|
Bitschwiller-lès-Thann
Bitschwiller-lès-Thann (, literally ''Bitschwiller near Thann''; ) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. The town lies in the Thur River Valley near the Vosges mountains. History The town is first mentioned about 1250. Before the early 1900s the town was known only as Bitschwiller. It was destroyed by Norman mercenaries during the Hundred Years' War. By 1624 about 100 people lived in this village. Immigrants from Germany and Switzerland arrived during the 1650s. The entire Alsace region was fought over many times between the French and Germans. Germany ruled this area (including Bitschwiller) in 1874-1918 and again 1940-1945. This was and continues to be an industrialised area. Iron mining began in the 1470s but only for a short while. Mining returned in 1735 and a metalworks was built. A foundry opened in 1739. A weaving factory opened in 1826. As the industrialization continued, steam engines and locomotives were buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of The Haut-Rhin Department
The following is a list of the 366 communes of the French department of Haut-Rhin. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):BANATIC Périmètre des EPCI à fiscalité propre. Accessed 3 July 2020. *CA *CA *CA * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, French throne between the English House of Plantagenet and the French royal House of Valois. Over time, the war grew into a broader power struggle involving factions from across Western Europe, fuelled by emerging nationalism on both sides. The Hundred Years' War was one of the most significant conflicts of the Middle Ages. For 116 years, interrupted by several Ceasefire, truces, five generations of kings from two rival Dynasty, dynasties fought for the throne of the dominant kingdom in Western Europe. The war's effect on European history was lasting. Both sides produced innovations in military technology and tactics, including professional standing armies and artillery, that permanently changed warfare in Europe; chivalry, which had reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters (for their latitude), with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 45 and 63 latitude, most notably in northwestern Europe, northwestern America, as well as New Zealand. Precipitation Locations with oceanic climates tend to feature frequent cloudy conditions with precipitation, low hanging clouds, and frequent fronts and storms. Thunderstorms are normally few, since strong daytime heating and hot and cold air masses meet infrequently in the region. In most areas with an oceanic climate, precipitation comes in the form of rain for the majority of the year. However, some areas with this climate see some snowfall annually during winter. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transilien Paris – Saint-Lazare
Transilien Paris-Saint-Lazare is one of the sectors in the Paris Transilien suburban rail network. The trains on this sector depart from Gare Saint-Lazare in central Paris and serve the north and north-west of Île-de-France region with Transilien lines "J" and "L". Transilien services from Paris – Saint-Lazare are part of the SNCF Saint-Lazare rail network. The two lines are the busiest lines in the Transilien system, excluding lines signed as part of the RER. Line J The trains on Line J travel between Gare Saint-Lazare in Paris and the north-west of Île-de-France region, with termini in Ermont–Eaubonne, Gisors and Vernon. The line has a total of 2600,000 passengers per weekday. List of Line J stations Gisors Branch *Paris-Saint-Lazare * Asnières-sur-Seine station *Bois-Colombes station * Colombes station *Le Stade station *Argenteuil station * Val d'Argenteuil station *Cormeilles-en-Parisis station *La Frette–Montigny station *Herblay station *Conflans-Sainte-Hono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
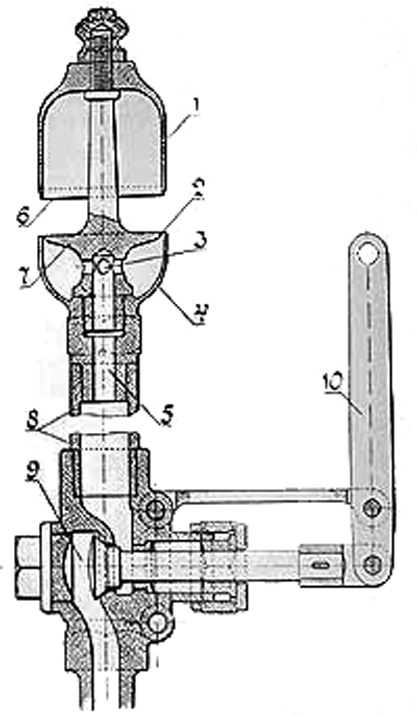
Steam Whistle
A steam whistle is a device used to produce sound in the form of a whistle using live steam, which creates, projects, and amplifies its sound by acting as a vibrating system (compare to train horn). Operation The whistle consists of the following main parts, as seen on the drawing: the whistle bell (1), the steam orifice or aperture (2), and the valve (9). When the lever (10) is actuated (usually via a pull cord), the valve opens and lets the steam escape through the orifice. The steam will alternately compress and rarefy in the bell, creating the sound. The pitch, or tone, is dependent on the length of the bell; and also how far the operator has opened the valve. Some locomotive engineers invented their own distinctive style of whistling. Uses of steam whistles Steam whistles were often used in factories, and similar places to signal the start or end of a shift, etc. steam-powered railway locomotives, traction engines, and steam ships have traditionally been fitted wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foundry
A foundry is a factory that produces metal castings. Metals are cast into shapes by melting them into a liquid, pouring the metal into a mold, and removing the mold material after the metal has solidified as it cools. The most common metals processed are aluminum and cast iron. However, other metals, such as bronze, brass, steel, magnesium, and zinc, are also used to produce castings in foundries. In this process, parts of desired shapes and sizes can be formed. Foundries are one of the largest contributors to the manufacturing recycling movement, melting and recasting millions of tons of scrap metal every year to create new durable goods. Moreover, many foundries use sand in their molding process. These foundries often use, recondition, and reuse sand, which is another form of recycling. Process In metalworking, casting involves pouring liquid metal into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowing it to cool and solidify. The solidified pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zürich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2020 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federalism, Federal assembly-independent Directorial system, directorial republic with elements of a direct democracy , leader_title1 = Federal Council (Switzerland), Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Walter Thurnherr , legislature = Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lès
The word ''lès'' (, and with liaison) is an archaic French preposition meaning "near", "next to". Today it occurs only in place names to distinguish places of the same name. The word ''lès'' has two variants: ''lez'' and ''les''. The latter should not be confused with the plural definite article ''les'' (e.g. ''les-Bains'', "the Baths"). Etymology The word ''lès'' and its variants derive from late Latin ''latus'', "side". Examples Lès * Villeneuve-lès-Avignon, near Avignon * Beaumont-lès-Valence, near Valence * Saint-Rémy-lès-Chevreuse, near Chevreuse * Margny-lès-Compiègne, near Compiègne * Asnières-lès-Dijon, near Dijon * Fontaine-lès-Dijon, near Dijon * Hauteville-lès-Dijon, near Dijon * Neuilly-lès-Dijon, near Dijon * Perrigny-lès-Dijon, near Dijon * Plombières-lès-Dijon, near Dijon * Sennecey-lès-Dijon, near Dijon * Garges-lès-Gonesse, near Gonesse * Bonchamp-lès-Laval, near Laval * Fontaine-lès-Luxeuil, near Luxeuil-les-Bains * Sainte-Foy- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vosges Mountains
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a single geomorphological unit and low mountain range of around in area. It runs in a north-northeast direction from the Burgundian Gate (the Belfort–Ronchamp– Lure line) to the Börrstadt Basin (the Winnweiler– Börrstadt–Göllheim line), and forms the western boundary of the Upper Rhine Plain. The Grand Ballon is the highest peak at , followed by the Storkenkopf (), and the Hohneck ().IGN maps available oGéoportail/ref> Geography Geographically, the Vosges Mountains are wholly in France, far above the Col de Saverne separating them from the Palatinate Forest in Germany. The latter area logically continues the same Vosges geologic structure but traditionally receives this different name for historical and political reasons. From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |