|
Birley Collieries
The Birley Collieries were a group of coal mines set in the Shire Brook Valley in south-east Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England. They were connected to the railway system by a branch line from the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway at Woodhouse East Junction, about 800 yards east of Woodhouse station. From 1877 to his death in 1926, William Dunn Gainsford was owner of the Birley Collieries, with his cousin Alfred John Gainsford serving as Managing Director. The collieries The Birley collieries were owned by the Sheffield Coal Company who also owned nearby Brookhouse and North Staveley collieries. These collieries stood either side of the M.S.& L.R. line less than a mile to the east of Woodhouse East Junction. In 1866 the Sheffield Coal Company, which had been founded in 1805, signed an agreement with the Earl Manvers to work below his lands in the Frecheville, Woodhouse and Hackenthorpe area, just outside the then Sheffield boundary. Over the following ten yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Site Of Birley East Colliery (geograph 1924697)
Site most often refers to: * Archaeological site * Campsite, a place used for overnight stay in an outdoor area * Construction site * Location, a point or an area on the Earth's surface or elsewhere * Website, a set of related web pages, typically with a common domain name It may also refer to: * Site, a National Register of Historic Places property types, National Register of Historic Places property type * SITE (originally known as ''Sculpture in the Environment''), an American architecture and design firm * Site (mathematics), a category C together with a Grothendieck topology on C * ''The Site'', a 1990s TV series that aired on MSNBC * SITE Intelligence Group, a for-profit organization tracking jihadist and white supremacist organizations * SITE Institute, a terrorism-tracking organization, precursor to the SITE Intelligence Group * Sindh Industrial and Trading Estate, a company in Sindh, Pakistan * SITE Centers, American commercial real estate company * SITE Town, a densely p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
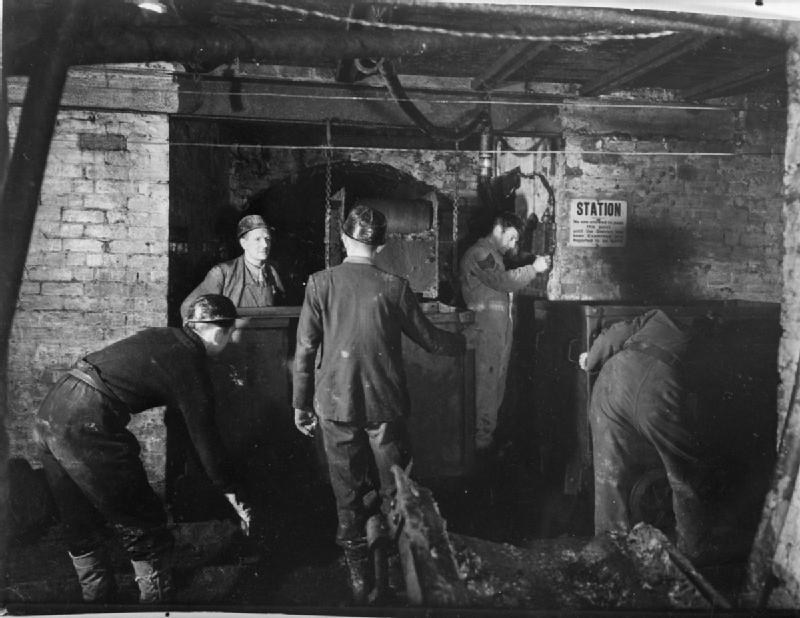
Bevin Boy
Bevin Boys were young British men Conscription in the United Kingdom, conscripted to work in coal mines between December 1943 and March 1948, to increase the rate of coal production, which had declined through the early years of World War II. The programme was named after Ernest Bevin, the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party politician who was Minister of Labour and National Service in the wartime coalition government. Chosen by lot as ten per cent of all male conscripts aged 18–25, plus some volunteering as an alternative to military conscription, nearly 48,000 Bevin Boys performed vital and dangerous civil conscription service in coal mines. Although the last ballot took place in May 1945 (shortly before Victory in Europe Day, VE Day), the final conscripts were not released from service until March 1948. Few chose to remain working in the Coal mining in the United Kingdom, mining industry after demobilisation; most left for further education or for employment in other se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In Sheffield
Transport in Sheffield, England is developed around the city's unusual topography and medieval street plan. Once an isolated town, the transport infrastructure changed dramatically in the 19th and 20th centuries. The city now has road and rail links with the rest of the country, and road, bus and trams for local transport. National and international travel Sheffield is linked into the national motorway network via the M1 and M18 motorways. The M1 skirts the north-east of the city, linking Sheffield with London to the south and Leeds to the north; the M18 branches from the M1 close to Sheffield, linking the city with Doncaster and the Humber ports. The Sheffield Parkway connects the city centre with the motorways. There are eight park and ride sites for motorists visiting the city, three of them close to M1 junctions and offering connections to local public transport. The topography of Sheffield makes it unsuitable for a large rail system. The Midland Main Line is the major r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Mines In Sheffield
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as stratum, rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is formed when dead plant matter decays into peat and is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years. Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands called coal forests that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian) and Permian times. Many significant coal deposits are younger than this and originate from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Coal is used primarily as a fuel. While coal has been known and used for thousands of years, its usage was limited until the Industrial Revolution. With the invention of the steam engine, coal consumption increased. In 2020, coal supplied about a quarter of the world's primary energ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Barclay & Sons Co
Andrew is the English form of a given name common in many countries. In the 1990s, it was among the top ten most popular names given to boys in English-speaking countries. "Andrew" is frequently shortened to "Andy" or "Drew". The word is derived from the el, Ἀνδρέας, ''Andreas'', itself related to grc, ἀνήρ/ἀνδρός ''aner/andros'', "man" (as opposed to "woman"), thus meaning "manly" and, as consequence, "brave", "strong", "courageous", and "warrior". In the King James Bible, the Greek "Ἀνδρέας" is translated as Andrew. Popularity Australia In 2000, the name Andrew was the second most popular name in Australia. In 1999, it was the 19th most common name, while in 1940, it was the 31st most common name. Andrew was the first most popular name given to boys in the Northern Territory in 2003 to 2015 and continuing. In Victoria, Andrew was the first most popular name for a boy in the 1970s. Canada Andrew was the 20th most popular name chosen for male ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thos
Jackals are medium-sized canids native to Africa and Eurasia. While the word "jackal" has historically been used for many canines of the subtribe canina, in modern use it most commonly refers to three species: the closely related black-backed jackal (''Lupulella mesomelas'') and side-striped jackal (''Lupulella adusta'') of sub-Saharan-Africa, and the golden jackal (''Canis aureus'') of south-central Europe and Asia. The African golden wolf (''Canis lupaster'') was also formerly considered as a jackal. While they do not form a monophyletic clade, all jackals are opportunistic omnivores, predators of small to medium-sized animals and proficient scavengers. Their long legs and curved canine teeth are adapted for hunting small mammals, birds, and reptiles, and their large feet and fused leg bones give them a physique well-suited for long-distance running, capable of maintaining speeds of for extended periods of time. Jackals are crepuscular, most active at dawn and dusk. Their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Coal Board
The National Coal Board (NCB) was the statutory corporation created to run the nationalised coal mining industry in the United Kingdom. Set up under the Coal Industry Nationalisation Act 1946, it took over the United Kingdom's collieries on "vesting day", 1 January 1947. In 1987, the NCB was renamed the British Coal Corporation, and its assets were subsequently privatised. Background Collieries were taken under government control during the First and Second World Wars. The Sankey Commission in 1919 gave R. H. Tawney, Sidney Webb and Sir Leo Chiozza Money the opportunity to advocate nationalisation, but it was rejected. Coal reserves were nationalised during the war in 1942 and placed under the control of the Coal Commission, but the mining industry remained in private hands. At the time, many coal companies were small, although some consolidation had taken place in the years before the war. Formation and organisation The NCB was one of a number of public corporations cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
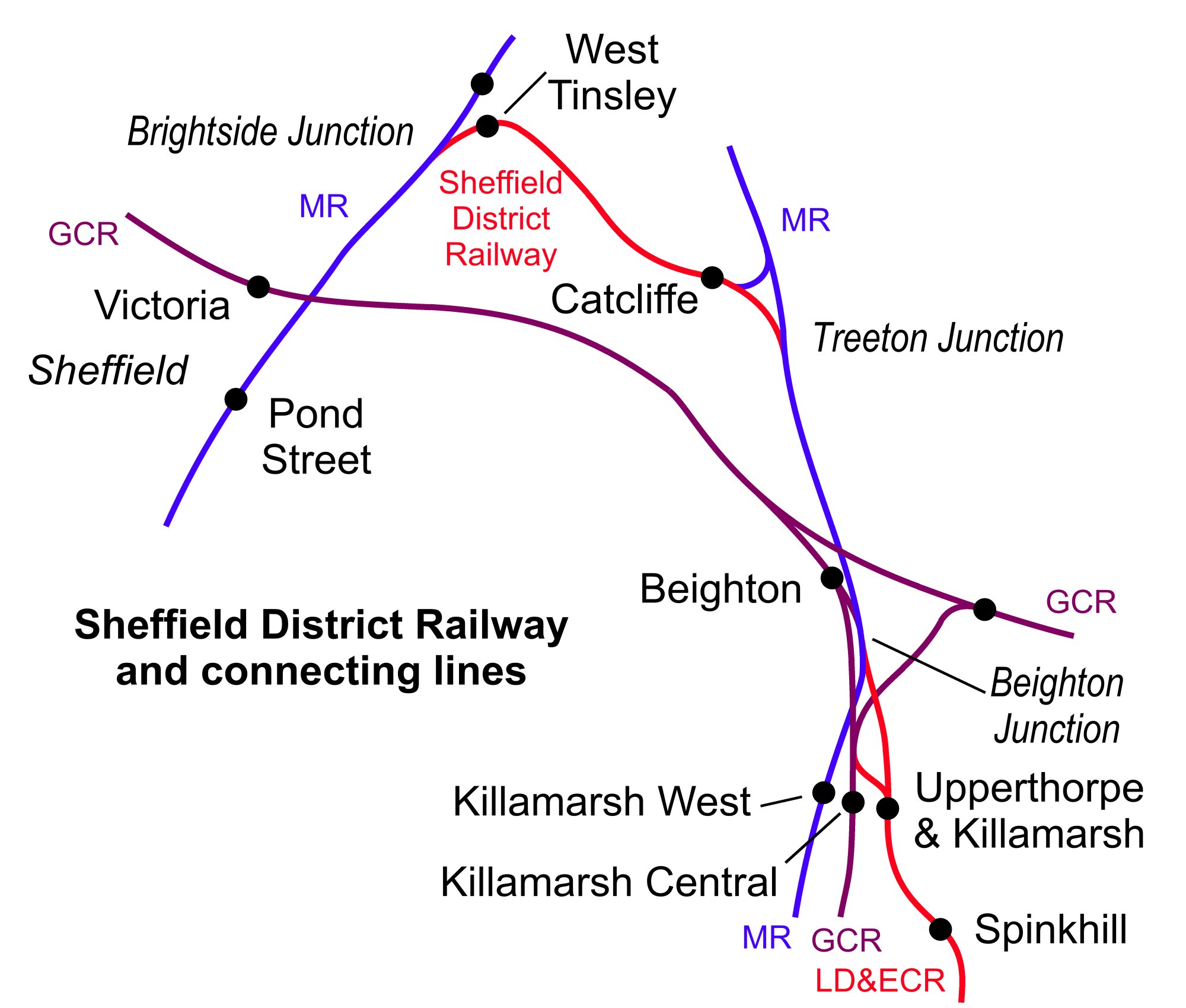
Beighton Railway Station
Beighton railway station is a former railway station near the village of Beighton on the border between Derbyshire and South Yorkshire, England. Three stations Beighton station existed on three sites at different times: * the first station, believed to have been little more than a halt, was opened by the North Midland Railway when it built its to line, which is now predominantly a freight route. At south of it stood approximately halfway between what is now Beighton Junction and the overbridge which still carries passenger trains east–west between and . This original station was opened when the line opened in June 1840, it was not near to or convenient for the village of Beighton and closed in January 1843. * in 1849 the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR) completed its Sheffield to Worksop line, which included a branch from just east of to join the North Midland line at what became known as Beighton Junction. They built Beighton's second station a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Northern Railway (Great Britain)
The Great Northern Railway (GNR) was a British railway company incorporated in 1846 with the object of building a line from London to York. It quickly saw that seizing control of territory was key to development, and it acquired, or took leases of, many local railways, whether actually built or not. In so doing, it overextended itself financially. Nevertheless, it succeeded in reaching into the coalfields of Nottinghamshire, Derbyshire and Yorkshire, as well as establishing dominance in Lincolnshire and north London. Bringing coal south to London was dominant, but general agricultural business, and short- and long-distance passenger traffic, were important activities too. Its fast passenger express trains captured the public imagination, and its Chief Mechanical Engineer Nigel Gresley became a celebrity. Anglo-Scottish travel on the East Coast Main Line became commercially important; the GNR controlled the line from London to Doncaster and allied itself with the North Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paddy Mails
Paddy mails, generally considered as being workmen's trains, were operated by, or for many companies to transport their workers to their place of work or between their sites of work. Originally they were operated by railway contractors, on temporary tracks laid to remove spoil from their workings, to transport workers from their "shanty villages" to the work site. Many of these navvies as they were known were of Irish origin, hence the name given to the trains (see: Paddy). Once the main line was built the name passed to the workmen's specials, which in many cases, were operated along the main line railways and sometimes operated by the main line companies to an exchange point where the trains were taken over by the industrial company. In a time before the provision of pit-head baths it was illegal to travel in a normal service train in working clothes, so special trains were provided, usually of the railway company's most ancient coaches. There is a preserved example of such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London & North Eastern Railway
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as '' Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished from the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.jpg)