|
Bingen (Rhein) Hauptbahnhof
Bingen (Rhein) Hauptbahnhof is a railway station in the German city of Bingen am Rhein on the West Rhine Railway. It is located in the borough of Bingerbrück. The station that serves central Bingen is called Bingen Stadt. The station is served by InterCityExpress, Intercity and regional trains. It is a junction station where the Nahe Valley Railway branches of the West Rhine Railway (left bank line). It formerly also included a marshalling yard. The station is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 4 station. Location Bingen Hbf is located in the district of Bingerbrück in the city of Bingen am Rhein and extends along the Rhine almost to the Nahe. Bingen Stadt (town) station is less than 2 kilometres to the southeast. The town station is located in the town's centre and its bus station gives better access to the town's bus services than the Hauptbahnhof. Three of the attractions of ''The Industrial Heritage Trail Rhine-Main'' (''Route der Industriekultur Rhein-Main''), wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bingen Am Rhein
Bingen am Rhein () is a town in the Mainz-Bingen district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. The settlement's original name was Bingium, a Celtic word that may have meant "hole in the rock", a description of the shoal behind the ''Mäuseturm'', known as the ''Binger Loch''. Bingen was the starting point for the ''Via Ausonia'', a Roman military road that linked the town with Trier. Bingen is well known for, among other things, the story about the Mouse Tower, in which the Bishop of Hatto I of Mainz was allegedly eaten by mice. Saint Hildegard von Bingen, an important polymath, abbess, mystic and musician, one of the most influential medieval composers and one of the earliest Western composers whose music is widely preserved and performed, was born 40 km away from Bingen, in Bermersheim vor der Höhe. Bingen am Rhein was also the birthplace of the celebrated poet Stefan George, along with many other influential figures. Geography Location Bingen is situated just southeast of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
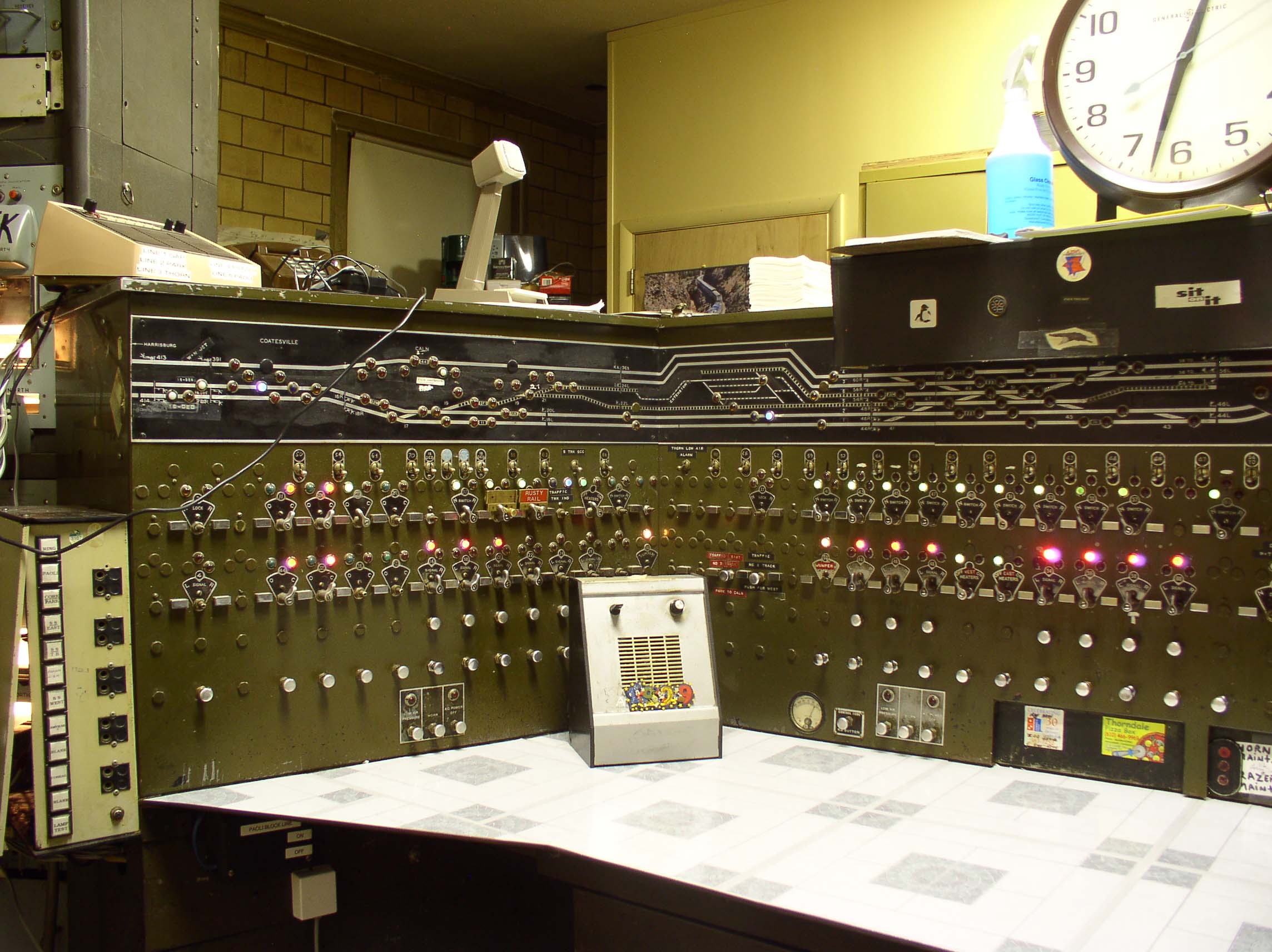
Centralized Traffic Control
Centralized traffic control (CTC) is a form of railway signalling that originated in North America. CTC consolidates train routing decisions that were previously carried out by local signal operators or the train crews themselves. The system consists of a centralized train dispatcher's office that controls railroad interlockings and traffic flows in portions of the rail system designated as CTC territory. One hallmark of CTC is a control panel with a graphical depiction of the railroad. On this panel, the dispatcher can keep track of trains' locations across the territory that the dispatcher controls. Larger railroads may have multiple dispatcher's offices and even multiple dispatchers for each operating division. These offices are usually located near the busiest yards or stations, and their operational qualities can be compared to air traffic towers. Background Key to the concept of CTC is the notion of ''traffic control'' as it applies to railroads. Trains moving in opposite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindenburg Bridge
The Hindenburg Bridge (german: Hindenburgbrücke) was a railway bridge over the Rhine between Rüdesheim am Rhein, Rüdesheim in the German state of Hesse and Bingen am Rhein, Bingen-Kempten state of Rhineland-Palatinate, named in 1918 after Generalfeldmarschall, Field Marshal Paul von Hindenburg, later President of Germany (1919–1945), German President. The bridge was put in service in 1915, destroyed in the Second World War and never rebuilt. Since 2002 the remains of the Hindenburg bridge has been the easternmost point of the UNESCO World Heritage Site of the Rhine Gorge, Upper Middle Rhine Valley. Bingerbrück–Rüdesheim train ferry The bridge was preceded by the Bingerbrück–Rüdesheim train ferry, opened in November 1861, making the first connection between the Nassau Rhine Railway of the Nassau State Railway (german: Nassauische Staatsbahn) and the Nahe Valley Railway of the ''Rhine-Nahe Railway Company'' (''Rhein-Nahe-Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft''). This created a freight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rüdesheim Am Rhein
Rüdesheim am Rhein is a German winemaking town in the Rhine Gorge, and part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site in this region. It lies in the Rheingau-Taunus-Kreis district in the ''Regierungsbezirk'' of Darmstadt, Hessen. Known as Rüdesheim, it is officially Rüdesheim am Rhein, to distinguish it from Rüdesheim an der Nahe. It is a major tourist attraction, especially for foreign visitors. Geography Location Rüdesheim lies at the foot of the Niederwald on the Rhine's right bank in the Rheingau wine region. The town belongs to the Frankfurt Rhine Main Region and to the World Heritage Site Rhine Gorge. It has a picturesque Old Town, located in the Rheingau landscape celebrated in Rhine romanticism. Territorial structure Rüdesheim am Rhein as a municipality consists of five quarters: * Rüdesheim am Rhein (initial part and center) * Eibingen including Windeck, Eibingen Abbey and Nothgottes * Assmannshausen * Aulhausen including the former and * Presberg Assmannshau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bingerbrück–Rüdesheim Train Ferry
The Bingerbrück–Rüdesheim train ferry was operated as a train ferry from 1862 to 1900 across the Rhine between Bingerbrück now in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate and Rüdesheim now in the state of Hesse. On 15 December 1859 was the Rhenish Railway Company (german: Rheinische Eisenbahngesellschaft ) put the final section of its Left Rhine railway from Cologne to Bingerbrück into operation. A few months later, on 26 May 1860, the ''Rhine-Nahe Railway Company'' (''Rhein-Nahe Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'') completed the Nahe Valley Railway from Bingerbrück to Neunkirchen in the Saarland. Both rail lines could be used to supply the demand for coal in the Middle and Upper Rhine. The supply of the Wiesbaden and Frankfurt area by rail was only possible by a roundabout route via the Rhine-Main Railway to Mainz and Darmstadt. In 1862 the ''Nassau Rhine Railway'' (''Nassauische Rheinbahn'', now part of the East Rhine line) was opened between Rudesheim and Oberlahnstein, providi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nassau State Railway
The Nassau State Railway (german: Nassauische Staatsbahn) took over the privately built railway lines on the Rhine and Lahn rivers in the Duchy of Nassau from the ''Nassau Rhine and Lahn Railway Company'' in 1861 and extended them further. It was taken over by the Prussian State Railways in 1866. Establishment After the Taunus Railway (''Taunus-Eisenbahn'') from Frankfurt reached Wiesbaden in 1840, a private company was founded to continue the line along the Rhine. This was originally called the ''Wiesbaden Railway Company'' (''Wiesbadener Eisenbahngesellschaft''); from 1853 it was called the ''Nassau Rhine Railway Company'' (''Nassauische Rhein Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft''); and after 1855 it was called the ''Nassau Rhine and Lahn Railway Company'' (''Nassauische Rhein- und Lahn Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft''). The company was given a concession on 23 June 1853 by the Duchy of Nassau for the construction of the Nassau Rhine Valley Railway from Wiesbaden to Rüdesheim and Oberlahnstein. On 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , "Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on its namesake Main River, it forms a continuous conurbation with the neighboring city of Offenbach am Main and its urban area has a population of over 2.3 million. The city is the heart of the larger Rhine-Main metropolitan region, which has a population of more than 5.6 million and is Germany's second-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr region. Frankfurt's central business district, the Bankenviertel, lies about northwest of the geographic center of the EU at Gadheim, Lower Franconia. Like France and Franconia, the city is named after the Franks. Frankfurt is the largest city in the Rhine Franconian dialect area. Frankfurt was a city state, the Free City of Frankfurt, for nearly five centuries, and was one of the most import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiesbaden
Wiesbaden () is a city in central western Germany and the capital of the state of Hesse. , it had 290,955 inhabitants, plus approximately 21,000 United States citizens (mostly associated with the United States Army). The Wiesbaden urban area is home to approximately 560,000 people. Wiesbaden is the second-largest city in Hesse after Frankfurt, Frankfurt am Main. The city, together with nearby Frankfurt am Main, Darmstadt, and Mainz, is part of the Frankfurt Rhine Main Region, a metropolitan area with a combined population of about 5.8 million people. Wiesbaden is one of the oldest spa towns in Europe. Its name translates to "meadow baths", a reference to its famed hot springs. It is also internationally famous for its architecture and climate—it is also called the "Nice of the North" in reference to the city in France. At one time, Wiesbaden had 26 hot springs. , fourteen of the springs are still flowing. In 1970, the town hosted the tenth ''Hessentag Landesfest'' (En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhenish Railway Company
The Rhenish Railway Company (German language, German: ''Rheinische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'', RhE) was along with the Cologne-Minden Railway Company (CME) and the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company (BME) one of the railway companies that in the mid-19th century built the first railways in the Ruhr and large parts of today's North Rhine-Westphalia. Foundation The industrialists of the Rhineland and the Bergisches Land, then part of Prussia, sought to avoid paying the high tolls for using the Rhine imposed by the Netherlands and very early in its development, saw the possibility of the new means of transport, the railway. As early as the 1830s committees were established the cities of the Rhineland to promote proposals for building railways. Some of the members of the Cologne committee under David Hansemann (1790–1864)—a merchant and banker from Aachen—and the Aachen Committee favoured a railway line through Belgium to the seaport of Antwerp via Liege. Belgium, which had bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Hesse
The Grand Duchy of Hesse and by Rhine (german: link=no, Großherzogtum Hessen und bei Rhein) was a grand duchy in western Germany that existed from 1806 to 1918. The Grand Duchy originally formed from the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt in 1806 as the Grand Duchy of Hesse (german: Großherzogtum Hessen, link=no). It assumed the name Hesse and bei Rhein in 1816 to distinguish itself from the Electorate of Hesse, which had formed from neighbouring Hesse-Kassel. Colloquially, the grand duchy continued to be known by its former name of Hesse-Darmstadt. In 1806, the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt seceded from the Holy Roman Empire and joined Napoleon's new Confederation of the Rhine. The country was promoted to the status of Grand Duchy and received considerable new territories, principally the Duchy of Westphalia. After the French defeat in 1815, the Grand Duchy joined the new German Confederation. Westphalia was taken by Prussia, but Hesse received Rheine-Hesse in return. A consti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick II, more commonly known as Frederick the Great, who was the third son of Frederick William I.Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Frederick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliaries (Roman Military)
The (, lit. "auxiliaries") were introduced as non-citizen troops attached to the citizen legions by Augustus after his reorganisation of the Imperial Roman army from 30 BC. By the 2nd century, the Auxilia contained the same number of infantry as the legions and, in addition, provided almost all of the Roman army's cavalry (especially light cavalry and archers) and more specialised troops. The ''auxilia'' thus represented three-fifths of Rome's regular land forces at that time. Like their legionary counterparts, auxiliary recruits were mostly volunteers, not conscripts. The Auxilia were mainly recruited from the ''peregrini'', free provincial subjects who did not hold Roman citizenship and constituted the vast majority of the population in the 1st and 2nd centuries (c. 90% in the early 1st century). In contrast to the legions, which only admitted Roman citizens, members of the Auxilia could be recruited from territories outside of Roman control. Reliance on the various co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |