|
Black Hours Of Galeazzo Maria Sforza
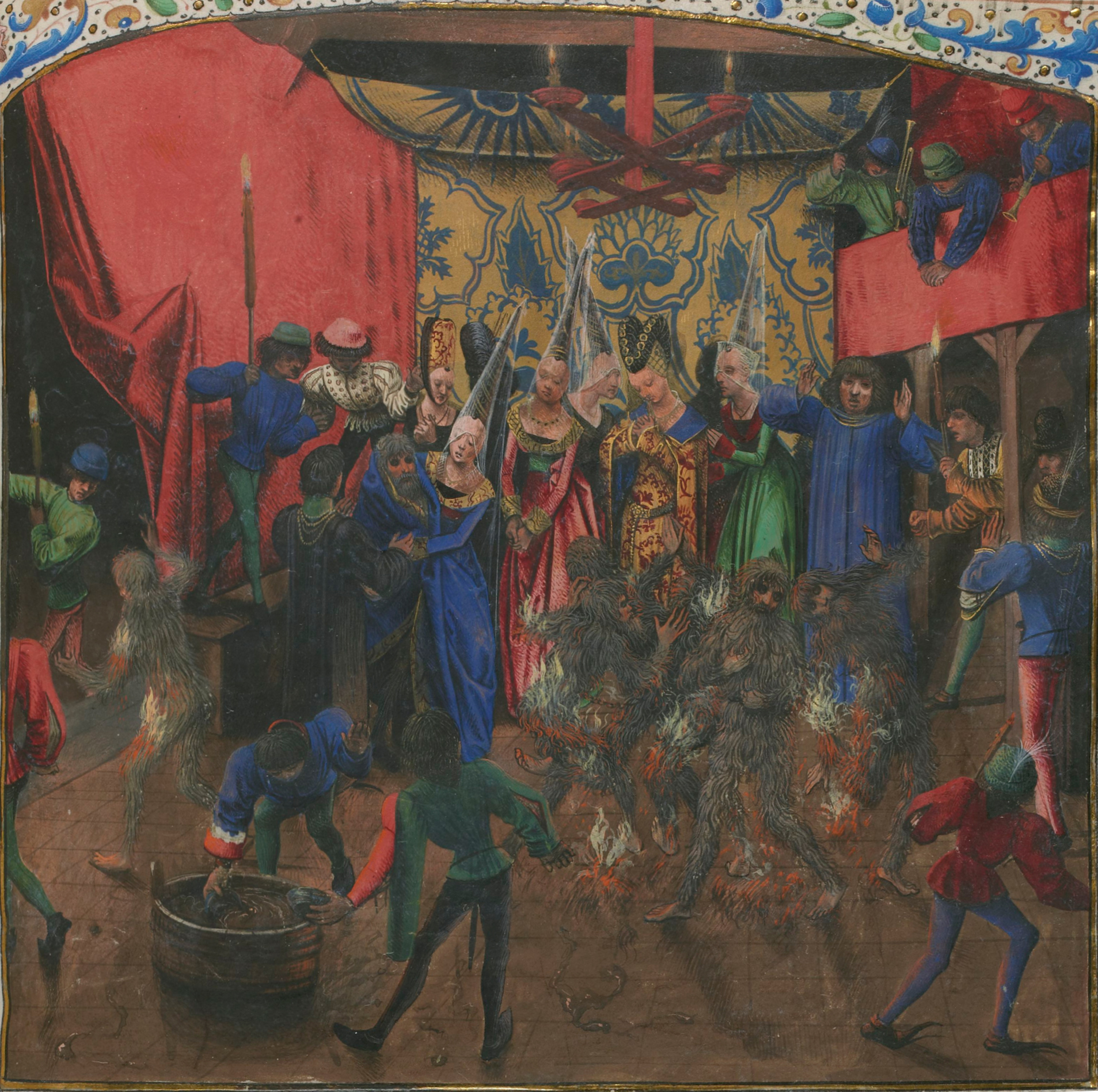
__NOTOC__ The Black Hours of Galeazzo Maria Sforza, M 1856 is an illuminated book of hours, now in the Austrian National Library in Vienna (Codex Vindobon. 1856). The book used to be the property of Galeazzo Maria Sforza, the fifth Duke of Milan. It was produced in Bruges, Flanders, probably between 1466 and 1477. Its name derives from its black borders and dark colour scheme, also found in the New York Black Hours, Morgan MS 493, and of a type favoured by the Burgundian court. It is one of about seven surviving black books of hours, all luxury books from the circle of the Burgundian court around this time. It is identified by some with the Black Hours of Charles the Bold that is mentioned in contemporary records, but others disagree. It measures , has 154 folios and includes 15 full-page miniatures, 24 small-format miniatures, as well as 71 figurative or ornamental initials, and borders with medallions. The illuminations of the book are entirely attributed to the anonymous M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sforza Black Hours - ÖNB Cod1856 F32verso-33recto
The House of Sforza () was a ruling family of Renaissance Italy, based in Milan. They acquired the Duchy of Milan following the extinction of the Visconti family in the mid-15th century, Sforza rule ending in Milan with the death of the last member of the family's main branch in 1535. History The first son of Muzio Attendolo Sforza, Francesco I Sforza, married Bianca Maria (1425–1468) in 1441. She was the daughter and only heir of the last Duke of Milan, (Filippo Maria Visconti). He thus acquired the title of Duke of Milan (1450–1466), ruled Milan for 16 years, and made the Sforzas the heirs of the house of Visconti. The family also held the seigniory of Pesaro, starting with Muzio Attendolo's second son, Alessandro (1409–1473). The Sforza held Pesaro until 1512, after the death of Costanzo II Sforza. Muzio's third son, Bosio (1411–1476), founded the branch of Santa Fiora, who held the title of count of Cotignola; the Sforza ruled the small county of Santa Fiora in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Books Of Hours
__NOTOC__ Black books of hours are a type of luxury Flemish illuminated manuscript books of hours using pages of vellum that were soaked with black dye or ink before they were lettered or illustrated, for an unusual and dramatic effect. The text is usually written with gold or silver ink. There are seven surviving examples, all dating from about 1455–1480. The parchment was soaked in an iron-copper solution and as a result could only be inscribed with gold or silver lettering. The process was both expensive and corrosive to parchment, so surviving examples are few and generally in poor condition. These manuscripts were produced in the mid- to late-15th century for high-ranking members of the court of Philip the Good and Charles the Bold. Given their novel visual appeal, they were probably prized more highly than more conventional illuminated books. The Burgundian court had a preference for dark, somber colourisation, and the extant works in this style were mostly commissione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15th-century Illuminated Manuscripts
The 15th century was the century which spans the Julian dates from 1 January 1401 ( MCDI) to 31 December 1500 ( MD). In Europe, the 15th century includes parts of the Late Middle Ages, the Early Renaissance, and the early modern period. Many technological, social and cultural developments of the 15th century can in retrospect be seen as heralding the "European miracle" of the following centuries. The architectural perspective, and the modern fields which are known today as banking and accounting were founded in Italy. The Hundred Years' War ended with a decisive French victory over the English in the Battle of Castillon. Financial troubles in England following the conflict resulted in the Wars of the Roses, a series of dynastic wars for the throne of England. The conflicts ended with the defeat of Richard III by Henry VII at the Battle of Bosworth Field, establishing the Tudor dynasty in the later part of the century. Constantinople, known as the capital of the world an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliothèque Nationale De France
The Bibliothèque nationale de France (, 'National Library of France'; BnF) is the national library of France, located in Paris on two main sites known respectively as ''Richelieu'' and ''François-Mitterrand''. It is the national repository of all that is published in France. Some of its extensive collections, including books and manuscripts but also precious objects and artworks, are on display at the BnF Museum (formerly known as the ) on the Richelieu site. The National Library of France is a public establishment under the supervision of the Ministry of Culture. Its mission is to constitute collections, especially the copies of works published in France that must, by law, be deposited there, conserve them, and make them available to the public. It produces a reference catalogue, cooperates with other national and international establishments, and participates in research programs. History The National Library of France traces its origin to the royal library founded at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the ''Venus de Milo''. A central landmark of the city, it is located on the Right Bank of the Seine in the city's 1st arrondissement (district or ward). At any given point in time, approximately 38,000 objects from prehistory to the 21st century are being exhibited over an area of 72,735 square meters (782,910 square feet). Attendance in 2021 was 2.8 million due to the COVID-19 pandemic, up five percent from 2020, but far below pre-COVID attendance. Nonetheless, the Louvre still topped the list of most-visited art museums in the world in 2021."The Art Newspaper", 30 March 2021. The museum is housed in the Louvre Palace, originally built in the late 12th to 13th century under Philip II. Remnants of the Medieval Louvre fortress are visible in the basement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
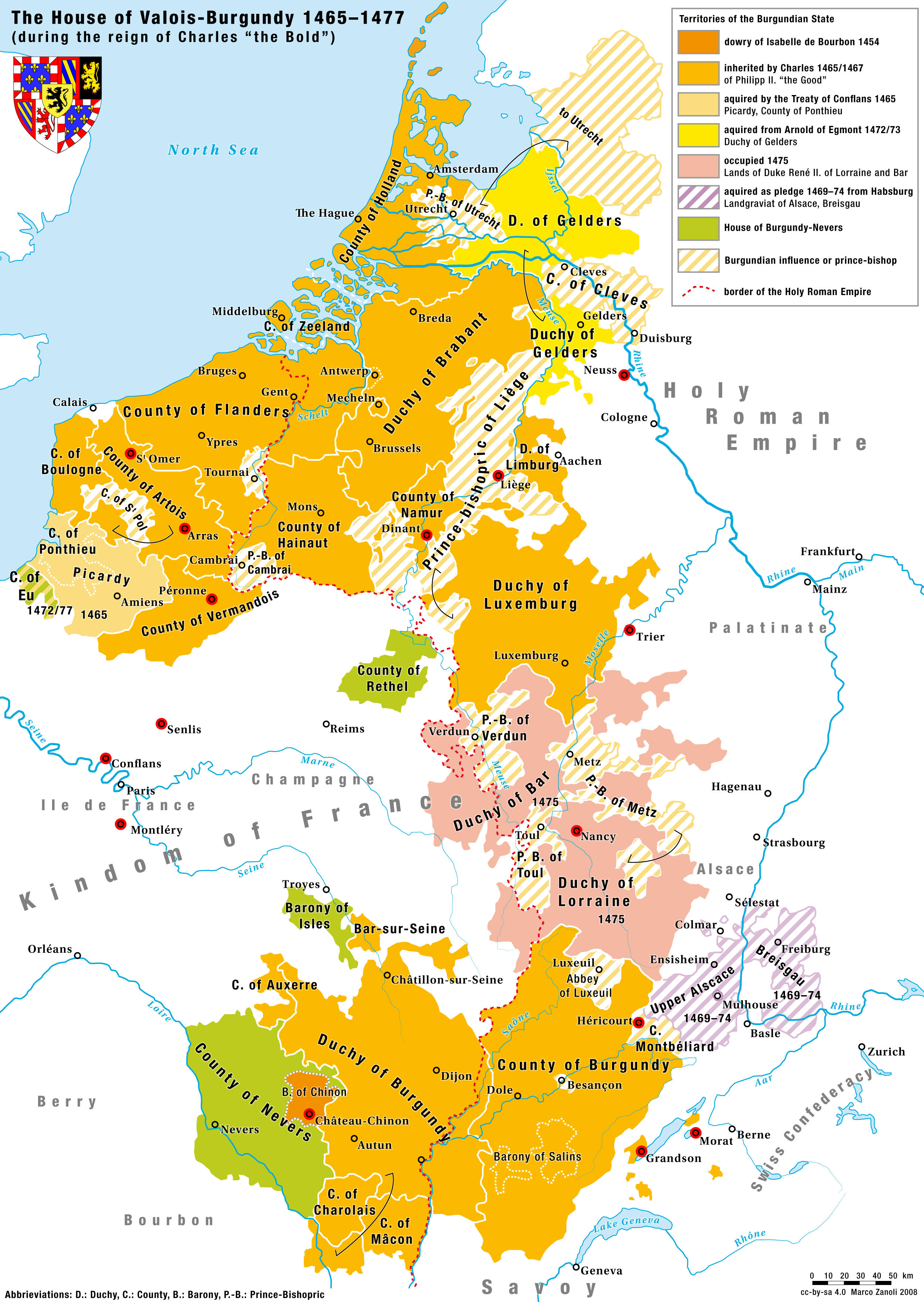
Charles The Bold
Charles I (Charles Martin; german: Karl Martin; nl, Karel Maarten; 10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), nicknamed the Bold (German: ''der Kühne''; Dutch: ''de Stoute''; french: le Téméraire), was Duke of Burgundy from 1467 to 1477. Charles's main objective was to be crowned king by turning the growing Burgundian State into a territorially continuous kingdom. He declared himself and his lands independent, bought Upper Alsace and conquered Zutphen, Guelders and Lorraine, uniting at last Burgundian northern and southern possessions. This caused the enmity of several European powers and triggered the Burgundian Wars. Charles's early death at the Battle of Nancy at the hands of Swiss mercenaries fighting for René II, Duke of Lorraine, was of great consequence in European history. The Burgundian domains, long wedged between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg Empire, were divided, but the precise disposition of the vast and disparate territorial possessions involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine De Schryver
Antoine Philippe De Schryver (1924–2005) was a Belgian art historian and professor at the University of Ghent, where he lectured on History of Book Illumination. He was specialized in the field of illuminated manuscripts in the Southern Netherlands, 15th century painting, and artists at the Burgundian Court. Education and career Antoine De Schryver was born in Lochristi on 27 March 1924. He studied art history and archeology at the University of Ghent and obtained his degree in 1950. From 1951, he worked as a scientific assistant at the Royal Institute for Cultural Heritage. Between 1953 and 1955, he was a candidate for the National Fund for Scientific Research, obtaining his doctoral degree in art history and archeology in 1957. In addition, he was appointed as curator of the Museum of Archeology in Ghent in that same year. He would carry out this function until 1971. Throughout the 1950s, De Schryver obtained a number of travel scholarships, amongst which The National Trust Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackletter
Blackletter (sometimes black letter), also known as Gothic script, Gothic minuscule, or Textura, was a script used throughout Western Europe from approximately 1150 until the 17th century. It continued to be commonly used for the Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish languages until the 1870s, and for the German language until the 1940s, when Hitler's distaste for the supposedly "Jewish-influenced" script saw it officially discontinued in 1941. Fraktur is a notable script of this type, and sometimes the entire group of blackletter faces is incorrectly referred to as Fraktur. Blackletter is sometimes referred to as Old English, but it is not to be confused with the Old English language, which predates blackletter by many centuries and was written in the insular script or in Futhorc. Along with Italic type and Roman type, blackletter served as one of the major typefaces in the history of Western typography. Origins Carolingian minuscule was the direct ancestor of blackletter. Blacklett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master Of Anthony Of Burgundy
The Master of Anthony of Burgundy was a Flanders, Flemish illuminated manuscript, miniature painter active in Bruges between about 1460 and 1490, apparently running a large workshop, and producing some of the most sophisticated work of the final flowering of Flemish Illuminated manuscript, illumination. He was first identified by Winkler in 1921; his name is derived from one of his most elevated patrons, Antoine, bastard of Burgundy, Anthony of Burgundy, Philip the Good's illegitimate son, though he also worked for the Duke of Burgundy, Dukes and other bibliophiles in Burgundian court circles, who had already been allocated "Masters" by art historians. His contributions to the heavily illustrated Froissart of Louis of Gruuthuse (BnF Fr 2643-6) from the early 1470s, on which several of the leading illuminators of the day worked, show him excelling some more famous names, like Loiset Lyédet. The young Master of the Dresden Prayer Book worked as his assistant on this book, suggesting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Hours
The book of hours is a Christian devotional book used to pray the canonical hours. The use of a book of hours was especially popular in the Middle Ages and as a result, they are the most common type of surviving medieval illuminated manuscript. Like every manuscript, each manuscript book of hours is unique in one way or another, but most contain a similar collection of texts, prayers and psalms, often with appropriate decorations, for Christian devotion. Illumination or decoration is minimal in many examples, often restricted to decorated capital letters at the start of psalms and other prayers, but books made for wealthy patrons may be extremely lavish, with full-page miniatures. These illustrations would combine picturesque scenes of country life with sacred images. Books of hours were usually written in Latin (the Latin name for them is ''horae''), although there are many entirely or partially written in vernacular European languages, especially Dutch. The closely related p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Books Of Hours
__NOTOC__ Black books of hours are a type of luxury Flemish illuminated manuscript books of hours using pages of vellum that were soaked with black dye or ink before they were lettered or illustrated, for an unusual and dramatic effect. The text is usually written with gold or silver ink. There are seven surviving examples, all dating from about 1455–1480. The parchment was soaked in an iron-copper solution and as a result could only be inscribed with gold or silver lettering. The process was both expensive and corrosive to parchment, so surviving examples are few and generally in poor condition. These manuscripts were produced in the mid- to late-15th century for high-ranking members of the court of Philip the Good and Charles the Bold. Given their novel visual appeal, they were probably prized more highly than more conventional illuminated books. The Burgundian court had a preference for dark, somber colourisation, and the extant works in this style were mostly commissione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |