|
Binswanger's Disease
Binswanger's disease, also known as subcortical leukoencephalopathy and subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy, is a form of small-vessel vascular dementia caused by damage to the white brain matter. White matter atrophy can be caused by many circumstances including chronic hypertension as well as old age.Giovannetti, T. Personal Interview. 16 October 2009 This disease is characterized by loss of memory and intellectual function and by changes in mood. These changes encompass what are known as executive functions of the brain. It usually presents between 54 and 66 years of age, and the first symptoms are usually mental deterioration or stroke. It was described by Otto Binswanger in 1894, and Alois Alzheimer first used the phrase "Binswanger's disease" in 1902. However, Jerzy Olszewski is credited with much of the modern-day investigation of this disease which began in 1962. Signs and symptoms Symptoms include mental deterioration, language disorder, transient ischemic at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Impairment
Cognitive impairment is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to the cognition process or different areas of cognition. Cognition, also known as cognitive function, refers to the mental processes of how a person gains knowledge, uses existing knowledge, and understands things that are happening around them using their thoughts and senses. Cognitive impairment can be in different domains or aspects of a person's cognitive function including memory, attention span, planning, reasoning, decision-making, language (comprehension, writing, speech), executive functioning, and visuospatial functioning. The term cognitive impairment covers many different diseases and conditions and may also be symptom or manifestation of a different underlying condition. Examples include impairments in overall intelligence (as with intellectual disabilities), specific and restricted impairments in cognitive abilities (such as in learning disorders like dyslexia), neurops ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axons
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences) is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons ( pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three types group A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mini–mental State Examination
The mini–mental state examination (MMSE) or Folstein test is a 30-point questionnaire that is used extensively in clinical and research settings to measure cognitive impairment. It is commonly used in medicine and allied health to screen for dementia. It is also used to estimate the severity and progression of cognitive impairment and to follow the course of cognitive changes in an individual over time; thus making it an effective way to document an individual's response to treatment. The MMSE's purpose has been not, on its own, to provide a diagnosis for any particular nosological entity. Administration of the test takes between 5 and 10 minutes and examines functions including registration (repeating named prompts), attention and calculation, recall, language, ability to follow simple commands and orientation. It was originally introduced by Folstein ''et al.'' in 1975, in order to differentiate organic from functional psychiatric patients but is very similar to, or even d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
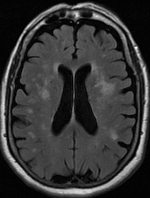
Leukoaraiosis
Leukoaraiosis is a particular abnormal change in appearance of white matter near the lateral ventricles. It is often seen in aged individuals, but sometimes in young adults. On MRI, leukoaraiosis changes appear as white matter hyperintense, hyperintensities (WMHs) in T2 FLAIR images. On CT scans, leukoaraiosis appears as hypodense periventricular white-matter lesions. The term "leukoaraiosis" was coined in 1986 by Vladimir Hachinski, Hachinski, Potter, and Merskey as a descriptive term for rarefaction ("araiosis") of the white matter, showing up as decreased density on CT and increased signal intensity on T2/FLAIR sequences (white matter hyperintensities) performed as part of MRI brain scans. These white matter changes are also commonly referred to as periventricular white matter disease, or white matter hyperintensities (WMH), due to their bright white appearance on Magnetic resonance imaging#How MRI works, T2 MRI scans. Many patients can have leukoaraiosis without any associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to form images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry (medical), gantry to measure X-ray Attenuation#Radiography, attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce Tomography, tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is Contraindication, contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perseveration
Perseveration, in the fields of psychology, psychiatry, and speech–language pathology, is the repetition of a particular response (such as a word, phrase, or gesture) regardless of the absence or cessation of a stimulus. It is usually caused by a brain injury or other organic disorder. Symptoms include "lacking ability to transition or switch ideas appropriately with the social context, as evidenced by the repetition of words or gestures after they have ceased to be socially relevant or appropriate", or the "act or task of doing so", and are not better described as stereotypy (a highly repetitive idiosyncratic behaviour). In a broader sense, it is used for a wide range of functionless behaviours that arise from a failure of the brain to either inhibit prepotent responses or to allow its usual progress to a different behavior, and includes impairment in set shifting and task switching in social and other contexts. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
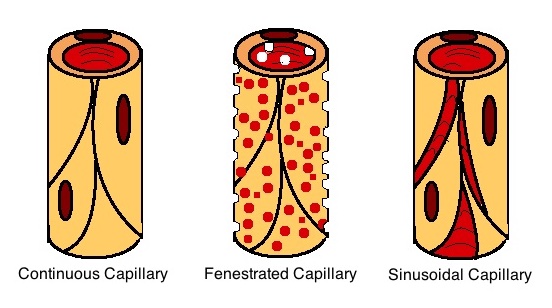
Capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
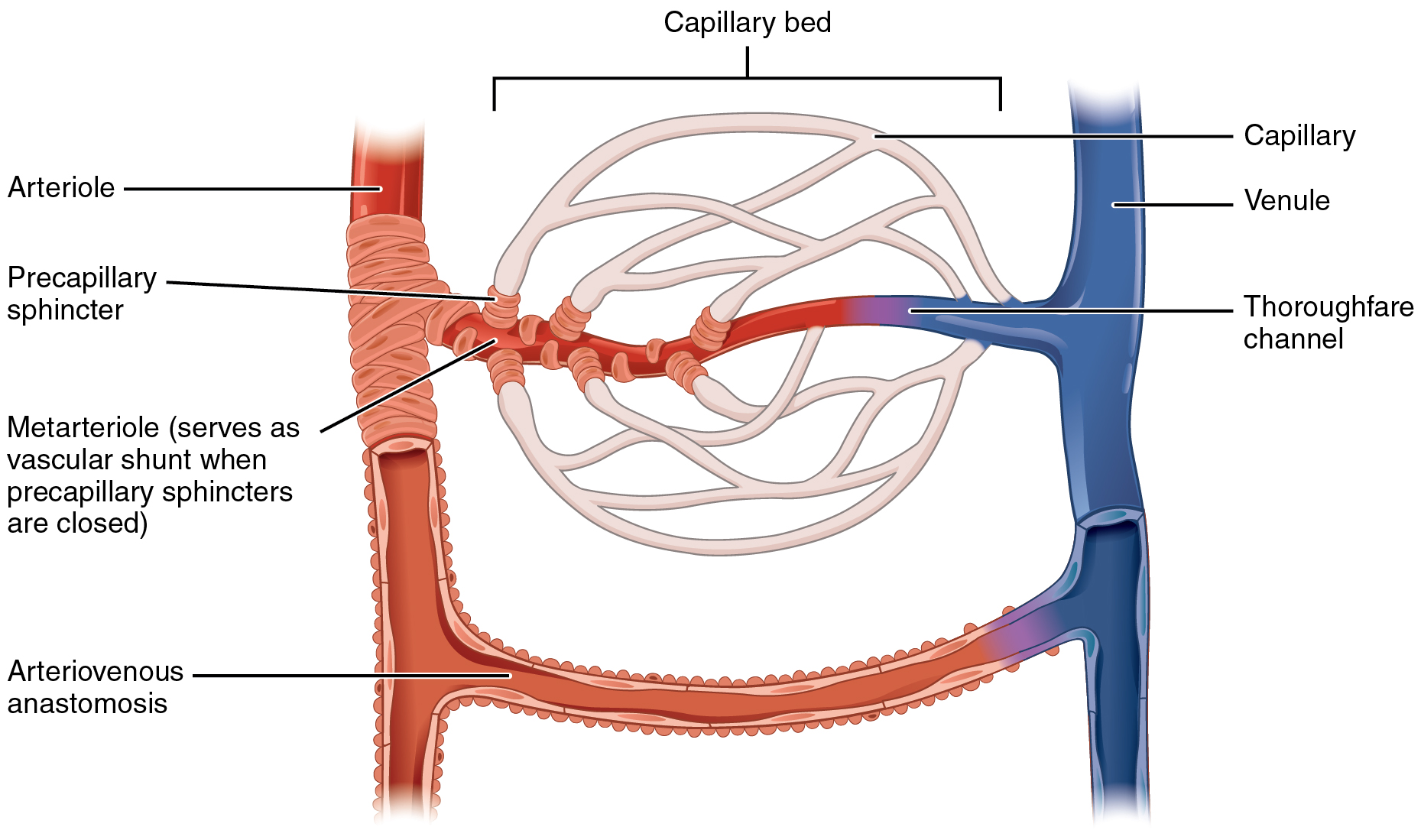
Microcirculation
The microcirculation is the circulation of the blood in the smallest blood vessels, the microvessels of the microvasculature present within organ tissues. The microvessels include terminal arterioles, metarterioles, capillaries, and venules. Arterioles carry oxygenated blood to the capillaries, and blood flows out of the capillaries through venules into veins. In addition to these blood vessels, the microcirculation also includes lymphatic capillaries and collecting ducts. The main functions of the microcirculation are the delivery of oxygen and nutrients and the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2). It also serves to regulate blood flow and tissue perfusion, thereby affecting blood pressure and responses to inflammation which can include edema (swelling). Most vessels of the microcirculation are lined by flattened cells of the endothelium and many of them are surrounded by contractile cells called pericytes. The endothelium provides a smooth surface for the flow of blood and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Brain Barrier
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma. Plasma, which constitutes 55% of blood fluid, is mostly water (92% by volume), and contains proteins, glucose, mineral ions, and hormones. The blood cells are mainly red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and (in mammals) platelets (thrombocytes). The most abundant cells are red blood cells. These contain hemoglobin, which facilitates oxygen transport by reversibly binding to it, increasing its solubility. Jawed vertebrates have an adaptive immune system, based largely on white blood cells. White blood cells help to resist infections and parasites. Platelets are important in the clotting of blood. Blood is circulated around the body through blood vessels by the pumpi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by elevated blood levels of cholesterol. These lesions may lead to narrowing of the arterial walls due to buildup of atheromatous plaques. At the onset, there are usually no symptoms, but if they develop, symptoms generally begin around middle age. In severe cases, it can result in coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney disorders, depending on which body part(s) the affected arteries are located in the body. The exact cause of atherosclerosis is unknown and is proposed to be multifactorial. Risk factors include dyslipidemia, abnormal cholesterol levels, elevated levels of inflammatory biomarkers, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking (both active and passive smoking), obesity, genetic factors, family history, lifes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
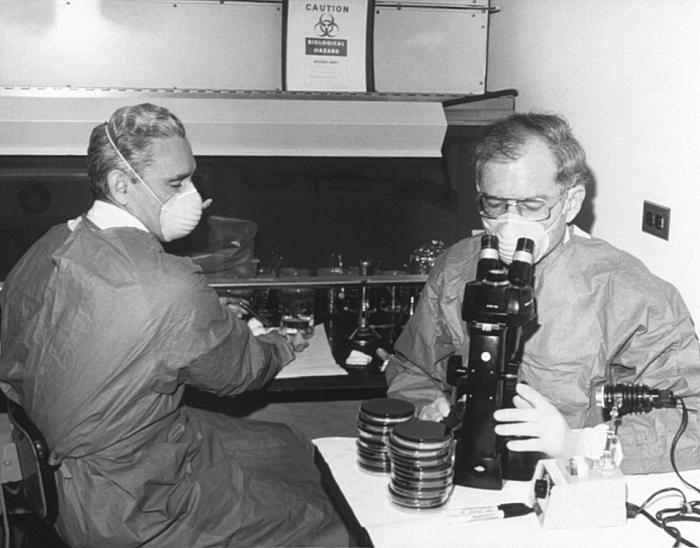
Pathology
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area that includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue (biology), tissue and human cell samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be "Pathophysiology, pathophysiologies"). The suffix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomyopathy) and psych ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |