|
Biraj Mohan Das Gupta
Biraj Mohan Das Gupta or Dasgupta (, c. 1889 – 1945) was a Bengali parasitologist, known for his discovery, with Robert Knowles, of the '' Plasmodium'' species now known as '' Plasmodium knowlesi''. Biography After qualifying as a physician, Das Gupta was appointed in 1921 to a position as a researcher and assistant surgeon at the Calcutta School of Tropical Medicine. At the Calcutta School of Tropical Medicine, in 1931 H. G. M. Campbell detected the ''Plasmodium'' species now known as ''P. knowlesi'' in a macaque imported from Singapore. Campbell showed his discovery to his supervisor Lionel Everard Napier, who injected the strain into three monkeys, one of which developed symptoms of malaria. Aware of the Protozoological Department's search for a monkey malaria strain, Napier and Campbell gave the infected monkey to Das Gupta, working under Knowles. Das Gupta maintained the ''Plasmodium'' species by serial passage in monkeys until Knowles returned from leave. In 1932, Kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, commercial, and financial hub of East India, Eastern India and the main port of communication for North-East India. According to the 2011 Indian census, Kolkata is the List of cities in India by population, seventh-most populous city in India, with a population of 45 lakh (4.5 million) residents within the city limits, and a population of over 1.41 crore (14.1 million) residents in the Kolkata metropolitan area, Kolkata Metropolitan Area. It is the List of metropolitan areas in India, third-most populous metropolitan area in India. In 2021, the Kolkata metropolitan area crossed 1.5 crore (15 million) registered voters. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and Southeast Asia. Bengal proper covered the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal (present-day Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal). Calcutta, the city which grew around Fort William, was the capital of the Bengal Presidency. For many years, the Governor of Bengal was concurrently the Viceroy of India and Calcutta was the de facto capital of India until 1911. The Bengal Presidency emerged from trading posts established in Mughal Bengal during the reign of Emperor Jahangir in 1612. The East India Company (HEIC), a British monopoly with a Royal Charter, competed with other European companies to gain influence in Bengal. After the decisive overthrow of the Nawab of Bengal in 1757 and the Battle of Buxar in 1764, the HEIC expanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods: *Between 1612 and 1757 the East India Company set up Factory (trading post), factories (trading posts) in several locations, mostly in coastal India, with the consent of the Mughal emperors, Maratha Empire or local rulers. Its rivals were the merchant trading companies of Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, and France. By the mid-18th century, three ''presidency towns'': Madras, Bombay and Calcutta, had grown in size. *During the period of Company rule in India (1757–1858), the company gradually acquired sovereignty over large parts of India, now called "presidencies". However, it also increasingly came under British government over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcutta School Of Tropical Medicine
Calcutta School of Tropical Medicine (CSTM) is a medical institute from Kolkata, India dedicated in the field of tropical disease. It was established in 1914 by Leonard Rogers (1868–1962) of the Indian Medical Service, professor of pathology at the Calcutta Medical College. It was, till 2003, affiliated with the University of Calcutta. Now it is under the West Bengal University of Health Sciences. Prominent researchers like U. N. Bramhachari, Ernest Muir, Ronald Ross, Rabindra Nath Chaudhuri, Ram Narayan Chakravarti and Jyoti Bhusan Chatterjee worked in this institute. Notable alumni * Ram Baran Yadav, first president of Nepal * Baba Amte Murlidhar Devidas Amte, popularly known as Baba Amte, (26 December 1914 – 9 February 2008) was an Indian social worker and social activist known particularly for his work for the rehabilitation and empowerment of people suffering from leprosy ..., Indian Social Worker and social activist who worked for the empowerment and rehabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitologist
Parasitology is the study of parasites, their hosts, and the relationship between them. As a biological discipline, the scope of parasitology is not determined by the organism or environment in question but by their way of life. This means it forms a synthesis of other disciplines, and draws on techniques from fields such as cell biology, bioinformatics, biochemistry, molecular biology, immunology, genetics, evolution and ecology. Fields The study of these diverse organisms means that the subject is often broken up into simpler, more focused units, which use common techniques, even if they are not studying the same organisms or diseases. Much research in parasitology falls somewhere between two or more of these definitions. In general, the study of prokaryotes falls under the field of bacteriology rather than parasitology. Medical The parasitologist F.E.G. Cox noted that "Humans are hosts to nearly 300 species of parasitic worms and over 70 species of protozoa, some derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Knowles (parasitologist)
Robert Knowles (30 October 1883 – 3 August 1936, Calcutta) was a British parasitologist, known for his discovery, with Biraj Mohan Das Gupta, of the ''Plasmodium'' species now known as ''Plasmodium knowlesi''. Biography Knowles matriculated at Downing College, Cambridge and graduated in 1905 with B.A. Receiving medical education at St Mary's Hospital, London St Mary's Hospital is an NHS hospital in Paddington, in the City of Westminster, London, founded in 1845. Since the UK's first academic health science centre was created in 2008, it has been operated by Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, wh ..., he was made M.R.S.C in 1907 and L.R.C.P. Lond. in 1907. As a British officer in the Indian Medical Service he was made lieutenant on 1 February 1908, captain on 1 February 1911, major on 1 August 1919, and lieutenant-colonel on 1 August 1927; upon his death in 1936 he held the rank of colonel. He became a professor of protozoology at the Calcutta School of Tropical Medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmodium
''Plasmodium'' is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of ''Plasmodium'' species involve development in a blood-feeding insect host which then injects parasites into a vertebrate host during a blood meal. Parasites grow within a vertebrate body tissue (often the liver) before entering the bloodstream to infect red blood cells. The ensuing destruction of host red blood cells can result in malaria. During this infection, some parasites are picked up by a blood-feeding insect (mosquitoes in majority cases), continuing the life cycle. ''Plasmodium'' is a member of the phylum Apicomplexa, a large group of parasitic eukaryotes. Within Apicomplexa, ''Plasmodium'' is in the order Haemosporida and family Plasmodiidae. Over 200 species of ''Plasmodium'' have been described, many of which have been subdivided into 14 subgenera based on parasite morphology and host range. Evolutionary relationships among different ''Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
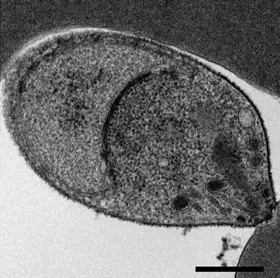
Plasmodium Knowlesi
''Plasmodium knowlesi'' is a parasite that causes malaria in humans and other primates. It is found throughout Southeast Asia, and is the most common cause of human malaria in Malaysia. Like other ''Plasmodium'' species, ''P. knowlesi'' has a life cycle that requires infection of both a mosquito and a warm-blooded host. While the natural warm-blooded hosts of ''P. knowlesi'' are likely various Old World monkeys, humans can be infected by ''P. knowlesi'' if they are fed upon by infected mosquitoes. ''P. knowlesi'' is a eukaryote in the phylum Apicomplexa, genus ''Plasmodium'', and subgenus ''Plasmodium''. It is most closely related to the human parasite ''Plasmodium vivax'' as well as other ''Plasmodium'' species that infect non-human primates. Humans infected with ''P. knowlesi'' can develop uncomplicated or severe malaria similar to that caused by ''Plasmodium falciparum''. Diagnosis of ''P. knowlesi'' infection is challenging as ''P. knowlesi'' very closely resembles other spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ram Nath Chopra
Sir Ram Nath Chopra CIE, IMS (17 August 1882 – 13 June 1973) was an Indian Medical Service officer and a doyen of science and medicine of India. He is considered the "Father of Indian Pharmacology" for his work on pharmaceuticals and his quest for self-sufficiency of India in drugs through the experimental evaluation of indigenous and traditional drugs. After service in the army, he established a research laboratory where he worked as a professor of a pharmacology at the Calcutta School of Tropical Medicine which was established in 1921. Chopra was born in Gujranwala. His father Raghu Nath was a government official. After school in Lahore he went to the Government College there and then went to England in 1903 and studied at the Downing College, Cambridge. In 1905 he qualified in the Natural Sciences Tripos and was admitted BA. He received a B.Chir. in 1908 and an MA in 1909. He worked under Walter E. Dixon professor of the newly established position in pharmacology. He w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1880s Births
Year 188 (CLXXXVIII) was a leap year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known in the Roman Empire as the Year of the Consulship of Fuscianus and Silanus (or, less frequently, year 941 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 188 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Publius Helvius Pertinax becomes pro-consul of Africa from 188 to 189. Japan * Queen Himiko (or Shingi Waō) begins her reign in Japan (until 248). Births * April 4 – Caracalla (or Antoninus), Roman emperor (d. 217) * Lu Ji (or Gongji), Chinese official and politician (d. 219) * Sun Shao, Chinese general of the Eastern Wu state (d. 241) Deaths * March 17 – Julian, pope and patriarch of Alexandria * Fa Zhen (or Gaoqing), Chinese scholar (b. AD 100) * Lucius Antistius Burrus, Roman politician (executed) * Ma Xiang, Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1945 Deaths
1945 marked the end of World War II and the fall of Nazi Germany and the Empire of Japan. It is also the only year in which Nuclear weapon, nuclear weapons Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, have been used in combat. Events Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix. January * January 1 – WWII: ** Nazi Germany, Germany begins Operation Bodenplatte, an attempt by the ''Luftwaffe'' to cripple Allies of World War II, Allied air forces in the Low Countries. ** Chenogne massacre: German prisoners are allegedly killed by American forces near the village of Chenogne, Belgium. * January 6 – WWII: A German offensive recaptures Esztergom, Kingdom of Hungary (1920–1946), Hungary from the Russians. * January 12 – WWII: The Soviet Union begins the Vistula–Oder Offensive in Eastern Europe, against the German Army (Wehrmacht), German Army. * January 13 – WWII: The Soviet Union begins the East Prussian Offensive, to eliminate German forces in East Pruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengali Scientists
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to: *something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia * Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region * Bengali language, the language they speak ** Bengali alphabet, the writing system ** Bengali–Assamese script *** Bengali (Unicode block), a block of Bengali characters in Unicode * Bengali, Nancowry, a village in Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India * , a ship launched in 1837 and wrecked in 1951 * Bengali, member of the ThunderCats * Bengali-Fodé Koita, Guinean footballer * Bengali Keïta, Guinean centre-back * Bengali Market, ancient market in New Delhi, India * Bengali River, river in northern Bangladesh * Bengali Singh, Indian politician * Abdul Wahid Bengali, 19th-century theologian * Ali Sher Bengali, 16th-century Sufi * Athar Ali Bengali, politician and teacher * Izzatullah Bengali, 18th-century Persian language author * Mohamed Bengali, Ivorian footballer * Muhammad Salih Bengali, 18th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |