|
Bill Robertson (Australian Intelligence Officer)
William Thomas Robertson, (2 February 1917 – 2 January 2011) was the fourth Director-General of the Australian Secret Intelligence Service, Director-General of the Australian Secret Intelligence Service (ASIS), from 1968 until 1975, when was dismissed by Prime Minister Gough Whitlam; the reasons for Roberton's dismissal have remained a matter of controversy. During the Second World War, Robertson served as an Australian Army officer. He served as an infantry officer in North African campaign, North Africa, where he was wounded in action, and in Greek campaign, Greece, before being appointed to staff officer, staff roles in New Guinea campaign, New Guinea. During 1944–45, he was attached to the British Army in North West Europe campaign, North West Europe and held senior staff roles with two different British Division (military), divisions. In 1952, Robertson was a founding member of the ASIS; its existence was to remain Crimes Act 1914, officially secret for two and a half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Director-General Of The Australian Secret Intelligence Service
The Director-General of the Australian Secret Intelligence Service is the executive officer of the Australian Secret Intelligence Service (ASIS), Australia's foreign intelligence agency. The Director-General of ASIS is directly responsible to the Minister for Foreign Affairs A foreign affairs minister or minister of foreign affairs (less commonly minister for foreign affairs) is generally a cabinet minister in charge of a state's foreign policy and relations. The formal title of the top official varies between cou ..., and regularly meets with the Minister to brief them on ASIS activities. Australian Secret Intelligence Service. The current director is Kerri Hartland. List of directors-general There have been ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets '' infant''. The individual-soldier term ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant Colonel
Lieutenant colonel ( , ) is a rank of commissioned officers in the armies, most marine forces and some air forces of the world, above a major and below a colonel. Several police forces in the United States use the rank of lieutenant colonel. The rank of lieutenant colonel is often shortened to simply "colonel" in conversation and in unofficial correspondence. Sometimes, the term 'half-colonel' is used in casual conversation in the British Army. In the United States Air Force, the term 'light bird' or 'light bird colonel' (as opposed to a 'full bird colonel') is an acceptable casual reference to the rank but is never used directly towards the rank holder. A lieutenant colonel is typically in charge of a battalion or regiment in the army. The following articles deal with the rank of lieutenant colonel: * Lieutenant-colonel (Canada) * Lieutenant colonel (Eastern Europe) * Lieutenant colonel (Turkey) * Lieutenant colonel (Sri Lanka) * Lieutenant colonel (United Kingdom) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
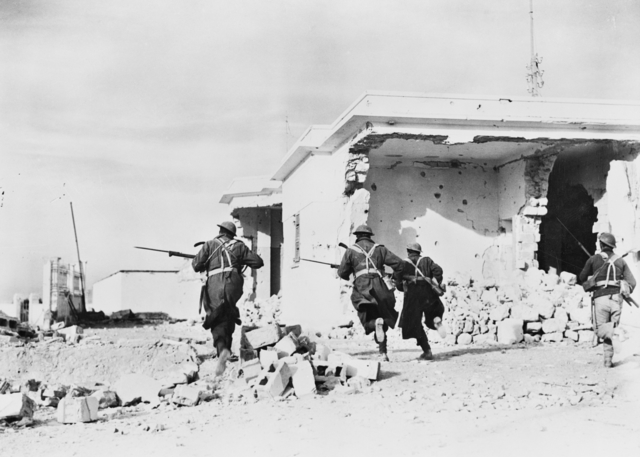
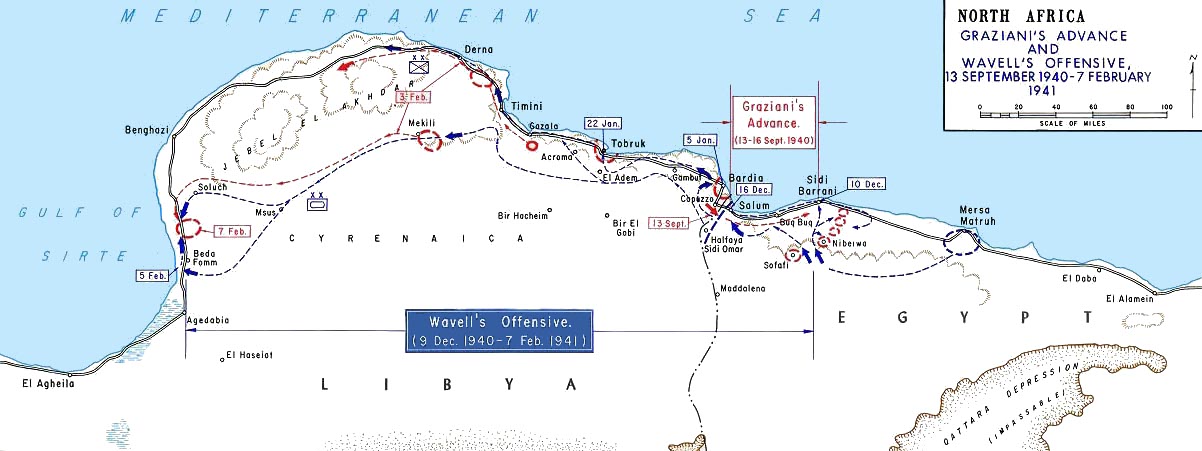
British Capture Of Tobruk
The British capture of Tobruk was a battle fought between 21 and 22 January 1941, as part of Operation Compass, the first offensive of the Western Desert Force (WDF) in the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. After defeating the Italians in the Battle of Bardia (3–5 January 1941), the 6th Australian Division and the 7th Armoured Division pressed on and made contact with the Italian garrison in Tobruk on 6 January. The Italians had fortified Tobruk, their only naval base in Eastern Cyrenaica, before the war but after being routed at the Attack on Nibeiwa, the Battle of Sidi Barrani and the Battle of Bardia the Italian 10th Army had lost eight of its nine divisions and had only the 61st Infantry Division "Sirte" and stragglers to defend the port. The Tobruk garrison suffered 2,048 casualties and 20,000 men were taken prisoner for 400 Australian and British casualties. The WDF continued its westwards advance towards Derna and Mechili. Background Operation Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th Division (Australia)
The 6th Division was an infantry division of the Australian Army. It was raised briefly in 1917 during World War I, but was broken up to provide reinforcements before seeing action. It was not re-raised until the outbreak of World War II, when it was formed as a unit of the Second Australian Imperial Force (2nd AIF). Throughout 1940–41 it served in the North African Campaign, the Greek campaign, on Crete and in Syria, fighting against the Germans, Italians and Vichy French. In 1942, the division left the Middle East and returned to Australia to meet the threat of Japan's entry into the war. Part of the division garrisoned Ceylon for a short period of time, before the division was committed to the New Guinea campaign. In New Guinea, its component brigades had a major role in the successful counter-offensive along the Kokoda Track, at Buna–Gona and around Salamaua–Lae in 1942–43. Throughout late 1943–44, the division was re-organised in Australia before being comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2/8th Australian Infantry Battalion
The 2/8th Battalion was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army that served during World War II. Raised as part of the Second Australian Imperial Force at Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, Victoria on 30 October 1939, the 2/8th was initially attached to the 17th Brigade (Australia), 17th Brigade, 6th Division (Australia), 6th Division. It was later transferred to the 19th Brigade (Australia), 19th Brigade and with this formation the battalion saw action in Egypt, Libya, Greece and Crete before returning to Australia. A period of garrison duty in Darwin followed in 1942–1943, after which the battalion concentrated with other 6th Division units on the Atherton Tablelands, remaining there throughout 1943–1944. In late 1944, the battalion was sent to New Guinea to fight the Japanese as part of the Aitape–Wewak campaign. The battalion was disbanded at Puckapunyal on 14 December 1945. History Formation The 2/8th Battalion was established at the Royal Melbourne Showgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captain (OF-2)
The army rank of captain (from the French ) is a commissioned officer rank historically corresponding to the command of a company of soldiers. The rank is also used by some air forces and marine forces. Today, a captain is typically either the commander or second-in-command of a company or artillery battery (or United States Army cavalry troop or Commonwealth squadron). In the Chinese People's Liberation Army, a captain may also command a company, or be the second-in-command of a battalion. In some militaries, such as United States Army and Air Force and the British Army, captain is the entry-level rank for officer candidates possessing a professional degree, namely, most medical professionals (doctors, pharmacists, dentists) and lawyers. In the U.S. Army, lawyers who are not already officers at captain rank or above enter as lieutenants during training, and are promoted to the rank of captain after completion of their training if they are in the active component, or after a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimes Act 1914
The ''Crimes Act 1914'' (Cth) is an Act of the Parliament of Australia which addresses the most serious federal offences — that is, crimes against the Commonwealth. It was the first major federal criminal law since the Federation of Australia in 1901, since most criminal law of Australia was, and still is, handled by the states and territories rather than at the federal level. Act Amongst other things, Volume 2 of the Act deals with offences against the administration of justice in federal proceedings, piracy, and offences relating to postal services. Structure Volume 1 *Part I – Preliminary; *Part IAA – Search, information gathering, arrest and related powers (other than powers under delayed notification search warrants; *Part IAAA – Delayed notification search warrants; *Part IAAB – Monitoring of compliance with control orders etc.; *Part IAB – Controlled operations; *Part IABA – Integrity testing; *Part IAC – Assumed identities; *Part IACA – Witn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division (military)
A division is a large military unit or formation, usually consisting of between 6,000 and 25,000 soldiers. In most armies, a division is composed of several regiments or brigades; in turn, several divisions typically make up a corps. Historically, the division has been the default combined arms unit capable of independent operations. Smaller combined arms units, such as the American regimental combat team (RCT) during World War II, were used when conditions favored them. In recent times, modern Western militaries have begun adopting the smaller brigade combat team (similar to the RCT) as the default combined arms unit, with the division they belong to being less important. While the focus of this article is on army divisions, in naval usage " division" has a completely different meaning, referring to either an administrative/functional sub-unit of a department (e.g., fire control division of the weapons department) aboard naval and coast guard ships, shore commands, and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North West Europe Campaign
The North West Europe campaign was a campaign by the Commonwealth of Nations, British Commonwealth armed forces in North West Europe, including its skies and adjoining waters during World War II. The term Western Front (WWII), Western Front has also sometimes been used informally. The United States military refers to this campaign as the European Theater of Operations. Hence the battle honour "North-West Europe" was awarded to any unit involved in land, sea and air campaigns and operations in, over or near Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway and the United Kingdom during World War II. It includes many more specific campaigns and/or battle honours. Subsidiary battle honours The battle honour "North-West Europe campaign of 1940, was awarded to some army units that were involved in the Battle of France, and was restricted to the Belgian and French Channel ports. During this campaign, the French Army was responsible for the rest of the Western Front from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkhas, and 28,330 volunteer reserve personnel. The modern British Army traces back to 1707, with antecedents in the English Army and Scots Army that were created during the Restoration in 1660. The term ''British Army'' was adopted in 1707 after the Acts of Union between England and Scotland. Members of the British Army swear allegiance to the monarch as their commander-in-chief, but the Bill of Rights of 1689 and Claim of Right Act 1689 require parliamentary consent for the Crown to maintain a peacetime standing army. Therefore, Parliament approves the army by passing an Armed Forces Act at least once every five years. The army is administered by the Ministry of Defence and commanded by the Chief of the General Staff. The Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea Campaign
The New Guinea campaign of the Pacific War lasted from January 1942 until the end of the war in August 1945. During the initial phase in early 1942, the Empire of Japan invaded the Australian-administered Mandated Territory of New Guinea (23 January) and the Australian Territory of Papua (21 July) and overran western New Guinea (beginning 29/30 March), which was a part of the Netherlands East Indies. During the second phase, lasting from late 1942 until the Japanese surrender, the Allies—consisting primarily of Australian forces—cleared the Japanese first from Papua, then the Mandate and finally from the Dutch colony. The campaign resulted in a crushing defeat and heavy losses for the Empire of Japan. As in most Pacific War campaigns, disease and starvation claimed more Japanese lives than enemy action. Most Japanese troops never even came into contact with Allied forces, and were instead simply cut off and subjected to an effective blockade by Allied naval forces. Garrison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)