|
Bogor Agricultural University Alumni
Bogor ( su, , nl, Buitenzorg) is a city in the West Java province, Indonesia. Located around south of the national capital of Jakarta, Bogor is the 6th largest city in the Jakarta metropolitan area and the 14th overall nationwide. Estimasi Penduduk Menurut Umur Tunggal Dan Jenis Kelamin 2014 Kementerian Kesehatan The city covers an area of 118.50 km2, and it had a population of 950,334 in the 2010 Census and 1,043,070 in the 2020 Census.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021. The official estimate for mid 2022 is 1,099,422. Bogor is an important economic, scientific, cultural, and tourist center, as well as a mountain resort. During the |
Dutch Language
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German and English. ''Afrikaans'' is a separate but somewhat mutually intelligible daughter languageAfrikaans is a daughter language of Dutch; see , , , , , . Afrikaans was historically called Cape Dutch; see , , , , , . Afrikaans is rooted in 17th-century dialects of Dutch; see , , , . Afrikaans is variously described as a creole, a partially creolised language, or a deviant variety of Dutch; see . spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, evolving from the Cape Dutch dialects of Southern Africa. The dialects used in Belgium (including Flemish) and in Suriname, meanwhile, are all guided by the Dutch Language Union. In Europe, most of the population of the Netherlands (where it is the only official language spoken country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javanese People
The Javanese ( id, Orang Jawa; jv, Ļ”«Ļ”║Ļ”┤Ļ”üĻ”ŚĻ”«, ''Wong Jawa'' ; , ''Tiyang Jawi'' ) are an ethnic group native to the central and eastern part of the Indonesian island of Java. With approximately 100 million people, Javanese people are the largest ethnic group in Indonesia and the whole Southeast Asia in general. Their native language is Javanese, it is the largest of the Austronesian languages in number of native speakers and also the largest regional language in Southeast Asia. The Javanese as the largest ethnic group in the region have dominated the historical, social, and political landscape in the past as well as in modern Indonesia and Southeast Asia. There are significant numbers of Javanese diaspora outside of central and eastern Java regions, including the other provinces of Indonesia, and also in another countries such as Suriname, Singapore, Malaysia, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Yemen and the Netherlands. The Javanese ethnic group h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Domestic Product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is often revised before being considered a reliable indicator. List of countries by GDP (nominal) per capita, GDP (nominal) per capita does not, however, reflect differences in the cost of living and the inflation, inflation rates of the countries; therefore, using a basis of List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, GDP per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP) may be more useful when comparing standard of living, living standards between nations, while nominal GDP is more useful comparing national economies on the international market. Total GDP can also be broken down into the contribution of each industry or sector of the economy. The ratio of GDP to the total population of the region is the GDP per capita, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time In Indonesia
The Indonesian Archipelago geographically stretches across four time zones from UTC+06:00 in Aceh to UTC+09:00 in Papua. However, the Indonesian government recognises only three time zones in its territory, namely: *Western Indonesia Time (WIB) ŌĆö seven hours ahead ( UTC+07:00) of the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC); *Central Indonesia Time (WITA) ŌĆö eight hours ahead ( UTC+08:00) of UTC; *Eastern Indonesia Time (WIT) ŌĆö nine hours ahead ( UTC+09:00) of UTC. The boundary between the Western and Central time zones was established as a line running north between Java and Bali through the provincial boundaries of West and Central Kalimantan. The border between the Central and Eastern time zones runs north from the eastern tip of Indonesian Timor to the eastern tip of Sulawesi. Daylight saving time (DST) is no longer observed anywhere in Indonesia. Current usage In Indonesia Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
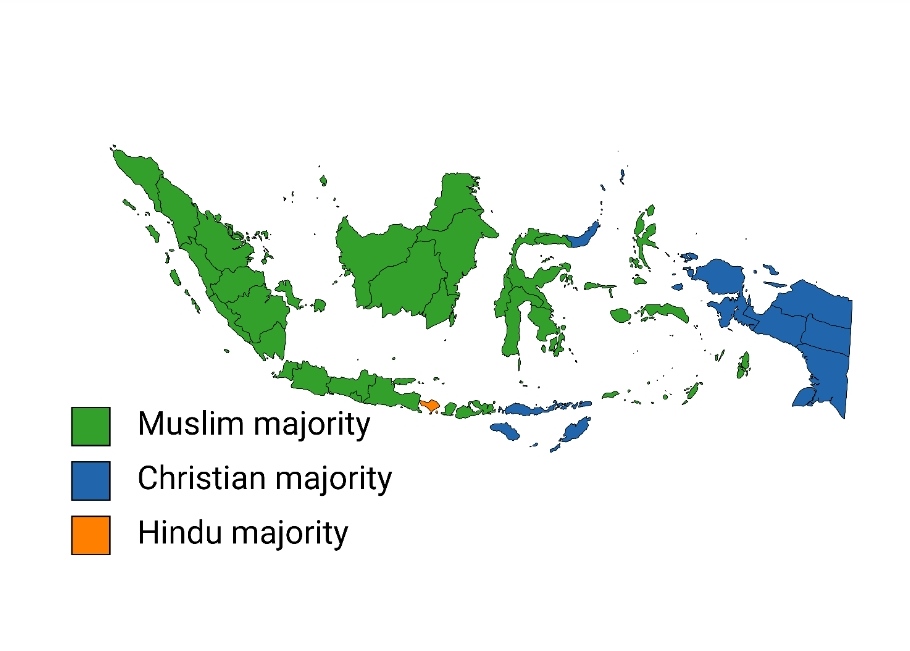
Religion In Indonesia
Several different religions are practised in Indonesia and in practice the country is a secular state. Indonesia is officially a presidential republic and a unitary state. Indonesia has the world's largest Muslim populationFrederick, William H.; Worden, Robert L., eds. (1993). ''Indonesia: A Country Study'', ChapteIslam and the first principle of Indonesia's philosophical foundation, Pancasila, requires its citizens to state "the One and almighty God". Consequently, atheists in Indonesia experience official discrimination in the context of registration of births and marriages and the issuance of identity cards. In addition, the Aceh province officially enforces Sharia law and is notorious for its discriminatory practices towards religious and sexual minorities. There are also pro-Sharia and fundamentalist movements in several parts of the country with overwhelming Muslim majorities. Several different religions are practised in the country, and their collective influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confucianism In Indonesia
The Supreme Council for the Confucian Religion in Indonesia ( id, Majelis Tinggi Agama Konghucu Indonesia, MATAKIN; Chinese: ÕŹ░Õ░╝ÕŁöµĢÖńĖĮµ£ā; pinyin: y├¼nn├Ł kŪÆngji├Āo zŪÆnghu├¼) is a Confucian church established in 1955 in Indonesia, comprising the communities of practitioners of Confucianism mostly among Chinese Indonesians. Together with the Hong Kong Confucian Academy it is one of the two branches that formed after the dissolution of mainland China's Confucian Church founded by Kang Youwei in the early 20th century. Official census (2018) According to the 2018 census, there were a total 71,999 of Confucianism in Indonesia. The percentages of Confucianism in Indonesia 0,03% in 2018. History * In 1883, Boen Tjhiang Soe (Wen Chang Ci µ¢ćµśīńźĀ), after being rebuilt in 1906, became the ''Boen Bio'' (''Wen Miao'' µ¢ćÕ╗¤ or ''Kong Miao'' ÕŁöÕ╗¤, "Temple of Culture" or "Temple of Confucius") at Jl. Kapasan No. 131 Surabaya. The colonial Dutch called it ''Geredja Boen Bio'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism In Indonesia
Hinduism in Indonesia, as of the 2018 census, is practised by about 1.74% of the total population, and almost 87% of the population in Bali. Hinduism is one of the six official religions of Indonesia. Hinduism came to Indonesia in the 1st-century through traders, sailors, scholars and priests. A syncretic fusion of pre-existing Javanese folk religion, culture and Hindu ideas, that from the 6th-century also synthesized Buddhist ideas as well, evolved as the Indonesian version of Hinduism. These ideas continued to develop during the Srivijaya and Majapahit empires. About 1400 CE, these kingdoms were introduced to Islam from coast-based Muslim traders, and thereafter Hinduism mostly vanished from many of the islands of Indonesia. Indonesia has the fourth-largest population of Hindus in the world, after India, Nepal and Bangladesh. Though being a minority religion, the Hindu culture has influenced the way of life and day-to-day activities in Indonesia. Outside of Bali, many adhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism In Indonesia
Buddhism has a long history in Indonesia, and is recognized as one of the six recognized religions in Indonesia, along with Islam, Christianity (Protestantism and Catholicism), Hinduism and Confucianism. According to the 2018 national census roughly 0.8% of the total citizens of Indonesia were Buddhists, and numbered around 2 million. Most Buddhists are concentrated in Jakarta, Riau, Riau Islands, Bangka Belitung, North Sumatra, and West Kalimantan. These totals, however, are probably inflated, as practitioners of Taoism and Chinese folk religion, which are not considered official religions of Indonesia, likely declared themselves as Buddhists on the most recent census. Today, the majority of Buddhists in Indonesia are Chinese, however small communities of native Buddhists (such as Javanese and Sasak) also exist. History Antiquity Buddhism is the second oldest religion in Indonesia after Hinduism, which arrived from India around the second century. The history of Buddhism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In Indonesia
Christianity is Indonesia's second-largest religion, after Islam. Indonesia also has the second-largest Christian population in Southeast Asia after the Philippines, the largest Protestant population in Southeast Asia, and the fourth-largest Christian population in Asia after the Philippines, China and India. Indonesia's 28.6 million Christians constituted 10.72% of the country's population in 2018, with 7.60% Protestant (20.25 million) and 3.12% Catholic (8.33 million). Some provinces in Indonesia are majority Christian (Protestant or Catholic). It is the second largest religion after Islam. According to the 2010 census, all Christian denominations account for around 10%, or around 23 million. The Indonesian government officially recognizes two main divisions of Christianity in Indonesia, namely Protestantism and the Catholic Church. Protestants make up about 70% of all Christians in Indonesia, and Catholics constitute 30% of all Christians in Indonesia. Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In Indonesia
Islam is the largest religion in Indonesia, with 86.7% of the Indonesian population identifying themselves as Muslim in a 2018 survey. Indonesia is the most populous Muslim-majority country, with approximately 231 million adherents. In terms of denomination, the overwhelming majority (98.8%) are Sunni Muslims, while 1-3 million (1%) are Shia, and are concentrated around Jakarta, and about 400,000 (0.2%) Ahmadi Muslims. In terms of schools of jurisprudence, based on demographic statistics, 99% of Indonesian Muslims mainly follow the Shafi'i school, although when asked, 56% does not adhere to any specific school. Trends of thought within Islam in Indonesia can be broadly categorized into two orientations: "modernism", which closely adheres to orthodox theology while embracing modern learning, and "traditionalism", which tends to follow the interpretations of local religious leaders and religious teachers at Islamic boarding schools ('' pesantren''). There is also a hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Groups In Indonesia
There are 1,340 recognised ethnic groups in Indonesia. The vast majority of those belong to the Austronesian peoples. Based on ethnic classification, the largest ethnic group in Indonesia is the Javanese who make up about 40% of the total population. The Javanese are concentrated on the island of Java, particularly in the central and eastern parts. The Sundanese are the next largest group; their homeland is located in the western part of the island of Java and the southern edge of Sumatra. The Sunda Strait is named after them. The Malays, Batak, Madurese, Betawi, Minangkabau, and Bugis are the next largest groups in the country. Many ethnic groups, particularly in Kalimantan and Papua (Indonesian province), Papua, have only hundreds of members. Most of the local languages belong to the Austronesian languages, Austronesian language family, although a significant number of people, particularly in eastern Indonesia, speak unrelated Papuan languages. Indonesians of Chinese Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minangkabau People
Minangkabau people ( min, Urang Minang; Indonesian or Malay: ''Orang Minangkabau'' or ''Minangkabo''; Jawi: ┘ģ┘å┌Ā┘āž©┘ł), also known as Minang, are an Austronesian ethnic group native to the Minangkabau Highlands of West Sumatra, Indonesia. The Minangkabau's West Sumatran homelands was the seat of the Pagaruyung Kingdom, believed by early historians to have been the cradle of the Malay race, and the location of the Padri War (1821 to 1837). Minangkabau are the ethnic majority in West Sumatra and Negeri Sembilan. Minangkabau are also a recognised minority in other parts of Indonesia as well as Malaysia, Singapore and the Netherlands. Etymology There are several etymology of the term Minangkabau. While the word "kabau" undisputedly translates to "Water Buffalo", the word "minang" is traditionally known as a pinang fruit that people usually chew along the 'Sirih' leaves. But there is also a folklore that mention that term Minangkabau (Minangkabau: ''Minang'' Jawi script: ┘ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |