|
Biesenthal
Biesenthal is a town in the district of Barnim in Brandenburg, Germany. It is the administrative seat of the ''Amt'' ("collective municipality") Amt Biesenthal-Barnim. Geography The town is located on the Finow river, about northeast of Berlin (centre). The surrounding Biesenthal Basin is part of the Barnim Plateau and the Barnim Nature Park, characterised by numerous kames and glacial lakes stemming from the Weichselian glaciation. History In the early Middle Ages, the region was settled by Polabian Slavs. Conquered by the Ascanian margraves of Brandenburg, ''Bizdal'' was first mentioned in a 1258 deed. A local parish was already documented in 1265; the present-day fieldstone church was probably erected at this time. The settlement on the ''Via Imperii'' trade route to Berlin was vested with market rights by Margrave John V in 1315. A castle was mentioned in 1337, it was purchased by the Hohenzollern elector John George of Brandenburg in 1577. Its ruins were cleared away aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biesenthal Rathaus
Biesenthal is a town in the district of Barnim in Brandenburg, Germany. It is the administrative seat of the ''Amt'' ("collective municipality") Amt Biesenthal-Barnim. Geography The town is located on the Finow river, about northeast of Berlin (centre). The surrounding Biesenthal Basin is part of the Barnim Plateau and the Barnim Nature Park, characterised by numerous kames and glacial lakes stemming from the Weichselian glaciation. History In the early Middle Ages, the region was settled by Polabian Slavs. Conquered by the Ascanian margraves of Brandenburg, ''Bizdal'' was first mentioned in a 1258 deed. A local parish was already documented in 1265; the present-day fieldstone church was probably erected at this time. The settlement on the ''Via Imperii'' trade route to Berlin was vested with market rights by Margrave John V in 1315. A castle was mentioned in 1337, it was purchased by the Hohenzollern elector John George of Brandenburg in 1577. Its ruins were cleared away after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amt Biesenthal-Barnim
Amt Biesenthal-Barnim is an ''Amt'' ("collective municipality") in the district of Barnim, in Brandenburg, Germany. Its seat is in the town Biesenthal. The ''Amt'' Biesenthal-Barnim consists of the following municipalities: #Biesenthal #Breydin #Marienwerder #Melchow # Rüdnitz #Sydower Fließ Demography File:Bevölkerungsentwicklung Amt Biesenthal-Barnim.pdf, Development of Population since 1875 within the Current Boundaries (Blue Line: Population; Dotted Line: Comparison to Population Development of Brandenburg state; Grey Background: Time of Nazi rule; Red Background: Time of Communist rule) File:Bevölkerungsprognosen Amt Biesenthal-Barnim.pdf, Recent Population Development and Projections (Population Development before Census 2011 (blue line); Recent Population Development according to the Census in Germany A national census in Germany (german: Volkszählung) was held every five years from 1875 to 1910. After the World Wars, only a few full population censuses have been h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnim Plateau
The Barnim Plateau is a plateau which is occupied by the northeastern parts of Berlin and the surrounding federal state of Brandenburg in Germany. Boundaries and Subdivision Boundaries The limits of the plateau are easily definable. The southern boundary is marked by the Berlin Valley, through which the River Spree flows. To the west, the boundary between Barnim and the Glien Plateau is marked by a north-south glacial valley. To the north and north east is the boundary with the Eberswald Valley, and in the east, Lubusz Land. Subdivision Traditionally the plateau is divided into the Upper and Lower Barnim, separated by a line running between Strausberg and Eberswalde. Typically, Lower Barnim does not reach higher than 80 metres above mean sea level (AMSL) whereas Upper Barnim is generally more than 100 metres AMSL. The highest point of the plateau is Semmelberg which stands at 157 metres AMSL. Settlements Until the growth of Berlin in the 19th century, Barnim was only spar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnim
Barnim () is a district in Brandenburg, Germany. It is bounded by (from the east and clockwise) Poland, the district of Märkisch-Oderland, the city state of Berlin and the districts of Oberhavel and Uckermark. History The name "Barnim" emerged in the 13th century and was applied to a large forest region east of the Havel and north of the Spree on the homonymous plateau, where noblemen used to hunt. The present district is roughly identical with, but somewhat smaller than this historical region. The district was established in 1993 by merging the former districts of Bernau and Eberswalde. Geography Barnim extends from the Oder River to the outskirts of Berlin. The Oder River forms the eastern border. From here the Oder Havel Canal (connecting Oder and Havel) and the historical Finow Canal lead westwards to Eberswalde and beyond. The portions north of these artificial waterways are called Schorfheide. This is a forest region with several large lakes, e.g. Werbellinsee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin–Szczecin Railway
The Berlin–Szczecin railway, also known in German as the Stettiner Bahn (Stettin Railway) is a mainline railway built by the ''Berlin-Stettin Railway Company'' between the German capital of Berlin and the now Polish city of Szczecin, then part of Prussia and known as Stettin. It is one of the oldest lines in Germany, built in 1842 and 1843 and was the company's trunk line. The line was duplicated between Berlin and Angermünde in 1863 and between Angermünde and Szczecin in 1873. The line is still used by regional trains on the Berlin–Angermünde route (some to or from Stralsund) and on the Angermünde–Szczecin route as well as the long-distance trains on the entire Berlin–Szczecin line. Between central Berlin and the suburban station of Bernau the line also has its own suburban tracks used by the Berlin S-Bahn. The line is also a major route for the transport of freight between Germany and Poland. Except for the section between Passow and Szczecin Gumieńce the entir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Subcamps Of Sachsenhausen
The following is a list of subcamps of the Sachsenhausen concentration camp established by Nazi Germany. The main camp, with around 50 barracks for slave-labour prisoners, was located from Berlin, and operated between 1938 and April 22, 1945. During World War II the prisoners included Germans, Poles, Soviet POWs, Roma, and later Jews. It is estimated that the number of victims of Sachsenhausen was 30,00035,000.List of subcamps of Sachsenhausen at Jewishgen.org Dozens of subcamps of Sachsenhausen existed directly in the capital city, serving individual business operators and factories. Sub-camps # # Beerfelde ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after 1922, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. The army was established in January 1918. The Bolsheviks raised an army to oppose the military confederations (especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army) of their adversaries during the Russian Civil War. Starting in February 1946, the Red Army, along with the Soviet Navy, embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces; taking the official name of "Soviet Army", until its dissolution in 1991. The Red Army provided the largest land warfare, land force in the Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its Soviet invasion of Manchuria, invasion of Manchuria assisted the unconditional surrender of Empire of Japan, Imperial Japan. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Occupation Zone
The Soviet Occupation Zone ( or german: Ostzone, label=none, "East Zone"; , ''Sovetskaya okkupatsionnaya zona Germanii'', "Soviet Occupation Zone of Germany") was an area of Germany in Central Europe that was occupied by the Soviet Union as a communist area, established as a result of the Potsdam Agreement on 1 August 1945. On 7 October 1949 the German Democratic Republic (GDR), commonly referred to in English as East Germany, was established in the Soviet Occupation Zone. The SBZ was one of the four Allied occupation zones of Germany created at the end of World War II with the Allied victory. According to the Potsdam Agreement, the Soviet Military Administration in Germany (German initials: SMAD) was assigned responsibility for the middle portion of Germany. Eastern Germany beyond the Oder-Neisse line, equal in territory to the SBZ, was to be annexed by Poland and its population expelled, pending a final peace conference with Germany. By the time forces of the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sachsenhausen Concentration Camp
Sachsenhausen () or Sachsenhausen-Oranienburg was a German Nazi concentration camp in Oranienburg, Germany, used from 1936 until April 1945, shortly before the defeat of Nazi Germany in May later that year. It mainly held political prisoners throughout World War II. Prominent prisoners included Joseph Stalin's oldest son, Yakov Dzhugashvili; assassin Herschel Grynszpan; Paul Reynaud, the penultimate Prime Minister of France; Francisco Largo Caballero, Prime Minister of the Second Spanish Republic during the Spanish Civil War; the wife and children of the Crown Prince of Bavaria; Ukrainian nationalist leader Stepan Bandera; and several enemy soldiers and political dissidents. Sachsenhausen was a labor camp, outfitted with several subcamps, a gas chamber, and a medical experimentation area. Prisoners were treated inhumanely, fed inadequately, and killed openly. After World War II, when Oranienburg was in the Soviet Occupation Zone, the structure was used by the NKVD as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
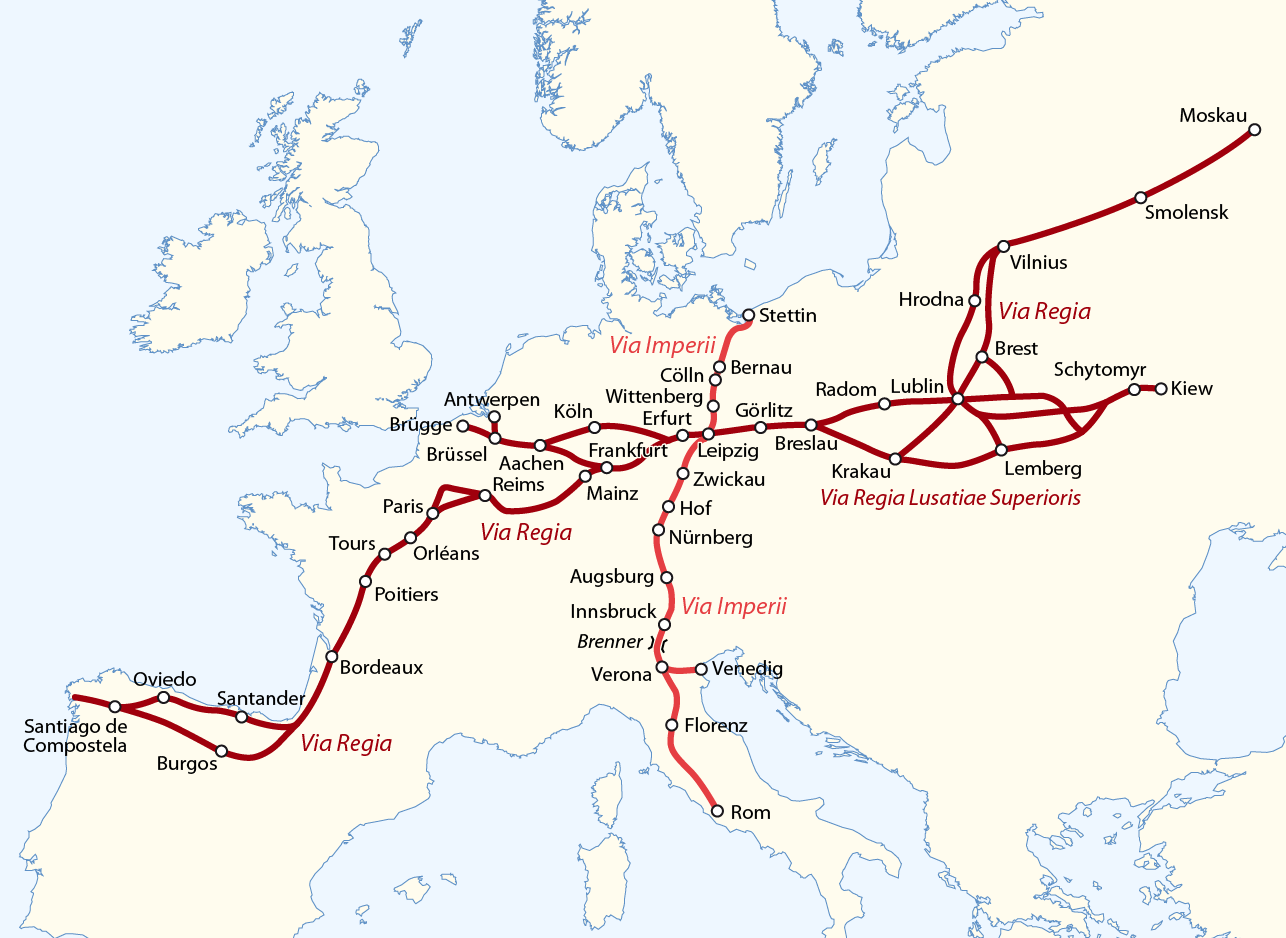
Via Imperii
Via Imperii (Imperial Road) was one of the most important of a class of roads known collectively as imperial roads (''german: Reichsstraßen'') of the Holy Roman Empire. This old trade route ran in a south–north direction from Venice on the Adriatic Sea and Verona in the Kingdom of Italy across the Brenner Pass through Germany to the Baltic coast passing the following cities: * Innsbruck in the County of Tyrol * Augsburg in the Prince-Bishopric of Augsburg * the Imperial city of Nuremberg * Bayreuth, Berneck, Münchberg and Hof in the Principality of Bayreuth * Plauen, Mylau and Reichenbach in the Vogtland region * Zwickau, Altenburg, Regis, Borna, Markkleeberg and Connewitz in the Margraviate of Meissen * Leipzig – intersection with east–west Via Regia * Wittenberg in Saxe-Wittenberg * Cölln/Berlin, capital of Brandenburg * Bernau bei Berlin * Stettin in the Duchy of Pomerania The cities on the route held the privilege of staple right, merchants were obliged t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle, famine, and disease, while some areas of what is now modern Germany experienced population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. Until the 20th century, historians generally viewed it as a continuation of the religious struggle initiated by the 16th-century Reformation within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Lutheran and Catholic states, but over the next 50 years the expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries destabilised the settlement. While most modern commentators accept differences over religion and Imperial authority were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |