|
Dunghutti
The Djangadi people, also spelt Dhungatti, Dainggati, Tunggutti or Dunghutti are an Aboriginal Australian people resident in the Macleay Valley of northern New South Wales ) , nickname = , image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , es .... Language Dhanggati / Dunghutti belongs to the Yuin–Kuric language family and is usually grouped with the Anēwan language. The Ngabu Bingayi Aboriginal Corporation promotes the revival study of their language learning as an ongoing activity in the Macleay Valley. Linguist Amanda Lissarrague has been active in assisting their efforts. The language is currently being taught at Kempsey TAFE. Part of the language was recorded and analysed by Nils Holmer and his wife. Country Ethnologist Norman Tindale estimated Djangadi traditional lands to have encompasse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bellbrook, New South Wales
Bellbrook is a locality in the Kempsey Shire of New South Wales, Australia along the Macleay River. The mountain village is classified by the National Trust as a heritage village and is part of the Macleay Valley Coast. Population Bellbrook had a population of 339 as of the 2021 census. an expansion of 21% from the population of 273. Etymology The town was laid out and gazetted as Bellbrook in 1892. Caroline McMaugh, wife of early settler John McMaugh, named the village. At that time, and still today, the distinctive call of bellbirds could be heard echoing through the dense scrub they inhabited along Nulla Nulla Creek. In 1882 the name Bellbrook was first adopted as the official title for the original post office. A postal receiving office at Bellbrook opened on 16 January 1882, became a post office on 1 January 1884 and closed on 10 April 1987. The present day post office is located at Bellbrook Hotel. Climate Located within the same post code as Crescent Head an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhanggati Language
Dhanggati (Dunghutti, Thangatti), previously known as Dyangadi (Djangadi),''Daingatti'' has also been given as a name, but may be a different language. is the extinct Australian Aboriginal language once spoken by the Djangadi of the Macleay Valley and surrounding high country of the Great Dividing Range in New South Wales. There is an ongoing program of language-revival. Ngaagu (Ngaku) and Burgadi (Burrgati) were probably dialects. The three together have been called the Macleay Valley language. Shared designated Ceremonial between surrounding tribes ie:Anaiwan, Gumbagerri and including tribes from further West from Armidale to the North at Tenderfield New South Wales and Southern tribes such as the tribes around Nowendoc, S.E New South Wales. Anaiwan Country did trade offs with the surrounding tribes for the use of a Ceremonial site which the 'University of New England' is now located at 'Booloominbah house' (erected 1888) when the then colonial settlement Armidale was becomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walcha, New South Wales
Walcha () is a town at the south-eastern edge of the Northern Tablelands, New South Wales, Australia. The town serves as the seat of Walcha Shire. Walcha is located by road from Sydney at the intersection of the Oxley Highway and Thunderbolts Way. The Apsley River passes through the town to tumble over the Apsley Falls before joining the Macleay River further on. Originally the river caused flooding in the town prior to a levee bank being constructed and saving the town from more floods. At the , Walcha had a population of 1,451 people. The Main North railway line is located west at a separate village called Walcha Road which serves as the railhead. This is served by the daily NSW TrainLink Xplorer service between Sydney and Armidale. The railway line was built at Walcha Road, because it was the closest point they could get to the town, due to the steep climb over the Great Dividing Range. History The area was occupied by the Dhanggati (or Dunghutti) People for 6000 year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
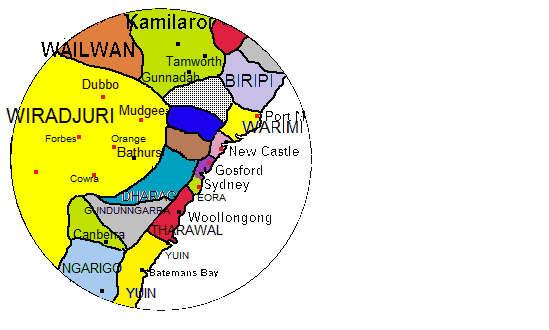
Yuin–Kuric Languages
The Murring–Kuric languages are a family of mainly extinct Australian Aboriginal languages that existed in the south east of Australia. They belong in the Pama–Nyungan family.AIATSIS Language and Peoples Thesaurus , accessed 23 Jan 2010. These languages are divided into the Yuin, Kuri, and Yora groups, although exact classifications vary between researchers. Yuin–Kuric languages were spoken by the original inhabitants of what are now the cities of and . Most are now |
Dunghutti Language
Dhanggati (Dunghutti, Thangatti), previously known as Dyangadi (Djangadi),''Daingatti'' has also been given as a name, but may be a different language. is the extinct Australian Aboriginal language once spoken by the Djangadi of the Macleay Valley and surrounding high country of the Great Dividing Range in New South Wales. There is an ongoing program of language-revival. Ngaagu (Ngaku) and Burgadi (Burrgati) were probably dialects. The three together have been called the Macleay Valley language. Shared designated Ceremonial between surrounding tribes ie:Anaiwan, Gumbagerri and including tribes from further West from Armidale to the North at Tenderfield New South Wales and Southern tribes such as the tribes around Nowendoc, S.E New South Wales. Anaiwan Country did trade offs with the surrounding tribes for the use of a Ceremonial site which the 'University of New England' is now located at 'Booloominbah house' (erected 1888) when the then colonial settlement Armidale was becomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macleay River
The Macleay River is a river that spans the Northern Tablelands and Mid North Coast districts of New South Wales, Australia. Course and features Formed by the confluence of the Gara River, Salisbury Waters and Bakers Creek, the Macleay River rises below Blue Nobby Mountain, east of Uralla within the Great Dividing Range. The river flows in a meandering course generally east by south, joined by twenty-six tributaries including the Apsley, Chandler, and Dyke rivers and passing through a number of spectacular gorges and waterfalls in Cunnawarra National Park and Oxley Wild Rivers National Park, before reaching its mouth at the Tasman Sea, near South West Rocks. The river descends over its course. The river flows through the town of Kempsey. At the river is traversed by the Pacific Highway via the Macleay River Bridge (Dhanggati language: ''Yapang gurraarrbang gayandugayigu''). At the time of its official opening in 2013, the bridge was the longest road bridge in Australi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gumbaynggirr
The Gumbaynggirr people, also rendered Kumbainggar, Gumbangeri and other variant spellings, are an Aboriginal Australian people of the Mid North Coast of New South Wales. Gumbathagang was a probable clan or sub-group. The traditional lands of the Gumbaynggirr nation stretch from Tabbimoble Yamba-Clarence River to Ngambaa-Stuarts Point, SWR- Macleay to Guyra and to Oban. History Clement Hodgkinson was the first European to make contact with the local Aboriginal community when he explored the upper reaches of the Nambucca and Bellinger Rivers in March 1841. Three decades later, loggers began to work their way up through the Orara River cedar stands in the 1870s. Over c.1873-1874, J.W. Lindt produced photographs of local indigenous people both in their environment and conducting actual traditional ceremonies in the Clarence River district, and made portraits in his studio. Contemporary commentary records them as "the first successful attempt at representing the native blacks t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point Lookout (New South Wales)
Point Lookout, a mountain on the Snowy Range, a spur of the Great Dividing Range, is located in the New England National Park on the eastern edge of the Northern Tablelands in the New England region of New South Wales, Australia. With an altitude of above sea level, Point Lookout is the second highest peak in the region. During cold spells the mountain may receive a light dusting of snow. Description Point Lookout is also the name of the main visitor location in the New England National Park. The Point Lookout Road is accessed via Waterfall Way and is east of and from , near . The lookouts have views east across the Bellinger River valley, out to the more developed areas of the north coast of New South Wales and the Tasman Sea on a clear day.New England National Park, NSW NPWS, 2007 On the escarpment only 10 minutes walk south is Banksia Point. There are a number of cabins and a hut here. These are available from the National Parks and Wildlife Service for short term sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Royal Range
The Mount Royal Range is a mountain range in the Hunter region of New South Wales, Australia. Location and features The Mount Royal Range is a spur on the eastern side of the Great Dividing Range. It diverges from the Liverpool Range at a point north of Scone, New South Wales, near Ben Halls Gap. The range generally extends to the southeast for about and then generally to the south southwest for about to Mount Royal. The range generally forms the divide between the Hunter River and Manning River drainage basins, both of which drain to the Tasman Sea. The range contains a number of prominent peaks including: * Brumlow Tops with an elevation of * Mount Polblue with an elevation of * Mount Barrington with an elevation of * Mount Royal with an elevation of * Mount Allyn with an elevation of * Prospero with an elevation of * Gulph Mountain * Gog and Magog * The Pinnacle * Paddys Ridge * Mount William * Mount Paterson * Mount Toonumbue * the Belgrave Pinnacle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Dividing Range
The Great Dividing Range, also known as the East Australian Cordillera or the Eastern Highlands, is a cordillera system in eastern Australia consisting of an expansive collection of mountain ranges, plateaus and rolling hills, that runs roughly parallel to the east coast of Australia and forms the fifth-longest land-based mountain chain in the world, and the longest entirely within a single country. It is mainland Australia's most substantial topographic feature and serves as the definitive watershed for the river systems in eastern Australia, hence the name. The Great Dividing Range stretches more than from Dauan Island in the Torres Strait off the northern tip of Cape York Peninsula, running the entire length of the eastern coastline through Queensland and New South Wales, then turning west across Victoria before finally fading into the Wimmera plains as rolling hills west of the Grampians region. The width of the Range varies from about to over .Shaw, John H., ''Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worimi Language
Worimi (also spelt Warrimay), or Gadjang (also spelt ''Kattang, Kutthung, Gadhang, Gadang, Gathang'') is an Australian Aboriginal language. It is the traditional language of the Worimi people, whose descendants now speak English. Work has started on revitalising the language with a dictionary and TAFE course in Gathang. Classification Worimi is most closely related to Awabakal, in the Yuin–Kuric group of Pama–Nyungan. Bowern (2011) considers Gadjang, Worimi, and Birrpayi to be separate languages. Phonology Vowels There is also the diphthong "ay", pronounced j Consonants Within the orthography, both voiceless and voiced stops are written, words begin with voiced stops only and only voiced stops may occur in consonant clusters or suffixes. There is some inconsistency in the orthography to choice of stop intervocalically, the dictionary/grammar written by Amanda Lissarrague prescribes voiceless stops intervocalically, but this is violated many times such as in ''magu' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anēwan
The Anēwan, also written Anaiwan and Anaywan, are an Aboriginal Australian people whose traditional territory spans the Northern Tablelands in New South Wales. The Anēwan people are a subgroup of the Djangadi tribe. Language The Anēwan language, also known as ''Nganyaywana'' has been classified by Robert M. W. Dixon as belonging to the ''Djan-gadi/Nganjaywana subgroup'' of Central New South Wales, and was one of three varieties of the group, the other dialects being Himberrong and Inuwon. For a long time Anēwan was regarded, like Mbabaram, as a linguistic isolate, ostensibly failing to fit into the known Australian patterns of language, since the material in word-lists taken down of its vocabulary appeared to lack cognates in contiguous languages such as Gamilaraay. The status of its seeming irregularity was solved in 1976 by Terry Crowley who showed that the differences were caused by initial consonant loss which, once accounted for, yielded up over 100 cognate terms bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)