|
Bezymyanka Airport
Bezymyanka Airport is an experimental aerodrome in the Aviakor aviation plant in the city of Samara, Russia. It is located east of the Bezymyanka railroad station in the Kirov district of Samara, east of the city center. To the east of the airport, the Smyshlyaevka airport is located. To the south, the settlements Chkalov, Padovka, and the Samara River. To the north, the Aviakor aviation plant and the TsSKB-Progress plant. The airport has a class 1 rating and can serve most airplane and helicopter types. The total runway length is . Founded in 1942, the first runway utilized bricks as its pavement. After World War II , the aviation plants 1 and 18 were evacuated to Kuibyshev (now known as Samara) from Moscow and Voronezh. At the earliest possible date they set up the production of Il-2 aircraft. In the second part of the 20th century, the airport served as the testing ground for a number of Tupolev, Ilyushin and Antonov aircraft produced by the above-mentioned aviation plants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samara, Russia
Samara ( rus, ąĪą░ą╝ą░╠üčĆą░, p=s╔É╦łmar╔Ö), known from 1935 to 1991 as Kuybyshev (; ), is the largest city and administrative centre of Samara Oblast. The city is located at the confluence of the Volga and the Samara rivers, with a population of over 1.14 million residents, up to 1.22 million residents in the urban agglomeration, not including Novokuybyshevsk, which is not conurbated. The city covers an area of , and is the eighth-largest city in Russia and tenth agglomeration, the third-most populous city on the Volga, as well as the Volga Federal District. Formerly a closed city, Samara is now a large and important social, political, economic, industrial, and cultural centre in Russia and hosted the European UnionŌĆöRussia Summit in May 2007. It has a continental climate characterised by hot summers and cold winters. The life of Samara's citizens has always been intrinsically linked to the Volga River, which has not only served as the main commercial thoroughfare of Russia th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilyushin
The public joint stock company Ilyushin Aviation Complex, operating as Ilyushin (russian: ąśą╗čīčÄ╠üčłąĖąĮ) or as Ilyushin Design Bureau, is a former Soviet and now a Russian aircraft manufacturer and design bureau, founded in 1933 by Sergey Vladimirovich Ilyushin. Soviet/Russian nomenclature identifies aircraft from Ilyushin with the prefix "Il-" ( ru , ąśą╗-). Ilyushin has its head office in Aeroport District, Northern Administrative Okrug, Moscow. History Ilyushin was established under the Soviet Union. Its operations began on 13 January 1933, by order of P. I. Baranov, People's Commissar of the Heavy Industry and the Head of the Main Department of Aviation Industry. In 1970, the position of chief designer was taken by G. V. Novozhilov In 2006 the Russian government merged Ilyushin with Mikoyan, Irkut, Sukhoi, Tupolev, and Yakovlev under a new company named United Aircraft Corporation. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airports Built In The Soviet Union
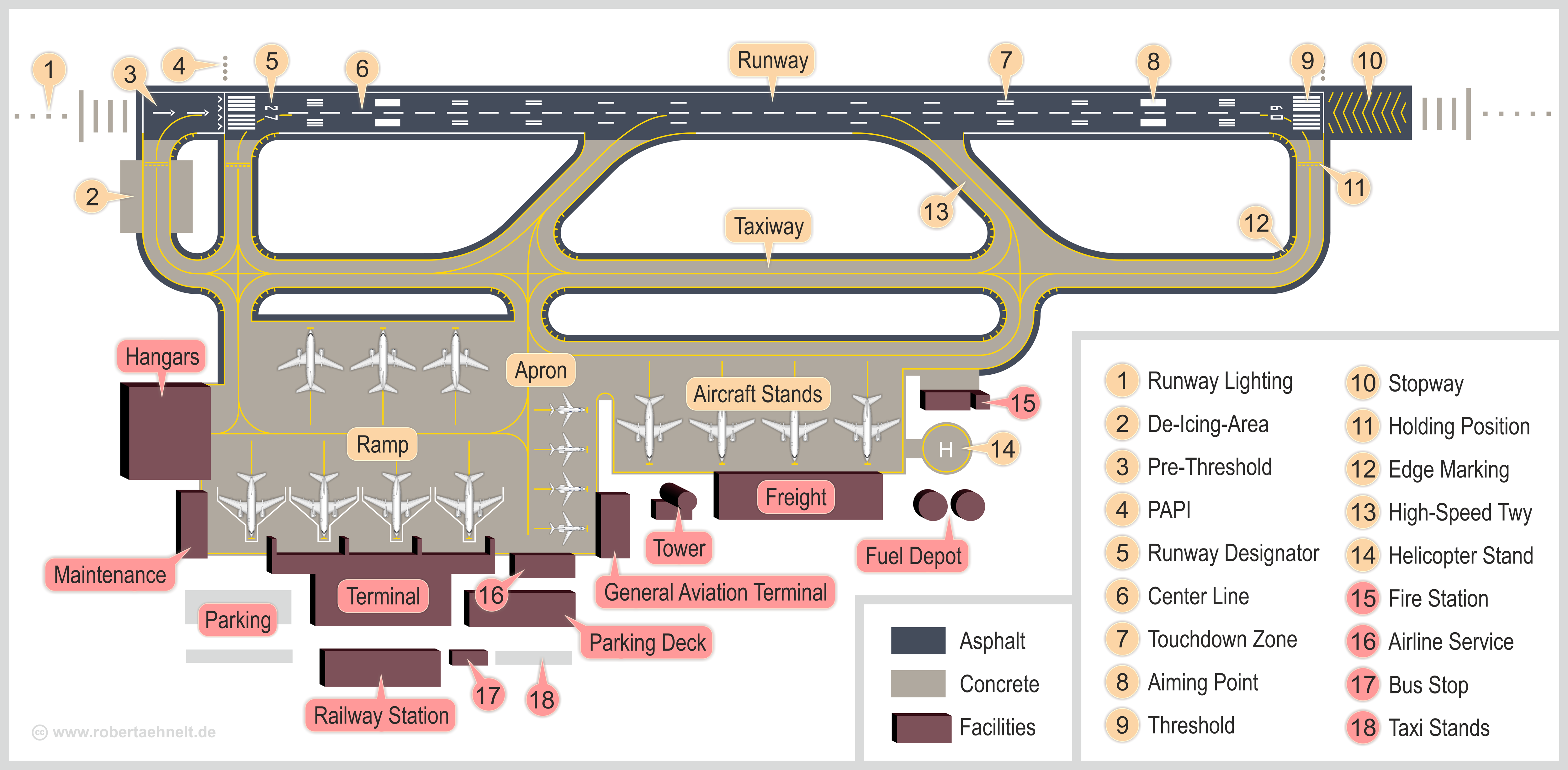
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Operating airports is extremely complicated, with a complex system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for tourism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
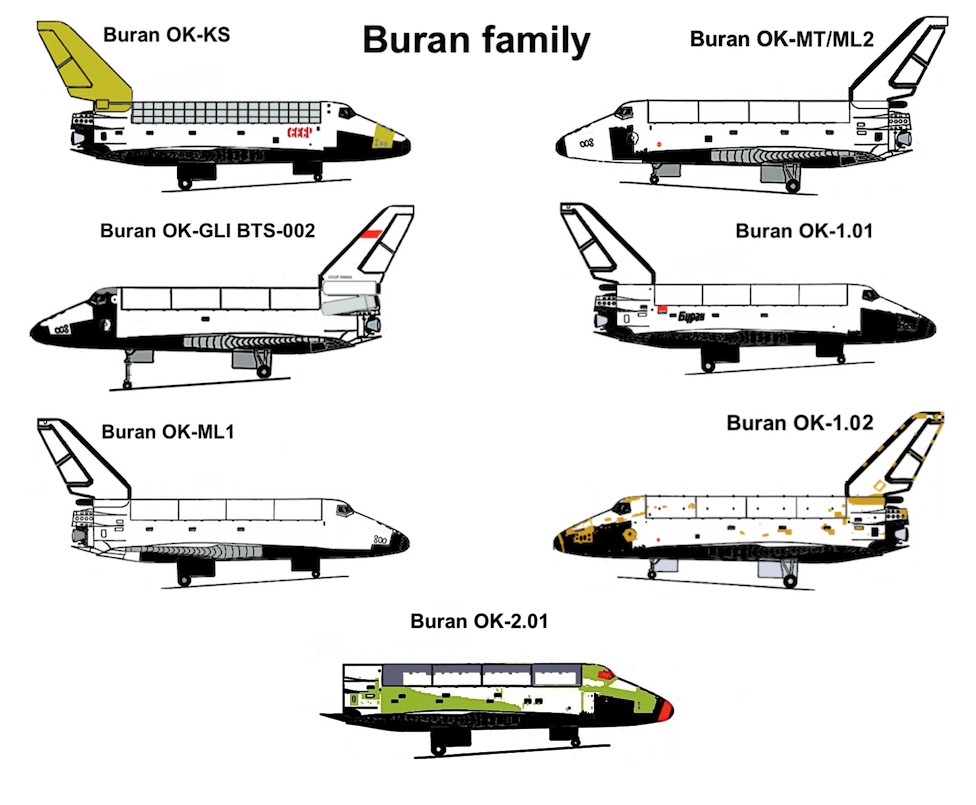
Buran Shuttle
''Buran'' (russian: ąæčāčĆą░ąĮ, , meaning "Snowstorm" or "Blizzard"; GRAU index serial number: 11F35 1K, construction number: 1.01) was the first spaceplane to be produced as part of the Soviet/Russian Buran program. Besides describing the first operational Soviet/Russian shuttle orbiter, "Buran" was also the designation for the entire Soviet/Russian spaceplane project and its orbiters, which were known as "Buran-class orbiters". Buran completed one uncrewed spaceflight in 1988, and was destroyed in the 2002 collapse of its storage hangar. The Buran-class orbiters used the expendable Energia rocket, a class of super heavy-lift launch vehicle. It is named after the Asian wind. Construction The construction of the Buran spacecraft began in 1980, and by 1984 the first full-scale orbiter was rolled out. Over 1000 companies all over the Soviet Union were involved in construction and development. The Buran spacecraft was made to be launched on the Soviet Union's super-heavy lift ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VM-T
The Myasishchev VM-T ''Atlant'' (Russian: ''ą£čÅčüąĖčēąĄą▓ ąÆą£-ąó ┬½ąÉčéą╗ą░ąĮčé┬╗'' ( "Atlas"), with the "VM-T" ("BM-T") standing for Vladimir MyasishchevTransport) was a variant of Myasishchev's M-4 ''Molot'' bomber (the "3M"), re-purposed as a strategic-airlift airplane An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad spe .... The VM-T was modified to carry Booster (rocketry), rocket boosters and the Soviet Union, Soviet spaceplane, space shuttles of the Buran program, ''Buran'' program. It is also known as the 3M-T. Design and development The design was conceived in 1978 when Myasishchev was asked to solve the problem of transporting rockets and other large space vehicles to the Baikonur Cosmodrome. Engineers used an old 3M (a modified M-4 bomber) and replaced the empennage wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikonur (spaceport)
''Baiqo├▒yr ─¤ary┼¤ aila─¤y'' rus, ąÜąŠčüą╝ąŠą┤čĆąŠą╝ ąæą░ą╣ą║ąŠąĮčāčĆ''Kosmodrom Baykonur'' , image = Baikonur Cosmodrome Soyuz launch pad.jpg , caption = The Baikonur Cosmodrome's " Gagarin's Start" Soyuz launch pad prior to the rollout of Soyuz TMA-13, 10 October 2008. , LID = GC0015 , type = Spaceport , owner-oper = RoscosmosRussian Aerospace Forces , location = Kazakhstan (leased to Russia) , opened = , built = , timezone = UTC+06:00 , utc = +06:00 , elevation-m = 90 , metric-elev = y , coordinates = , website = , image_map = , image_mapsize = , image_map_alt = , image_map_caption = , pushpin_map = Kazakhstan#Russia#Soviet Union , pushp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
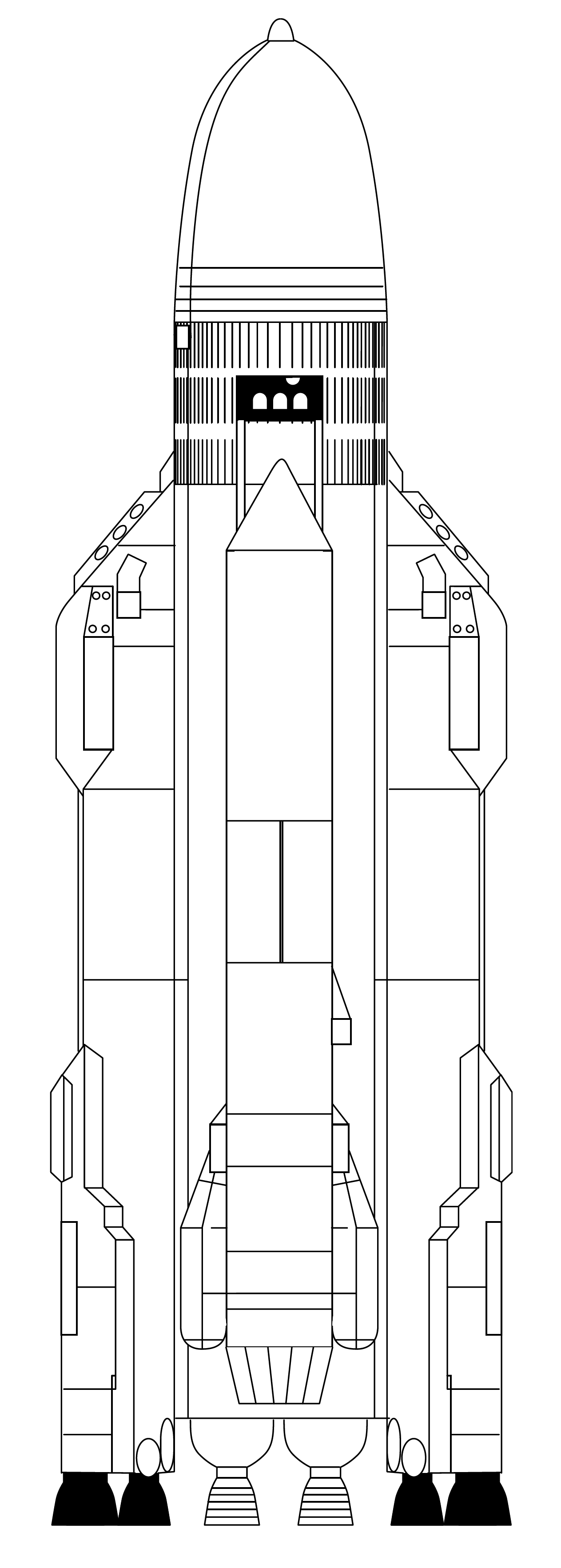
Energia (rocket)
Energia (russian: ąŁąĮąĄčĆą│ąĖčÅ, Energiya, Energy; GRAU 11K25) was a 1980s super-heavy lift launch vehicle. It was designed by NPO Energia of the Soviet Union as part of the Buran programme, Buran program for a variety of payloads including the Buran (spacecraft), Buran spacecraft. Control system main developer enterprise was the Khartron NPO "Electropribor". The Energia used four strap-on boosters each powered by a four-chamber RD-170 engine burning kerosene/Liquid oxygen, LOX, and a central core stage with four single-chamber RD-0120 (11D122) engines fueled by liquid hydrogen/LOX. The launch vehicle had two functionally different operational variants: Energia-Polyus, the initial test configuration, in which the Polyus (spacecraft), Polyus system was used as a final stage intended to put the payload into orbit, and Energia-Buran, in which the Buran programme, ''Buran'' orbiter was the payload and the source of the orbit insertion impulse. The launch vehicle had the capacity to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesetsk Cosmodrome
Plesetsk Cosmodrome ( rus, ąÜąŠčüą╝ąŠą┤čĆąŠą╝ ┬½ą¤ą╗ąĄčüąĄčåą║┬╗, r=Kosmodrom "Plesetsk", p=k╔Ösm╔É╦łdrom pl╩▓╔¬╦łs╩▓et═Īsk) is a Russian spaceport located in Mirny, Arkhangelsk Oblast, about 800 km north of Moscow and approximately 200 km south of Arkhangelsk, the cosmodrome dates to 1957. Originally developed as an ICBM site for the R-7 missile, it also served for numerous satellite launches using the R-7 and other rockets. Its high latitude makes it useful only for certain types of launches, especially the Molniya orbits, so for much of the site's history it functioned as a secondary location, with most orbital launches taking place from Baikonur, in the Kazakh SSR. With the end of the Soviet Union, Baikonur became a foreign territory, and Kazakhstan charged $115 million usage fees annually. Consequently, Plesetsk has seen considerably more activity since the 2000s. Overview Plesetsk () is used especially for military satellites placed into high inclination an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikonur Cosmodrome
The Baikonur Cosmodrome ( kk, ąæą░ą╣ęøąŠęŻčŗčĆ ęōą░čĆčŗčł ą░ą╣ą╗ą░ęōčŗ, translit=Baiqo├▒yr ─¤ary┼¤ aila─¤y, ; russian: ąÜąŠčüą╝ąŠą┤čĆąŠą╝ ąæą░ą╣ą║ąŠąĮčāčĆ, translit=Kosmodrom Baykonur, ) is a spaceport in an area of southern Kazakhstan leased to Russia. The Cosmodrome is the world's first spaceport for orbital and human launches and the largest (in area) operational Spaceport, space launch facility. All crewed Russian spaceflights are launched from Baikonur. The spaceport is in the Kazakh Steppe, desert steppe of Baikonur, about east of the Aral Sea and north of the river Syr Darya. It is near the Tyuratam railway station and is about above sea level. The spaceport is currently leased by the Government of Kazakhstan, Kazakh Government to the Russian Federation until 2050 and is managed jointly by the Roscosmos State Corporation, Roscosmos and the Russian Aerospace Forces. The shape of the area leased is an ellipse, measuring eastŌĆōwest by northŌĆōsouth, with the cosmodrome at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which is small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as a group, forming constellations. Because of the high launch cost to space, satellites are designed to be as lightweight and robust as possible. Most communication satellites are radio relay stations in orbit and carry dozens of transponders, each with a bandwidth of tens of megahertz. Satellites are placed from the surface to orbit by launch vehicles, high enough to avoid orbital decay by the atmosphere. Satellites can then change or maintain the orbit by propuls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Rocket
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload (spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pads, supported by a launch control center and systems such as vehicle assembly and fueling. Launch vehicles are engineered with advanced aerodynamics and technologies, which contribute to large operating costs. An orbital launch vehicle must lift its payload at least to the boundary of space, approximately and accelerate it to a horizontal velocity of at least . Suborbital vehicles launch their payloads to lower velocity or are launched at elevation angles greater than horizontal. Practical orbital launch vehicles are multistage rockets which use chemical propellants such as solid fuel, liquid hydrogen, kerosene, liquid oxygen, or Hypergolic propellants. Launch vehicles are classified by their orbital payload capacity, ranging from small-, medium-, heavy- to super-heavy lift. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonov
Antonov State Enterprise ( uk, ąöąĄčƹȹ░ą▓ąĮąĄ ą┐č¢ą┤ą┐čĆąĖčöą╝čüčéą▓ąŠ ┬½ąÉąĮč鹊ąĮąŠą▓┬╗), formerly the Aeronautical Scientific-Technical Complex named after Antonov (Antonov ASTC) ( uk, ąÉą▓č¢ą░čåč¢ą╣ąĮąĖą╣ ąĮą░čāą║ąŠą▓ąŠ-č鹥čģąĮč¢čćąĮąĖą╣ ą║ąŠą╝ą┐ą╗ąĄą║čü č¢ą╝ąĄąĮč¢ ąÉąĮč鹊ąĮąŠą▓ą░, ÉąØąóąÜ č¢ą╝. ąÉąĮč鹊ąĮąŠą▓ą░}), and earlier the Antonov Design Bureau, for its chief designer, Oleg Antonov, is a Ukrainian aircraft manufacturing and services company. Antonov's particular expertise is in the fields of very large aeroplanes and aeroplanes using unprepared runways. Antonov (model prefix "An-") has built a total of approximately 22,000 aircraft, and thousands of its planes are operating in the former Soviet Union and in developing countries. Antonov StC is a state-owned commercial company. Its headquarters and main industrial grounds were originally located in Novosibirsk, and in 1952 were transferred to Kyiv. On 12 May 2015 it was transferred from the Ministry of Economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)



