|
Blackbush Scrub
Blackbush scrub,Mojave Desert Wildflowers, Pam Mackay, p18, 252 or blackbrush scrub,Canyon Country Wildflowers, Damian Fagan, p 3, 105 is a vegetation type of the Western United States deserts characterized by low growing, dark gray blackbush (''Coleogyne ramosissima'') as the dominant species. Blackbush often occurs in pure stands, giving a uniform dark gray appearance to the landscape. Mojave Desert Blackbrush scrub occurs over a wide elevation range in the Mojave Desert. It may occur as an understory in Joshua tree woodland or pinyon-juniper woodland. Associates in the Mojave Desert include ephedra (''Ephedra nevadensis'', ''Ephedra viridis''), hop-sage ''Grayia spinosa'', turpentine broom ('' Thamnosma montana''), horsebrush ('' Tedradymia spp.''), cheesebush (''Ambrosia salsola''), and winter fat (''Krascheninnikovia lanata''). Colorado Plateau In the Colorado Plateau The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the West'' changed. Before about 1800, the crest of the Appalachian Mountains was seen as the western frontier. The frontier moved westward and eventually the lands west of the Mississippi River were considered the West. The U.S. Census Bureau's definition of the 13 westernmost states includes the Rocky Mountains and the Great Basin to the Pacific Coast, and the mid-Pacific islands state, Hawaii. To the east of the Western United States is the Midwestern United States and the Southern United States, with Canada to the north, and Mexico to the south. The West contains several major biomes, including arid and semi-arid plateaus and plains, particularly in the American Southwest; forested mountains, including three major ranges, the Sierra Neva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thamnosma Montana
''Thamnosma montana'', the turpentine broom, or Mojave desert-rue, is a shrub in the citrus family Rutaceae. It is native to the deserts of the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. Except immediately after heavy rains, its straight stems usually lack leaves, giving it a broom-like appearance. The Latin specific epithet ''montana'' refers to mountains or coming from mountains. Description It is a shrub with many straight, broom-like, yellow-green, 30 to 60 centimetres long. Except after heavy rains, it is usually found without leaves. Leaves and stems Stems are speckled with resin glands. Leaves are small and occur only after rains, then fall off (drought deciduous). Inflorescence and fruit Flowers occur at intervals along the stem. Each has a greenish base of blunt sepals. The corolla is oval with rounded ends. The petals royal purple in color. Like most other parts of the plant, petals are studded with visible resin glands. The tips of the petals curve outward, reveali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Communities Of California
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have lost the ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Of The Mojave Desert
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena. The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French ''nature'' and is derived from the Latin word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant "birth". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word ''physis'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
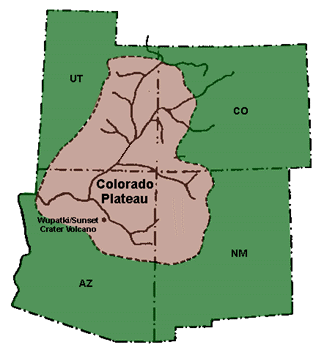
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries. The Colorado Plateau is largely made up of high desert, with scattered areas of forests. In the south-west corner of the Colorado Plateau lies the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Much of the Plateau's landscape is related to the Grand Canyon in both appearance and geologic history. The nickname "Red Rock Country" suggests the brightly colored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krascheninnikovia Lanata
''Krascheninnikovia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the subfamily Chenopodioideae of the family Amaranthaceae known as winterfat, so-called because it is a nutritious livestock forage. They are known from Eurasia and western North America. These are hairy perennials or small shrubs which may be monoecious or dioecious. They bear spike inflorescences of woolly flowers. Description The species of ''Krascheninnikovia'' are erect subshrubs or shrubs. The plants are densely covered with dendroid stellate hairs and additionally with simple, unbranched hairs. The alternate leaves stand solitary or grouped in fascicles, and can be petiolate or nearly sessile. The flat, non-fleshy leaf blades are linear to narrowly lanceolate to ovate, with entire margins, and truncate, cuneate, rounded, or subcordate base. The flowers are unisexual, the plants can be monoecious or dioecious. Male flowers form an interrupted spike or subcapitate inflorescence of glomeruled, ebracteate flowers. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambrosia Salsola
''Ambrosia salsola'', commonly called cheesebush, winged ragweed, burrobush, white burrobrush, and desert pearl, is a species of perennial shrub in the family Asteraceae native to deserts of the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico.Mojave Desert Wildflowers, Pam MacKay, 2nd Ed. 2013, p. 263 This species, notable for its foul smell, easily hybridizes with the white bur-sage (''Ambrosia dumosa''). Range and habitat It is common on sandy desert flats, desert dry washes, and is weedy in disturbed sites in creosote bush scrub, shadscale scrub, Joshua tree woodland, and Pinyon juniper woodland, ranging from Inyo County, California, to northwestern Mexico. It grows in sandy and gravelly soil, and sometimes on lava formations at elevations of . It is native to the southwestern United States (Arizona, California, Nevada, Utah) and northwestern Mexico (Sonora, Baja California, Baja California Sur), where it is a common plant of the local deserts, where it thrives on sandy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetradymia
''Tetradymia'' is a genus of North American shrubs in the groundsel tribe within the sunflower family.Candolle, Augustin Pyramus de, 1838. Prodromus Systematis Naturalis Regni Vegetabilis 6: 440 in Latin Horsebrush is a common name for plants in this genus. ; SpeciesFlann, C (ed) 2009+ Global Compositae Checklist Strother, J. L. 1974. Taxonomy of ''Tetradymia'' (Compositae: Senecioneae). Brittonia 26: 177–202. ; formerly included see '' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deserts
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the land surface of the Earth is arid or semi-arid. This includes much of the polar regions, where little precipitation occurs, and which are sometimes called polar deserts or "cold deserts". Deserts can be classified by the amount of precipitation that falls, by the temperature that prevails, by the causes of desertification or by their geographical location. Deserts are formed by weathering processes as large variations in temperature between day and night put strains on the rocks, which consequently break in pieces. Although rain seldom occurs in deserts, there are occasional downpours that can result in flash floods. Rain falling on hot rocks can cause them to shatter, and the resulting fragments and rubble strewn over the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephedra Viridis
''Ephedra viridis'', known by the common names green Mormon tea, green ephedra, and Indian tea, is a species of ''Ephedra''. It is indigenous to the Western United States The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the Wes ..., where it is a member of varied scrub, woodland, desert, and open habitats. It grows at elevations. Description The ''Ephedra viridis'' shrub is woody below, topped with many dense clusters of erect bright green twigs. They may yellow somewhat with age. Nodes along the twigs are marked by the tiny pairs of vestigial leaves, which start out reddish but soon dry to brown or black. Since the leaves are no longer functional, the stems are green and photosynthesis, photosynthetic. Male plants produce pollen cones at the nodes, each under a centimeter long with protr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephedra Nevadensis
''Ephedra nevadensis'', commonly known as Nevada ephedra, gray ephedra, Mormon tea and Nevada jointfir, is a species of gymnosperm native to dry areas of western North America. Its range extends west to California and Oregon, east to Texas, and south to Baja California, including areas of the Great Basin, Colorado plateau and desert Southwest. It is found in rocky and sandy soils, generally in areas without trees. Reproduction Nevada ephedra is wind-pollinated, with male plants growing in dryer areas and female plants growing in wetter ones, an arrangement which is believed to increase the production of seed. Cones mature and pollination occurs in March to June, with seeds ripening in May to August, although seeds are not produced every year. In the wild, seeds are often spread by rodents, and for cultivation, seeds can readily be collected and sown. The plant can also be propagated via transplants and cuttings. More than other North American ''Ephedra'' species, it is a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)