|
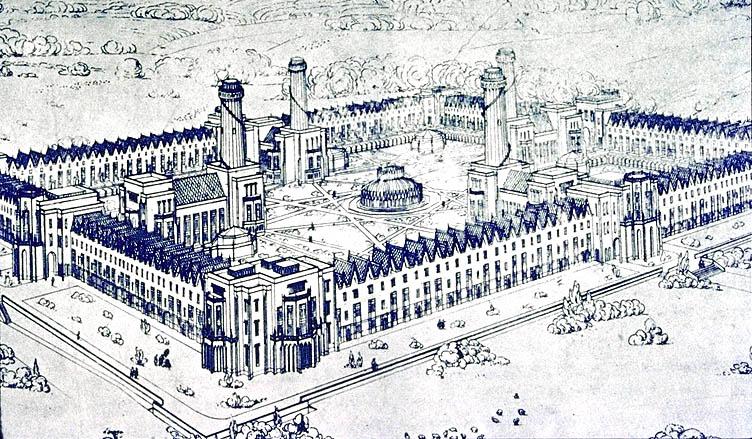
Bois-du-Luc
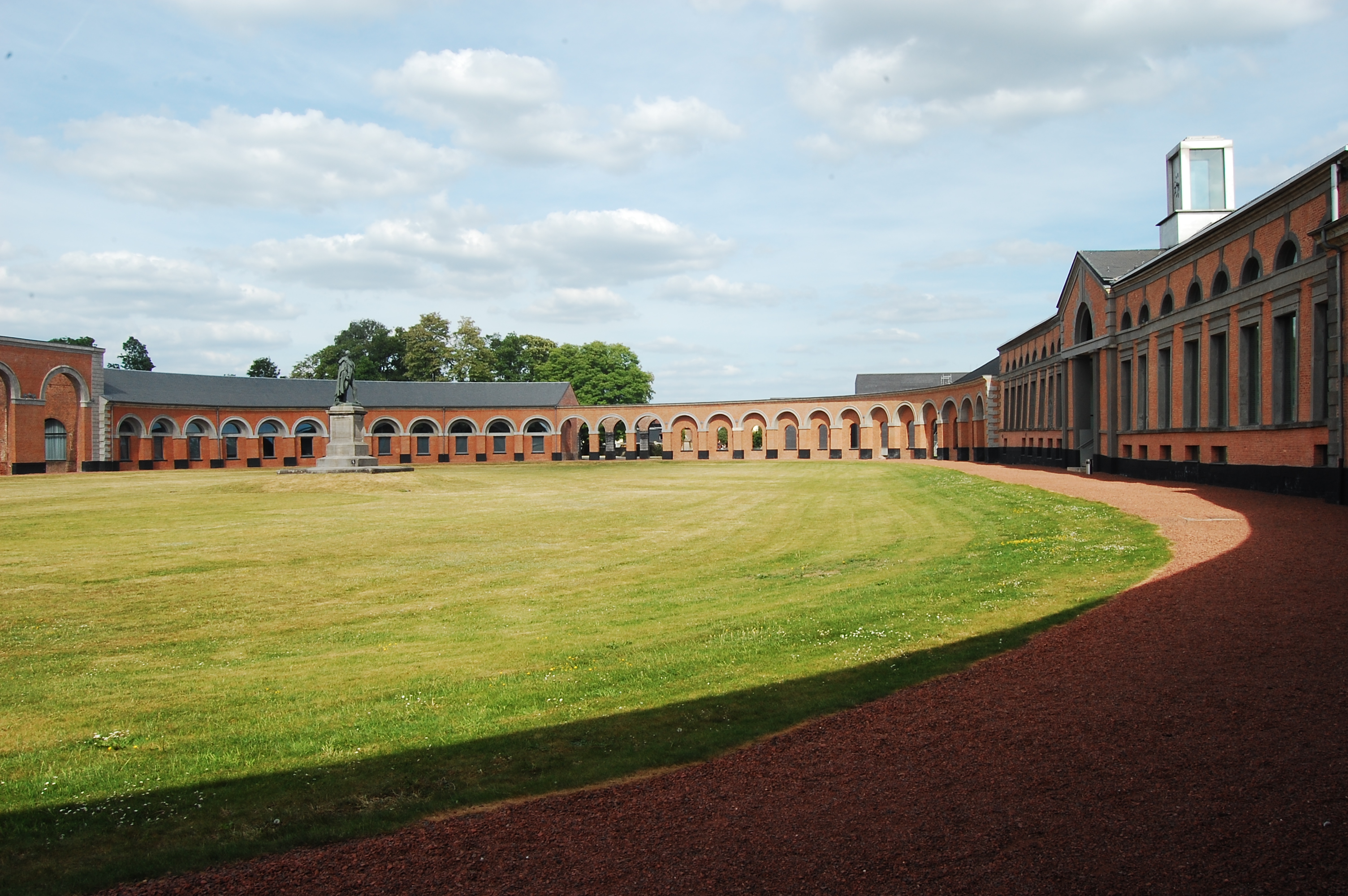
The Bois-du-Luc was a coal mine in Houdeng-Aimeries, near La Louvière, in Belgium which today is preserved as an industrial heritage site. As well as the site of the headquarters of the ''Société des Charbonnages de Bois-du-Luc et d'Havre'', the Bois du Luc was the site of the Saint Emmanuel Pit (''Fosse Saint-Emmanuel'') which belonged to the company. The ''Fosse Saint-Emmanuel'' was one of the oldest mines in Belgium, with recorded activity dating back to 1685. The company ceased mining in 1973. The Bois-du-Luc is particularly known for the surrounding company town (''cité ouvrière'') which was created for the mine works during the 19th century and is today one of the most notable surviving remnants of industrial paternalism in Belgium. It includes workers' housing which dates from the 1830s and covers approximately . The site, run as an ecomuseum since 1983, features on the European Route of Industrial Heritage and is one of the four Walloon mining sites listed by UNESCO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bois-du-Luc 08
The Bois-du-Luc was a coal mine in Houdeng-Aimeries, near La Louvière, in Belgium which today is preserved as an industrial heritage site. As well as the site of the headquarters of the ''Société des Charbonnages de Bois-du-Luc et d'Havre'', the Bois du Luc was the site of the Saint Emmanuel Pit (''Fosse Saint-Emmanuel'') which belonged to the company. The ''Fosse Saint-Emmanuel'' was one of the oldest mines in Belgium, with recorded activity dating back to 1685. The company ceased mining in 1973. The Bois-du-Luc is particularly known for the surrounding company town (''cité ouvrière'') which was created for the mine works during the 19th century and is today one of the most notable surviving remnants of industrial paternalism in Belgium. It includes workers' housing which dates from the 1830s and covers approximately . The site, run as an ecomuseum since 1983, features on the European Route of Industrial Heritage and is one of the four Walloon mining sites listed by UNESCO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Mining Sites Of Wallonia
The Major Mining Sites of Wallonia is a UNESCO World Heritage Site comprising four sites in Wallonia in southern Belgium associated with the Belgian coal mining industry of the 19th and 20th centuries. The four sites of the grouping, situated in the French-speaking Hainaut Province and Liège Province, comprise Grand-Hornu, the Bois-du-Luc, the Bois du Cazier and Blegny-Mine. Description The site was recognized by the UNESCO commission in 2012 and is officially described: History During the Industrial Revolution in the 19th century, mining and the heavy industry that relied on coal formed a major part of Belgium's economy. Most of this mining and industry took place in the '' sillon industriel'' ("industrial valley" in French), a strip of land running across the country where many of the largest cities in Wallonia are located. The named locations of this World Heritage Site are all situated in or near the area of the ''sillon industriel''. The mining sector in Belgium declin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houdeng-Aimeries
Houdeng-Aimeries ( wa, Oudè) is a village of Wallonia and a district of the municipality of La Louvière, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. The village contains two UNESCO World Heritage sites; its 16.93 m high boat lift was listed in 1998, together with the other three hydraulic boat lifts on the Canal du Centre near La Louvière, and Bois-du-Luc is a former coal mine today preserved as one of the four Walloon mining sites listed in 2012 under the Major Mining Sites of Wallonia The Major Mining Sites of Wallonia is a UNESCO World Heritage Site comprising four sites in Wallonia in southern Belgium associated with the Belgian coal mining industry of the 19th and 20th centuries. The four sites of the grouping, situated in t .... References Former municipalities of Hainaut (province) La Louvière {{Hainaut-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Louvière
La Louvière (; wa, El Lovire) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. The municipality consists of the following districts: Boussoit, Haine-Saint-Paul, Haine-Saint-Pierre, Houdeng-Aimeries, Houdeng-Gœgnies, La Louvière, Maurage, Saint-Vaast, Strépy-Bracquegnies, and Trivières. La Louvière is the capital of the ''Centre'' region, a former coal mining area in the ''Sillon industriel'', between the ''Borinage'' to the West and the ''Pays Noir'' to the East. History Mythical origins The legend of a mother wolf nursing a child at La Louvière is reminiscent of the mythical birth of Rome. The true origin of the city, however, dates from the 12th century. At that time, the forested, and presumably wolf-infested, territory of today’s La Louvière was named ''Menaulu'', from the Old French meaning “wolf’s lair”. This land was part of the larger community of Saint-Vaast, which itself belonged to the Aulne Abbey. By 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecomuseum
An ecomuseum is a museum focused on the identity of a place, largely based on local participation and aiming to enhance the welfare and development of local community, local communities. Ecomuseums originated in France, the concept being developed by Georges Henri Rivière and :fr:Hugues de Varine, Hugues de Varine, who coined the term ‘ecomusée’ in 1971. The term "éco" is a shortened form for "écologie", but it refers especially to a new idea of holistic interpretation of cultural heritage, in opposition to the focus on specific items and objects, performed by traditional museums. There are presently about 300 operating ecomuseums in the world; about 200 are in Europe, mainly in France, Italy, Spain, and Poland. Development In the 1960s and ‘70s, a new kind of museum, known as ecomuseums, emerged throughout Europe, predominately in France. Based on belief that museums and communities should be related to the whole of life, ecomuseums focused on integrating the family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Heritage
Industrial heritage refers to the physical remains of the history of technology and industry, such as manufacturing and mining sites, as well as power and transportation infrastructure. Another definition expands this scope so that the term also covers places used for social activities related to industry such as housing, museums, education or religious worship, among other structures with values from a variety of fields in order to highlight the interdisciplinary character of industrial heritage. It is also argued that it includes the so-called sociofacts or aspects of social and institutional organizations, and mentifacts that constitute the attitudinal characteristics and value systems industrial heritage sites. The scientific study of industrial remains is called industrial archaeology. The industrial heritage of a region is an aspect of its cultural heritage. It also forms part of a location's identity as it serves as evidence of progress and landmark achievements. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Emmanuel
Saint Emmanuel (died ''c.'' 304), was arrested and executed at Sirmium, in what is now Serbia, with 42 other martyrs, including Quadratus (Codratus) and Theodocius, in 304 as part of Diocletian's persecution of the Christians. Their feast day The calendar of saints is the traditional Christian method of organizing a liturgical year by associating each day with one or more saints and referring to the day as the feast day or feast of said saint. The word "feast" in this context d ... is 26 March. External links''Quadratus (Codratus), Theodosius, Emmanuel & Comp.'' 304 deaths Year of birth unknown {{saint-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Company Town
A company town is a place where practically all stores and housing are owned by the one company that is also the main employer. Company towns are often planned with a suite of amenities such as stores, houses of worship, schools, markets and recreation facilities. They are usually bigger than a model village ("model" in the sense of an ideal to be emulated). Some company towns have had high ideals, but many have been regarded as controlling and/or exploitative. Others developed more or less in unplanned fashion, such as Summit Hill, Pennsylvania, United States, one of the oldest, which began as a Lehigh Coal & Navigation Company mining camp and mine site nine miles (14.5 km) from the nearest outside road. Overview Traditional settings for company towns were where extractive industries – coal, metal mines, lumber – had established a monopoly franchise. Dam sites and war-industry camps founded other company towns. Since company stores often had a monopoly in company t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welfare Capitalism
Welfare capitalism is capitalism that includes social welfare policies and/or the practice of businesses providing welfare services to their employees. Welfare capitalism in this second sense, or industrial paternalism, was centered on industries that employed skilled labor and peaked in the mid-20th century. Today, welfare capitalism is most often associated with the models of capitalism found in Central Mainland and Northern Europe, such as the Nordic model and social market economy (also known as Rhine capitalism and social capitalism). In some cases welfare capitalism exists within a mixed economy, but welfare states can and do exist independently of policies common to mixed economies such as state interventionism and extensive regulation. Language "Welfare capitalism" or "welfare corporatism" is somewhat neutral language for what, in other contexts, might be framed as "industrial paternalism", "industrial village", "company town", "representative plan", "industrial betterm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Mining
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from iron ore and for cement production. In the United Kingdom and South Africa, a coal mine and its structures are a colliery, a coal mine is called a 'pit', and the above-ground structures are a 'pit head'. In Australia, "colliery" generally refers to an underground coal mine. Coal mining has had many developments in recent years, from the early days of men tunneling, digging and manually extracting the coal on carts to large open-cut and longwall mines. Mining at this scale requires the use of draglines, trucks, conveyors, hydraulic jacks and shearers. The coal mining industry has a long history of significant negative environmental impacts on local ecosystems, health impacts on local communities and workers, and contributes heavily to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Route Of Industrial Heritage
The European Route of Industrial Heritage (ERIH) is a tourist route of the most important industrial heritage sites in Europe. This is a tourism industry information initiative to present a network of industrial heritage sites across Europe. The aim of the project is to create interest for the common European heritage of the Industrialisation and its legacy. ERIH also wants to promote regions, towns and sites showing the industrial history and market them as visitor attractions in the leisure and tourism industry. History The concept of using a European Route of Industrial Heritage was born in 1999; it was recognised there had been no single event to shape the European landscape greater than the industrial revolution. That changed the working culture of all Europeans, and gave common experiences to communities across Europe whether it be deep mine coal working in the Rühr or South Wales. Four countries, Great Britain, Belgium, Germany and the Netherlands successfully applied for E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 193 member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the non-governmental, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 national commissions that facilitate its global mandate. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations's International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). Its constitution establishes the agency's goals, governing structure, and operating framework. UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the Second World War, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboration and dialogue among nations. It pursues this objective t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |