|
Blonde Rock, Nova Scotia
Blonde Rock is a shoal off the south-eastern tip of Nova Scotia, Canada. It is located at position 43° 20′ 28″ N, 65° 59′ 10″ W, and roughly south-southeast of Seal Island. At a low spring tide, only two feet of the rock are above water. The shoal was named after British Royal Navy frigate , which was wrecked on the shoal on 21 January 1782. The 60 American prisoners on board HMS ''Blonde'' made their way to Seal Island, Nova Scotia. American privateer Noah Stoddard in the Scammell rescued them and controversially allowed the British crew to return to Halifax in HMS ''Observer'', (which was involved in the Naval battle off Halifax en route), leading to his later exile in Nova Scotia as a Loyalist Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Cro ....Thomas Head Raddall. "Adv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoal
In oceanography, geomorphology, and geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material and rises from the bed of a body of water to near the surface. It often refers to those submerged ridges, banks, or bars that rise near enough to the surface of a body of water as to constitute a danger to navigation. Shoals are also known as sandbanks, sandbars, or gravelbars. Two or more shoals that are either separated by shared troughs or interconnected by past or present sedimentary and hydrographic processes are referred to as a shoal complex.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl Jr., and J.A. Jackson, eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. The term ''shoal'' is also used in a number of ways that can be either similar or quite different from how it is used in geologic, geomorphic, and oceanographic literature. Sometimes, this term refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland". Most of the population are native English-speakers, and the province's population is 969,383 according to the 2021 Census. It is the most populous of Canada's Atlantic provinces. It is the country's second-most densely populated province and second-smallest province by area, both after Prince Edward Island. Its area of includes Cape Breton Island and 3,800 other coastal islands. The Nova Scotia peninsula is connected to the rest of North America by the Isthmus of Chignecto, on which the province's land border with New Brunswick is located. The province borders the Bay of Fundy and Gulf of Maine to the west and the Atlantic Ocean to the south and east, and is separated from Prince Edward Island and the island of Newfoundland by the Northumberland and Cabot straits, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal Island (Nova Scotia)
Seal Island (also known as Great Seal Island) is an island on the outermost extreme of Southwestern Nova Scotia, Canada, in the Municipality of the District of Argyle in Yarmouth County. It is approximately long and wide and is surrounded on its east, south and west sides by dangerous shoals. It is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean and is the biggest of a group of five islands which extend north for . It is the second southernmost point of land of Nova Scotia. The southern tip of nearby Cape Sable Island is farther south than the southern tip of land on Seal Island. History During the American Revolution, Noah Stoddard's vessel the Scammell was commissioned in April 1782. Soon after, he rescued the 60 American prisoners on board H.M.S. ''Blonde'', who were stranded on Seal Island after hitting Blonde Rock, Nova Scotia. Stoddard allowed the British crew to return to Halifax. The island was settled in 1823 by two families from the Barrington area, the Hitchens and the Crowell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or " tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see '' Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude tides a day—is a third regular category. Tide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Museum Of The Atlantic
The Maritime Museum of the Atlantic is a maritime museum located in downtown Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. The museum is a member institution of the Nova Scotia Museum and is the oldest and largest maritime museum in Canada with a collection of over 30,000 artifacts including 70 small craft and a steamship: the CSS ''Acadia'', a 180-foot steam-powered hydrographic survey ship launched in 1913. History The museum was founded in 1948. It was first known as the Maritime Museum of Canada and located at HMC Dockyard, the naval base on Halifax Harbour. Several naval officers served as volunteer chairs of the museum until 1959 when Niels Jannasch was hired as the museum's founding director, serving until 1985. The museum moved through several locations over the next three decades before its current building was constructed in 1981 as part of a waterfront redevelopment program. The museum received the CSS ''Acadia'' in 1982. Today the museum is part of the Nova Scotia Museum system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal Island, Nova Scotia
Seal Island (also known as Great Seal Island) is an island on the outermost extreme of Southwestern Nova Scotia, Canada, in the Municipality of the District of Argyle in Yarmouth County. It is approximately long and wide and is surrounded on its east, south and west sides by dangerous shoals. It is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean and is the biggest of a group of five islands which extend north for . It is the second southernmost point of land of Nova Scotia. The southern tip of nearby Cape Sable Island is farther south than the southern tip of land on Seal Island. History During the American Revolution, Noah Stoddard's vessel the Scammell was commissioned in April 1782. Soon after, he rescued the 60 American prisoners on board H.M.S. ''Blonde'', who were stranded on Seal Island after hitting Blonde Rock, Nova Scotia. Stoddard allowed the British crew to return to Halifax. The island was settled in 1823 by two families from the Barrington area, the Hitchens and the Crowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noah Stoddard
Captain Noah Stoddard (1755–1850) of Fairhaven, Massachusetts was an American privateer who distinguished himself during the American Revolution by leading the Raid on Lunenburg (1782). In the raid, Stoddard led four other privateer vessels and attacked the British settlement at Lunenburg, Nova Scotia on July 1, 1782. In Nova Scotia, the assault on Lunenburg was the most spectacular raid of the war.Gwyn, p. 75 American Revolution Stoddard was involved in the first naval engagement of the American Revolution, Battle off Fairhaven, when patriots retrieved two vessels that had been captured by the British sloop of war, ''Falcon'', in Buzzards Bay. On May 14, 1775, American Captain Daniel Egery and Capt. Nathaniel Pope of Fairhaven in the sloop ''Success'' (40 guns, 30 men) retrieved two vessels captured by the British crew of Captain John Linzee (Lindsey), Royal Navy commander of HMS ''Falcon'' (14 guns, 110 men). Stoddard and the others took the first naval prisoners of the war, 13 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Battle Off Halifax
The Battle off Halifax took place on 28 May 1782 during the American Revolutionary War. It involved the American privateer ''Jack'' and the 14-gun Royal Naval brig off Halifax, Nova Scotia. Captain David Ropes commanded ''Jack'', and Lieutenant John Crymes commanded ''Observer''. The battle was "a long and severe engagement" in which Captain David Ropes was killed. Background During the American Revolution, Americans regularly attacked Nova Scotia by land and sea. American privateers devastated the maritime economy by raiding many of the coastal communities, such as the numerous raids on Liverpool and on Annapolis Royal. On the 7th of July, 1777, off the coast of Halifax, Sir George Collier, in command of , with a force of two British frigates and a brig, opened fire on and captured John Manley, the second in command of the Continental Navy, and the 13-gun frigate (229 men) off the coast of Nova Scotia. After a running battle lasting 39 hours, the British succeeded in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loyalist
Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Crown, notably with the loyalists opponents of the American Revolution, and United Empire Loyalists who moved to other colonies in British North America after the revolution. Historical loyalism 18th century North America In North America, the term ''loyalist'' characterised colonists who rejected the American Revolution in favour of remaining loyal to the king. American loyalists included royal officials, Anglican clergymen, wealthy merchants with ties to London, demobilised British soldiers, and recent arrivals (especially from Scotland), as well as many ordinary colonists who were conservative by nature and/or felt that the protection of Britain was needed. Colonists with loyalist sympathies accounted for an estimated 15 per cent to 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Nova Scotia
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

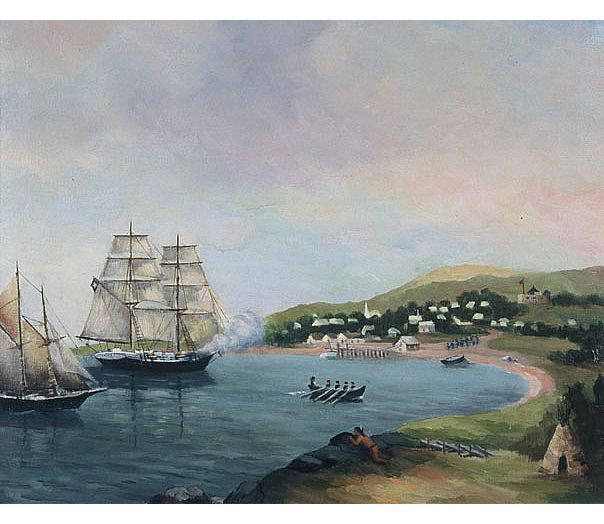
.jpg)