|
Black Crown
The Black Crown () is an important symbol of the Karmapa, the Lama who heads the Karma Kagyu school of Tibetan Buddhism. The crown signifies his power to benefit all sentient beings. Similar crowns in red are worn by the Shamarpa and the Tai Situpa, while Goshir Gyaltsab wears an orange crown. These crowns were bestowed by the Karmapa. Legend tells that in a previous eon, in a former life as an accomplished yogi, the Karmapa attained the eighth level or '' bhumi'' of the bodhisattvas. At this time, 100,000 dakinis (female buddhas) manifested their hair as a crown, and offered it to the Karmapa as a symbol of his accomplishment. Dusum Khyenpa, the 1st Karmapa, was regarded as an emanation of that yogi and his appearance was predicted by the historical Buddha Shakyamuni in the Samadhiraja Sutra: A bodhisattva with the lion's roar will appear. He will use the power he achieved in deep meditation to benefit countless beings. By seeing, hearing, touching or thinking o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Of China
''Huangdi'' (), translated into English as Emperor, was the superlative title held by monarchs of China who ruled various imperial regimes in Chinese history. In traditional Chinese political theory, the emperor was considered the Son of Heaven and the autocrat of all under Heaven. Under the Han dynasty, Confucianism replaced Legalism as the official political theory and succession in most cases theoretically followed agnatic primogeniture. The lineage of emperors descended from a paternal family line constituted a dynasty. The absolute authority of the emperor came with a variety of governing duties and moral obligations; failure to uphold these was thought to remove the dynasty's Mandate of Heaven and to justify its overthrow. In practice, emperors sometimes avoided the strict rules of succession and dynasties' ostensible "failures" were detailed in official histories written by their successful replacements. The power of the emperor was also limited by the imperial b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lumbini, in what is now Nepal, to royal parents of the Shakya clan, but renounced his home life to live as a wandering ascetic ( sa, śramaṇa). After leading a life of begging, asceticism, and meditation, he attained enlightenment at Bodh Gaya in what is now India. The Buddha thereafter wandered through the lower Indo-Gangetic Plain, teaching and building a monastic order. He taught a Middle Way between sensual indulgence and severe asceticism, leading to Nirvana, that is, freedom from ignorance, craving, rebirth, and suffering. His teachings are summarized in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind that includes meditation and instruction in Buddhist ethics such as right effort, mindfulness, and '' jhana''. He die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Om Mani Padme Hum
' ( sa, ॐ मणि पद्मे हूँ, ) is the six-syllabled Sanskrit mantra particularly associated with the four-armed Shadakshari form of Avalokiteshvara, the bodhisattva of compassion. It first appeared in the Mahayana ''Kāraṇḍavyūhasūtra'' where it is also referred to as the ''sadaksara'' (six syllabled) and the ''paramahrdaya'', or “innermost heart” of Avalokiteshvara. In this text the mantra is seen as the condensed form of all Buddhist teachings. The precise meaning and significance of the words remains much discussed by Buddhist scholars. The literal meaning in English has been expressed as "praise to the jewel in the lotus", or as a declarative aspiration possibly meaning "I in the jewel-lotus". ''Padma'' is the Sanskrit for the Indian lotus (''Nelumbo nucifera''), and ''mani'' for "jewel", as in a type of spiritual "jewel" widely referred to in Buddhism. The first word, '' aum/om'', is a sacred syllable in various Indian religions, and ''hum'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantra
A mantra ( Pali: ''manta'') or mantram (मन्त्रम्) is a sacred utterance, a numinous sound, a syllable, word or phonemes, or group of words in Sanskrit, Pali and other languages believed by practitioners to have religious, magical or spiritual powers. Feuerstein, Georg (2003), ''The Deeper Dimension of Yoga''. Shambala Publications, Boston, MA Some mantras have a syntactic structure and literal meaning, while others do not. The earliest mantras were composed in Vedic Sanskrit in India. At its simplest, the word ॐ (Aum, Om) serves as a mantra, it is believed to be the first sound which was originated on earth. Aum sound when produced creates a reverberation in the body which helps the body and mind to be calm. In more sophisticated forms, mantras are melodic phrases with spiritual interpretations such as a human longing for truth, reality, light, immortality, peace, love, knowledge, and action. Some mantras without literal meaning are musically uplifting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merit (Buddhism)
Merit ( sa, puṇya, italic=yes, pi, puñña, italic=yes) is a concept considered fundamental to Buddhist ethics. It is a beneficial and protective force which accumulates as a result of good deeds, acts, or thoughts. Merit-making is important to Buddhist practice: merit brings good and agreeable results, determines the quality of the next life and contributes to a person's growth towards enlightenment. In addition, merit is also shared with a deceased loved one, in order to help the deceased in their new existence. Despite modernization, merit-making remains essential in traditional Buddhist countries and has had a significant impact on the rural economies in these countries. Merit is connected with the notions of purity and goodness. Before Buddhism, merit was used with regard to ancestor worship, but in Buddhism it gained a more general ethical meaning. Merit is a force that results from good deeds done; it is capable of attracting good circumstances in a person's life, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandala
A mandala ( sa, मण्डल, maṇḍala, circle, ) is a geometric configuration of symbols. In various spiritual traditions, mandalas may be employed for focusing attention of practitioners and adepts, as a spiritual guidance tool, for establishing a sacred space and as an aid to meditation and trance induction. In the Eastern religions of Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Shinto it is used as a map representing deities, or especially in the case of Shinto, paradises, kami or actual shrines. A mandala generally represents the spiritual journey, starting from outside to the inner core, through layers. Hinduism In Hinduism, a basic mandala, also called a '' yantra'', takes the form of a square with four gates containing a circle with a center point. Each gate is in the general shape of a T. Mandalas often have radial balance. A '' yantra'' is similar to a mandala, usually smaller and using a more limited colour palette. It may be a two- or three-dimensional geometric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rangjung Rigpe Dorje
The sixteenth Gyalwa Karmapa, Rangjung Rigpe Dorje (; August 14, 1924 – November 5, 1981) was the spiritual leader of the Karma Kagyu lineage of Tibetan Buddhism. Followers believed him to be part of the oldest line of reincarnate lamas in Vajrayana Buddhism, known as the Karmapas, whose coming was predicted by the Buddha in the Samadhiraja Sutra. The 16th Karmapa was considered to be a "living Buddha" and was deeply involved in the transmission of the Vajrayana Buddhism to Europe and North America following the Chinese invasion of Tibet. He had many monikers, including “King of the Yogis”, and is the subject of numerous books and films. Biography Birth The 16th Karmapa was born in Denkhok in the Dergé province in Eastern Tibet, Kham, near the Dri Chu or Yangtze River. The previous Karmapa Khakhyab Dorje (1871-1922) left a letter setting forth the circumstances of his next incarnation. The Karmapa's attendant, Jampal Tsultrim, possessed the letter of prediction, which m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
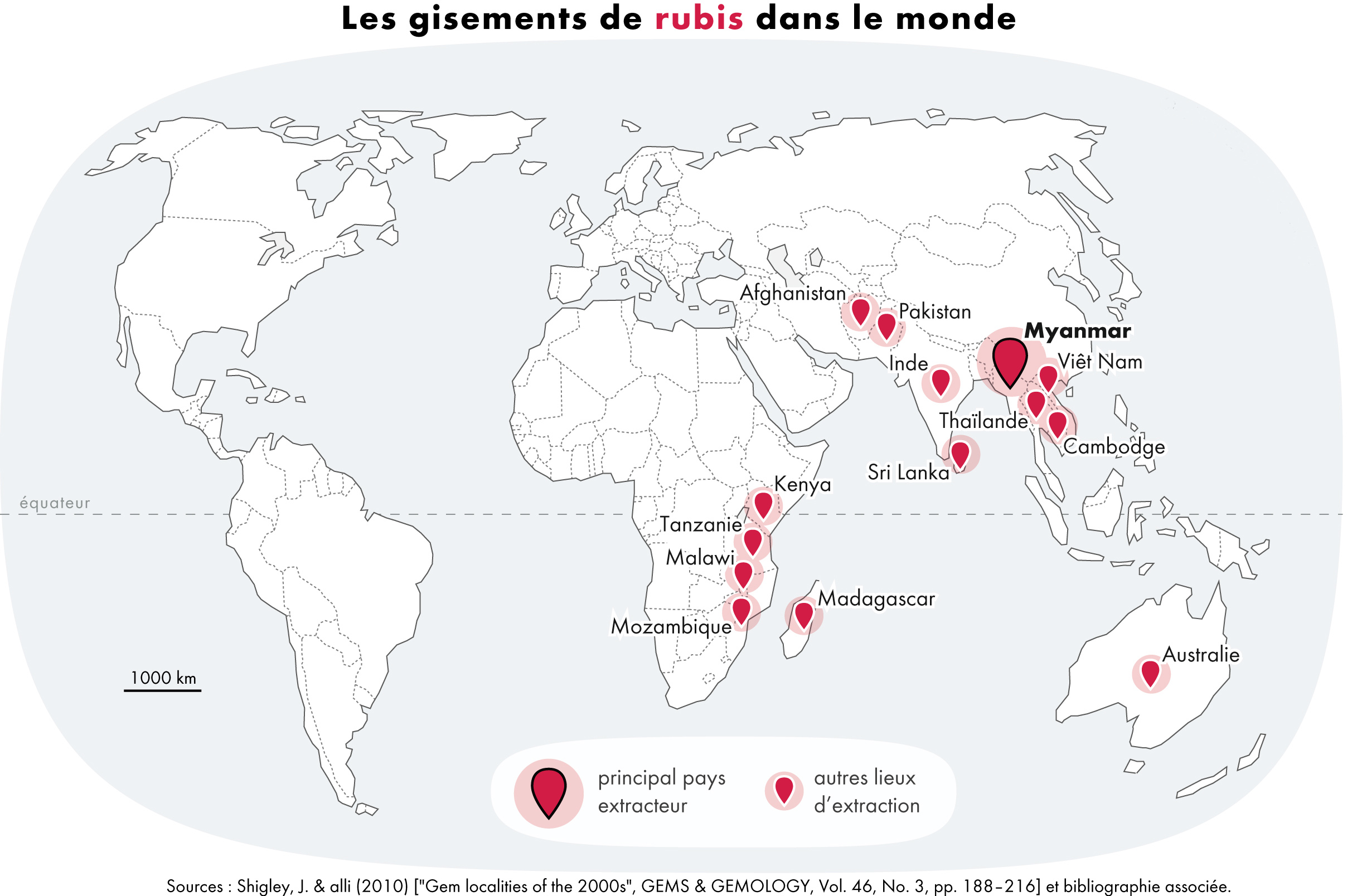
Ruby
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum (aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires. Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the element chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat (mass), carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a large premium over other rubies of similar quality. After color follows clarity: similar to diamonds, a clear stone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vajra
The Vajra () is a legendary and ritual weapon, symbolising the properties of a diamond (indestructibility) and a thunderbolt (irresistible force). The vajra is a type of club with a ribbed spherical head. The ribs may meet in a ball-shaped top, or they may be separate and end in sharp points with which to stab. The vajra is the weapon of Indra, the Vedic king of the devas and heaven. It is used symbolically by the dharmic traditions of Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, often to represent firmness of spirit and spiritual power. According to Hinduism, the vajra is considered one of the most powerful weapons in the universe. The use of the vajra as a symbolic and ritual tool spread from Hinduism to other religions in India and other parts of Asia. Etymology According to Asko Parpola, the Sanskrit () and Avestan both refer to a weapon of the Godhead, and are possibly from the Proto-Indo-European root ''*weg'-'' which means "to be(come) powerful". It is related to Proto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vajradhara
Vajradhara (Sanskrit: वज्रधर. (Also, the name of Indra, because 'Vajra' means diamond, as well as the thunderbolt, anything hard more generally) Tibetan: རྡོ་རྗེ་འཆང། rdo rje 'chang (Dorje Chang); zh, t=金剛總持, p=Jīngāng zǒng chí; Javanese: Kabajradharan; Japanese: 持金剛仏; English: Diamond-holder; Vietnamese: Kim Cang Tổng Trì) is the ultimate primordial Buddha, or Adi-Buddha, according to the Sakya, Gelug and Kagyu schools of Tibetan Buddhism. In the evolution of Indian Buddhism, Buddha Vajradhara gradually displaced Samantabhadra, who is the 'Primordial Buddha' in the Nyingma, or 'Ancient School.' However, the two are metaphysically equivalent. Achieving the 'state of Vajradhara' is synonymous with complete realisation. According to the Kagyu lineage, Buddhā Vajradhara is the primordial Buddha, the Dharmakaya Buddha. He is depicted as dark blue in color, expressing the quintessence of buddhahood itself and represe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



_at_Rumtek_Monastery%2C_Sikkim_in_1971.jpg)