|
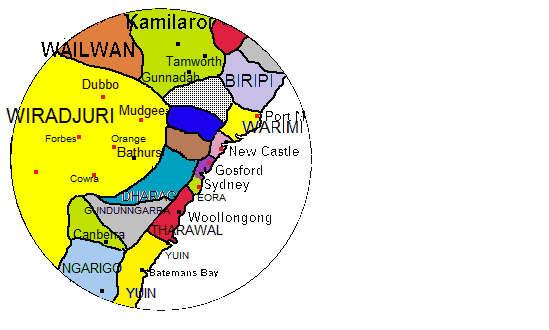
Biripi
The Birrbay people, also spelt Birpai, Biripi, Birippi and variant spellings, are an Aboriginal Australian people of New South Wales. They and share a dialect continuum with the Worimi people. Language The Gathang language (aka Gadjang or Worimi) is the speech of the Birrbay centred in Port Macquarie. Birpai is spelt Biripi in southern areas, such as Taree. Gathang was a community language spoken by the six tribes of the Worimi when required to meet. W. J. Enright found four elderly speakers of Gathang at Wauchope in 1932. Country Birbay are the traditional owners of some of Mid North Coast land, from Gloucester eastwards to the coast where the Manning River debouches into the Pacific at Taree Taree is a town on the Mid North Coast, New South Wales, Australia. Taree and nearby Cundletown were settled in 1831 by William Wynter. Since then Taree has grown to a population of 26,381, and is the centre of a significant agricultural distri .... They were mainly located north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manning River
Manning River (Birpai language, Biripi: ''Boolumbahtee''), an open and Breakwater (structure), trained mature wind wave, wave dominated estuary#Lagoon-type or bar-built, barrier estuary, is located in the Northern Tablelands and Mid North Coast districts of New South Wales, Australia. It is the only double delta river in the southern hemisphere in which there are two permanent entrances to the river, one at Old Bar, New South Wales, Old Bar and another at Harrington, New South Wales, Harrington, and is famously one of only two rivers in the world to have permanent multiple entrances with the other being the Nile, Nile river in Egypt. Course and features Manning River rises below Barrington Volcano, Mount Barrington, on the northeastern slopes of the Great Dividing Range within Barrington Tops National Park, east southeast of Ellerston, New South Wales, Ellerston, and flows generally southeast, joined by eleven tributary, tributaries including the Pigna Barney River, Pigna Barney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taree, New South Wales
Taree is a town on the Mid North Coast, New South Wales, Australia. Taree and nearby Cundletown were settled in 1831 by William Wynter. Since then Taree has grown to a population of 26,381, and is the centre of a significant agricultural district. It is 16 km from the Tasman Sea coast, and 317 km north of Sydney. Taree can be reached by train via the North Coast railway line, New South Wales, North Coast Railway, and by the Pacific Highway (Australia), Pacific Highway. Taree railway station is on the North Coast railway line, New South Wales, North Coast line of the NSW TrainLink network. It is serviced by six NSW TrainLink trains daily: three heading to Sydney, another three heading North to Grafton, Casino or Brisbane. Taree is within the Local government in Australia, local government area of Mid-Coast Council, the state electorate of Electoral district of Myall Lakes, Myall Lakes and the Federal electorate of Division of Lyne, Lyne. Name The name Taree is derived f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunghutti
The Djangadi people, also spelt Dhungatti, Dainggati, Tunggutti or Dunghutti are an Aboriginal Australian people resident in the Macleay Valley of northern New South Wales ) , nickname = , image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , es .... Language Dhanggati / Dunghutti belongs to the Yuin–Kuric language family and is usually grouped with the Anēwan language. The Ngabu Bingayi Aboriginal Corporation promotes the revival study of their language learning as an ongoing activity in the Macleay Valley. Linguist Amanda Lissarrague has been active in assisting their efforts. The language is currently being taught at Kempsey TAFE. Part of the language was recorded and analysed by Nils Holmer and his wife. Country Ethnologist Norman Tindale estimated Djangadi traditional lands to have encompasse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Macquarie
Port Macquarie is a coastal town in the local government area of Port Macquarie-Hastings. It is located on the Mid North Coast of New South Wales, Australia, about north of Sydney, and south of Brisbane. The town is located on the Tasman Sea coast, at the mouth of the Hastings River, and at the eastern end of the Oxley Highway (B56). The town with its suburbs had a population of 47,973 in June 2018. Estimated resident population, 30 June 2018. History Port Macquarie sits within Birpai (Biripi, Birripai, Bripi, Biripai, Birrbay) country, and the Birpai people are recognised as the traditional custodians of the land on which Port Macquarie is located. Port Macquarie was long known to the Birpai people as Guruk. The Birpai Local Aboriginal Land Council provides positive support, information and responsible governance for the Aboriginal community, while also cultivating strong links with the broader community. The site of Port Macquarie was first visited by Europeans in 1818 when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullroarer
The bullroarer, ''rhombus'', or ''turndun'', is an ancient ritual musical instrument and a device historically used for communicating over great distances. It consists of a piece of wood attached to a string, which when swung in a large circle produces a roaring vibrato sound. It dates to the Paleolithic period, being found in Ukraine dating from 18,000 BC. Anthropologist Michael Boyd, a bullroarer expert, documents a number found in Europe, Asia, Africa, the Americas, and Australia. In ancient Greece it was a sacred instrument used in the Dionysian Mysteries and is still used in rituals worldwide. It was a prominent musical technology among the Australian Aboriginal people, used in ceremonies and to communicate with different people groups across the continent. Many different cultures believe that the sounds they make have the power to ward off evil influences. Design, use, and sound A bullroarer consists of a weighted airfoil (a rectangular thin slat of wood about lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aboriginal Australian Ceremony
Australian Aboriginal culture includes a number of practices and ceremonies centered on a belief in the Dreamtime and other mythology. Reverence and respect for the land and oral traditions are emphasised. Over 300 languages and other groupings have developed a wide range of individual cultures. Due the colonization of Australia under terra nullius concept these cultures were treated as one monoculture. Australian Aboriginal art has existed for thousands of years and ranges from ancient rock art to modern watercolour landscapes. Aboriginal music has developed a number of unique instruments. Contemporary Australian Aboriginal music spans many genres. Aboriginal peoples did not develop a system of writing before colonisation, but there was a huge variety of languages, including sign languages. Oral tradition Cultural traditions and beliefs as well as historical tellings of actual events are passed down in Aboriginal oral tradition, also known loosely as oral history (although t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gumbaynggirr
The Gumbaynggirr people, also rendered Kumbainggar, Gumbangeri and other variant spellings, are an Aboriginal Australian people of the Mid North Coast of New South Wales. Gumbathagang was a probable clan or sub-group. The traditional lands of the Gumbaynggirr nation stretch from Tabbimoble Yamba-Clarence River to Ngambaa-Stuarts Point, SWR- Macleay to Guyra and to Oban. History Clement Hodgkinson was the first European to make contact with the local Aboriginal community when he explored the upper reaches of the Nambucca and Bellinger Rivers in March 1841. Three decades later, loggers began to work their way up through the Orara River cedar stands in the 1870s. Over c.1873-1874, J.W. Lindt produced photographs of local indigenous people both in their environment and conducting actual traditional ceremonies in the Clarence River district, and made portraits in his studio. Contemporary commentary records them as "the first successful attempt at representing the native blacks t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Hamilton Mathews
Robert Hamilton Mathews (1841–1918) was an Australian surveyor and self-taught anthropologist who studied the Aboriginal cultures of Australia, especially those of Victoria, New South Wales and southern Queensland. He was a member of the Royal Society of New South Wales and a corresponding member of the Anthropological Institute of London (later the Royal Anthropological Institute). Mathews had no academic qualifications and received no university backing for his research. Mathews supported himself and his family from investments made during his lucrative career as a licensed surveyor. He was in his early fifties when he began the investigations of Aboriginal society that would dominate the last 25 years of his life. During this period he published 171 works of anthropology running to approximately 2200 pages. Mathews enjoyed friendly relations with Aboriginal communities in many parts of south-east Australia. Marginalia in a book owned by Mathews suggest that Aboriginal p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nulla Nulla
A waddy, nulla-nulla or boondi is an Aboriginal Australian hardwood club or hunting stick for use as a weapon or as a throwing stick for hunting animals. ''Waddy'' comes from the Darug people of Port Jackson, Sydney.Peters, Pam, ''The Cambridge Australian English Style Guide'', Cambridge University Press, 1995, ''Boondi'' is the Wiradjuri word for this implement. Description and use A waddy is a heavy pointed club constructed of carved hardwood timber. Waddies were used in hand-to-hand combat and were capable of splitting a shield and of killing or stunning prey. They could be employed also as projectiles or to make fire and make ochre. They found further use in punishing those who broke Aboriginal law. Construction. The waddy was made by both men and women and could be painted or left unpainted. Its construction varied from tribe to tribe, but it was generally about one metre in length and sometimes had a stone head attached with beeswax Beeswax (''cera alba'') i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coolamon (vessel)
Coolamon is an anglicised NSW Aboriginal word used to describe an Australian Aboriginal carrying vessel. It is a multi-purpose shallow vessel, or dish with curved sides, ranging in length from 30 to 70 cm, and similar in shape to a canoe. Coolamons were traditionally used by Aboriginal women to carry water, fruit, nuts, as well as to cradle babies. Today when women gather bush tucker, they usually use a billy can, bucket or flour tin. Coolamons were carried on the head when travelling any distance, or under the arm if used as a cradle. If carried on the head, a ring pad (''akartne'' in Arrernte) was placed on the head, made out of possum and/or human hair string, twisted grass, or feather This helped to cushion and support the carriage of the coolamon; the same purpose as those used by women in traditional cultures around the world to carry vessels on their heads. The Pintupi of the Western Desert would attach a double strand of plaited rope (''ngalyibi'') made of hair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phratry
In ancient Greece, a phratry ( grc, φρᾱτρῐ́ᾱ, phrātríā, brotherhood, kinfolk, derived from grc, φρᾱ́τηρ, phrā́tēr, brother, links=no) was a group containing citizens in some city-states. Their existence is known in most Ionian cities and in Athens and it is thought that they existed elsewhere as well. Almost nothing is known about the functions and responsibilities of phratries outside Attica (the area around Athens). Within Athens, they played a prominent role in social and religious life, particularly in the major festival called the Apatouria. They played an important role in determining eligibility for Athenian citizenship and all citizens (with very few exceptions) and only citizens were enrolled in phratries. Particularly in anthropology, the term is also applied to similar descent groups of multiple clans in other societies. Ancient Greece The origins of the phratry in ancient Greece are unknown. It is possible that they are Ionian in origin and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |