: François de Sales; it, Francesco di Sales; 21 August 156728 December 1622) was a Bishop of Geneva and is revered as a saint in the Catholic Church. He became noted for his deep faith and his gentle approach to the religious divisions in his land resulting from the Protestant Reformation. He is known also for his writings on the topic of spiritual direction and spiritual formation, particularly the ''Introduction to the Devout Life'' and the ''Treatise on the Love of God''. Life Early years Francis de Sales was born two months premature on 21 August 1567 in the Château de Sales into the noble Sales family of the Duchy of Savoy, in what is today Thorens-Glières, Haute-Savoie, France. His father was François de Sales, Lord of Sales, and Novel, and by marriage, de Boisy. His mother was a noblewoman, Françoise de Sionnaz, the only child of the prominent magistrate, Melchior de Sionnaz, Seigneur de Vallières, de la Thuile, and de Boisy. This be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
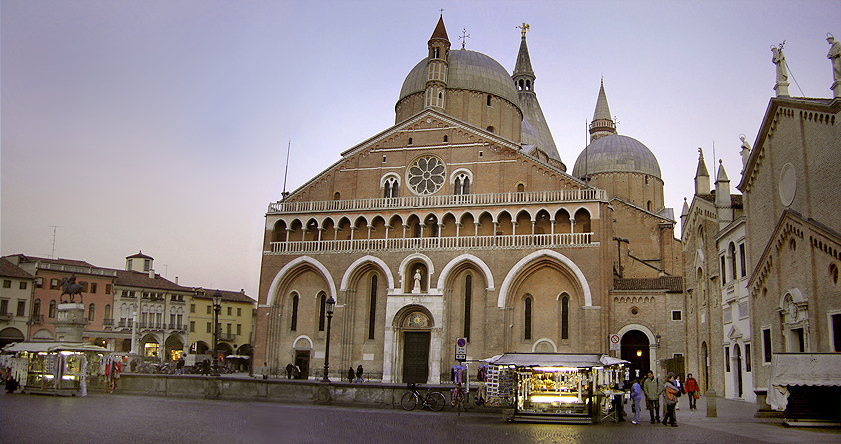
Basilica Of Saint Anthony Of Padua
The Pontifical Basilica of Saint Anthony of Padua ( it, Basilica Pontificia di Sant'Antonio di Padova) is a Catholic church and minor basilica in Padua, Veneto, Northern Italy, dedicated to St. Anthony of Padua. Although the basilica is visited as a place of pilgrimage by people from all over the world, it is not the cathedral of the city, a title belonging to the Cathedral-Basilica of St. Mary of Padua. The basilica is known locally as "il Santo". It is one of the national shrines recognized by the Holy See. History Construction of the Basilica probably began around 1232, just one year after the death of St. Anthony. It was completed in 1310 although several structural modifications (including the falling of the ambulatory and the construction of a new choir screen) took place between the end of the 14th and the mid-15th century. The Saint, according to his will, had been buried in the small church of ''Santa Maria Mater Domini'', probably dating from the late 12th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilica Del Carmine, Padua
The Basilica del Carmine is a 16th-century Roman Catholic church located on piazza Francesco Petrarca in Padua, region of Veneto, Italy. It was made a minor basilica in 1960 by pope John XXIII History The church and an attached monastery were founded by an order of Carmelite monks, hence the name. The order became established in Padua by the late 13th-century, and we have the first documentation of a church at the site by 1212. The adjacent monastery was refurbished in 1295, and the church was rebuilt in 1335 under the design of Lorenzo da Bologna. It was consecrated as ''Santa Maria del Carmine'' in 1446. In 1491, an earthquake nearly razed the building, requiring reconstruction in 1494. The bare brick facade only gained partial marble facing in the 18th-century; formerly, the facade had an open loggia. The church structure suffered various damaging events over the centuries, including another earthquake collapsing the roof in 1696; a fire during festivities burned the cupola in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palazzo Liviano
The Liviano Palace aka (''Palazzo Liviano'') is a building in Padua of the twentieth century, located in the capital of the old area of the city: it was built incorporating in its structure the remains of the Capitanio palace. Named in honor of the historian Tito Livio, now houses the School of Humanities, Social and Cultural Heritage and the Department of Cultural Heritage: Archeology, Art History, Film and Music of ' University of Padua and the Museum of Archaeological and Artistic Sciences. It is also connected with the Giants Room, an ancient frescoed structure that hosts concerts and conventions today. It is currently in the western part of Piazza Capitaniato, an ancient courtyard of the Carrara Palace restored at the time of Venetian domination, when the seat of one of the two Venetian captains who ruled Padua was built. History The palace was built on the initiative of Carlo Anti, rector of the University of Padua from 1932 to 1943, who in that period renovated many of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
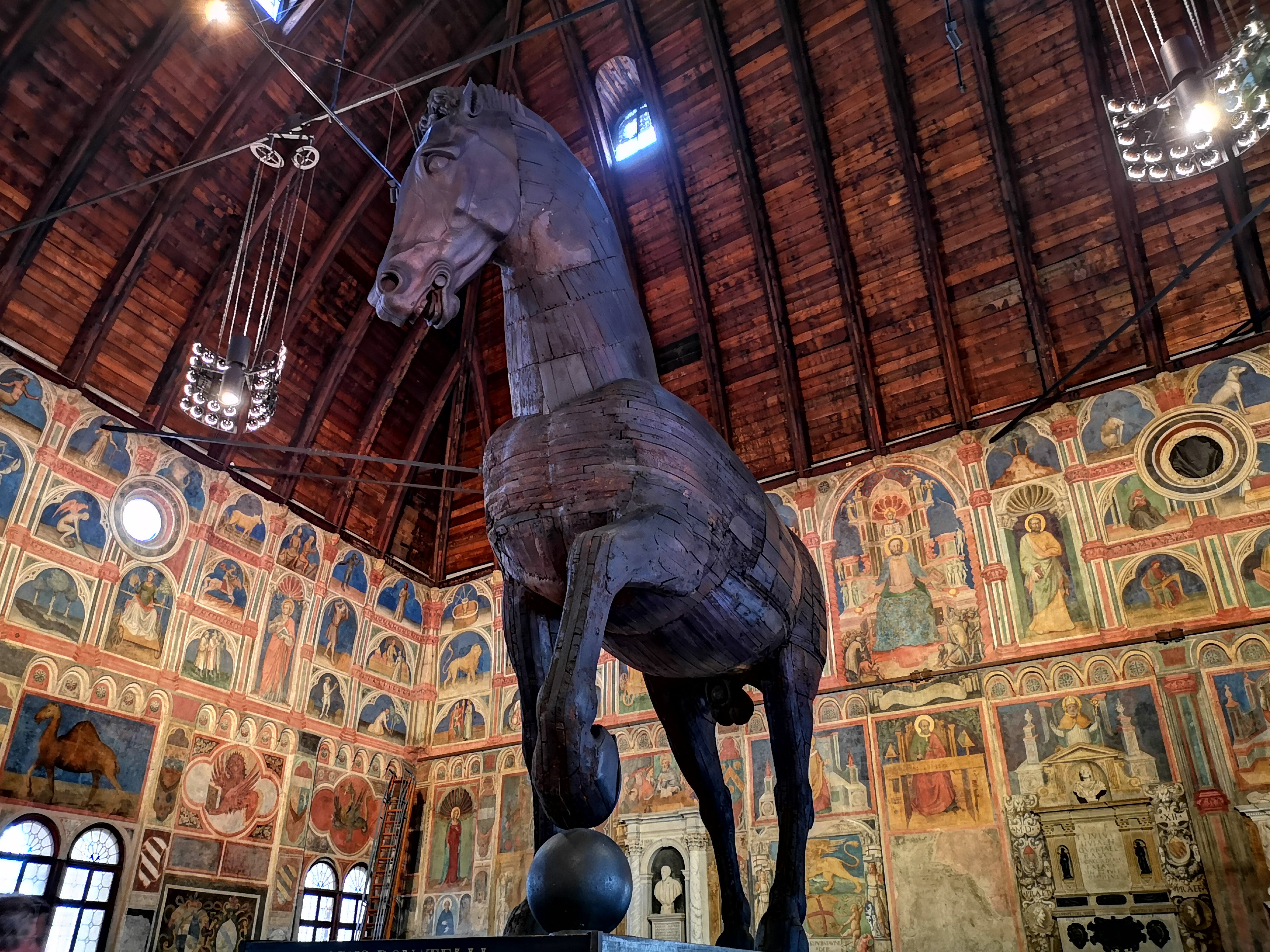
Palazzo Della Ragione, Padua
The Palazzo della Ragione is a medieval market hall, town hall and palace of justice building in Padua, in the Veneto region of Italy. The upper floor was dedicated to the town and justice administration; while the ground floor still hosts the historical covered market of the city. The palace separates the two market squares of Piazza delle Erbe from Piazza dei Frutti. It is popularly called "il Salone" (''the big Hall''). It is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Padua's 14th-century fresco cycles (since 2021). Details The building, with its great hall on the upper floor hence the name "Salone" ("big Hall"), is believed to be one of the largest medieval halls still extant; the hall is nearly rectangular, its length 81.5m, its breadth 27m, and its height 24 m; the walls are covered with allegorical frescoes. The building stands on arches, and the upper storey is surrounded by an open loggia, not unlike that which surrounds the Basilica Palladiana in Vicenza, that was i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueduct (water Supply)
An aqueduct is a watercourse constructed to carry water from a source to a distribution point far away. In modern engineering, the term ''aqueduct'' is used for any system of pipes, ditches, canals, tunnels, and other structures used for this purpose. The term ''aqueduct'' also often refers specifically to a bridge carrying an artificial watercourse. Aqueducts were used in ancient Greece, ancient Egypt, and ancient Rome. The simplest aqueducts are small ditches cut into the earth. Much larger channels may be used in modern aqueducts. Aqueducts sometimes run for some or all of their path through tunnels constructed underground. Modern aqueducts may also use pipelines. Historically, agricultural societies have constructed aqueducts to irrigate crops and supply large cities with drinking water. Etymology The word ''aqueduct'' is derived from the Latin words (''water'') and (''led'' or ''guided''). Ancient aqueducts Although particularly associated with the Romans, aqueducts we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padua Cathedral
Padua Cathedral, or Basilica Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Assumption ( it, Duomo di Padova; Basilica Cattedrale di Santa Maria Assunta), is a Catholic church and minor basilica located on the east end of Piazza Duomo, adjacent to the bishop's palace in Padua, Veneto, Italy. The cathedral, dedicated to the Assumption of the Virgin Mary, is the seat of the Bishop of Padua. The church building, first erected as a cathedral in the 4th century, has undergone major reconstructions over the centuries. History The present church is the third structure built on the same site. The first cathedral was erected after the Edict of Milan in 313 and destroyed by an earthquake on 3 January 1117. It was rebuilt in Romanesque style: the appearance of that medieval church can be seen in the frescoes by Giusto de' Menabuoi in the adjoining baptistery. The current building dates from a reconstruction during the sixteenth century. While in the past the design was attributed to Michelangelo, it wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabteilung'' of the Imperial Navy, had been disbanded in May 1920 in accordance with the terms of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles which banned Germany from having any air force. During the interwar period, German pilots were trained secretly in violation of the treaty at Lipetsk Air Base in the Soviet Union. With the rise of the Nazi Party and the repudiation of the Versailles Treaty, the ''Luftwaffe''s existence was publicly acknowledged on 26 February 1935, just over two weeks before open defiance of the Versailles Treaty through German rearmament and conscription would be announced on 16 March. The Condor Legion, a ''Luftwaffe'' detachment sent to aid Nationalist forces in the Spanish Civil War, provided the force with a valuable testing grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)