|
Bessan And Hakusan From Hideridake 2009-4-7
Bessan (; oc, Beçan) is a commune in the Hérault department of the Occitanie region in France. Its inhabitants are known as 'Bessanais' in French. Geography Built among vineyards on the river Hérault, Bessan is a mainly agricultural village. In the past, its port was used to ship wines and other spirits. Located a few kilometres from the Mediterranean Sea, it contains the Ricard distillery and Cactus Park botanical garden. History Around 600 BC, Greeks settled in Bessan on the oppidum of Monadière to trade. In 218 BC the Carthaginian general Hannibal crossed the region with his army and war elephants to attack the Romans, passing between Bessan and Montblanc. In 408-409 AD Béziers, Agde and the region were ransacked by an army of Germanic (Burgundians, Suevi, Vandals), Slavic (Alan) and other tribes. In 737, Charles Martel entered the province at the head of the French, temporarily pushing back the Saracens, and destroyed Béziers, Agde and the surrounding country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agde
Agde (; ) is a commune in the Hérault department in Southern France. It is the Mediterranean port of the Canal du Midi. Location Agde is located on the Hérault river, from the Mediterranean Sea, and from Paris. The Canal du Midi connects to the Hérault river at the Agde Round Lock ("L'Écluse Ronde d'Agde") just north of Agde, and the Hérault flows into the Mediterranean at Le Grau d'Agde. Agde station has high speed rail connections to Paris and Perpignan, and regional services to Narbonne, Montpellier and Avignon. History Foundation Agde (525 BCE) is one of the oldest towns in France, after Béziers (575 BCE) and Marseille (600 BCE). Agde ('' Agathe Tyche'', "good fortune") was a 5th-century BCE Greek colony settled by Phocaeans from Massilia. The Greek name was Agathe ( grc, Ἀγάθη). The symbol of the city, the bronze ''Ephebe of Agde'', of the 4th century BCE, recovered from the fluvial sands of the Hérault, was joined in December 2001 by two Early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joyeuse, Ardèche
Joyeuse (; oc, Juèsa) is a commune in the Ardèche department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in southern France. Geography Joyeuse lies in the historic region of Bas-Vivarais, in the valley of the Beaume, a tributary of the Ardèche. Population Personalities * Marcus Jallius Bassus, Roman consul, whose tomb is near Joyeuse * Charlemagne, founder of Joyeuse according to tradition * Duke Anne de Joyeuse * Cardinal François de Joyeuse * Duchess Henriette Catherine de Joyeuse *''la Grande Mademoiselle'' * François Boissel * See List of Dukes of Joyeuse Sights * The Château de Joyeuse is a classed as a monument historique. An earlier castle was largely destroyed and rebuilt in the 16th century. Today it serves as the mairie. * The Oratorian college is a monument historique. It was founded by Duchess Henriette in 1617 with the permission of Pope Paul V. It served as an educational institution until the French Revolution. It is now the home of a museum dealing with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Scipio
Antoine is a French given name (from the Latin ''Antonius'' meaning 'highly praise-worthy') that is a variant of Danton, Titouan, D'Anton and Antonin. The name is used in France, Switzerland, Belgium, Canada, West Greenland, Haiti, French Guiana, Madagascar, Benin, Niger, Burkina Faso, Ivory Coast, Guinea, Senegal, Mauritania, Western Sahara, Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Chad, Central African Republic, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Burundi, and Rwanda. It is a cognate of the masculine given name Anthony. Similar names include Antaine, Anthoine, Antoan, Antoin, Antton, Antuan, Antwain, Antwan, Antwaun, Antwoine, Antwone, Antwon and Antwuan. Feminine forms include Antonia, Antoinette, and (more rarely) Antionette. As a first name *Antoine Alexandre Barbier (1765–1825), a French librarian and bibliographer *Antoine Arbogast (1759–1803), a French mathematician *Antoine Arnauld (1612–1694), a French theologian, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causing the deaths of people, peaking in Europe from 1347 to 1351. Bubonic plague is caused by the bacterium ''Yersinia pestis'' spread by fleas, but it can also take a secondary form where it is spread by person-to-person contact via aerosols causing septicaemic or pneumonic plagues. The Black Death was the beginning of the second plague pandemic. The plague created religious, social and economic upheavals, with profound effects on the course of European history. The origin of the Black Death is disputed. The pandemic originated either in Central Asia or East Asia before spreading to Crimea with the Golden Horde army of Jani Beg as he was besieging the Genoese trading port of Kaffa in Crimea (1347). From Crimea, it was most likely carried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The appellation can also denote certain persons who hold a title of the peerage in the United Kingdom, or are entitled to courtesy titles. The collective "Lords" can refer to a group or body of peers. Etymology According to the Oxford Dictionary of English, the etymology of the word can be traced back to the Old English word ''hlāford'' which originated from ''hlāfweard'' meaning "loaf-ward" or "bread-keeper", reflecting the Germanic tribal custom of a chieftain providing food for his followers. The appellation "lord" is primarily applied to men, while for women the appellation " lady" is used. This is no longer universal: the Lord of Mann, a title previously held by the Queen of the United Kingdom, and female Lords Mayor are examples of women who are styled as "Lord". Historical usage Feudalism Under the feudal system, "lord" had a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amaury VI Of Montfort
Amaury de Montfort, Lord of Montfort-l'Amaury, (1192 – 1241) was the son of Simon de Montfort, 5th Earl of Leicester and Alix de Montmorency, and the older brother of Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester. Amaury inherited his father's French properties while his brother Simon inherited the English title of Earl of Leicester. Biography The Albigensian Crusade His father departed on the Albigensian Crusade in 1209. It is unknown when Amaury joined him in the south, but he could possibly arrive in spring 1210, when his mother came there bringing reinforcements for his father. He was knighted on 24 June 1213 in Castelnaudary in the course of a particularly solemn ceremony and continued to fight under his father's command until his death at Toulouse on 25 June 1218. As his father's successor, he inherited the Counts of Toulouse, County of Toulouse (that his father had taken from Raymond VI of Toulouse as a reward for his role in the Crusade) and other titles and lands in Langue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathars
Catharism (; from the grc, καθαροί, katharoi, "the pure ones") was a Christian dualist or Gnostic movement between the 12th and 14th centuries which thrived in Southern Europe, particularly in northern Italy and southern France. Followers were described as Cathars and referred to themselves as Good Christians; in modern times, they are mainly remembered for a prolonged period of religious persecution by the Catholic Church, which did not recognize their unorthodox Christianity. Catharism emerged in Western Europe in the Languedoc region of southern France in the 11th century. Adherents were sometimes referred to as Albigensians, after the French city Albi where the movement first took hold. Catharism was initially taught by ascetic leaders who set few guidelines, leading some Catharist practices and beliefs to vary by region and over time. The movement was greatly influenced by the Bogomils of the First Bulgarian Empire, and may have originated in the Byzantine E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon De Montfort, 5th Earl Of Leicester
{{Infobox noble , name = Simon de Montfort , title = 5th Earl of Leicester , image = File:Simon4demontfort.gif , caption = Seal of Simon de Montfort, depicting him riding a horse and blowing a hunting horn with a hound alongside, inscribed with his Latinised name: ''SIGILL MSIMONIS DE MONTE FORTI ("seal of Simon from the strong mountain") , alt = , CoA = , more = no , succession = , reign = , reign-type = , predecessor = , successor = , suc-type = , spouse = Alix de Montmorency , spouse-type = , issue = Amaury de MontfortSimon de Montfort, 6th Earl of LeicesterGuy de Montfort, Count of Bigorre Amicie de MontfortPetronilla , issue-link = , issue-pipe = , full name = , native_name = , styles = , other_titles = , noble family = Mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
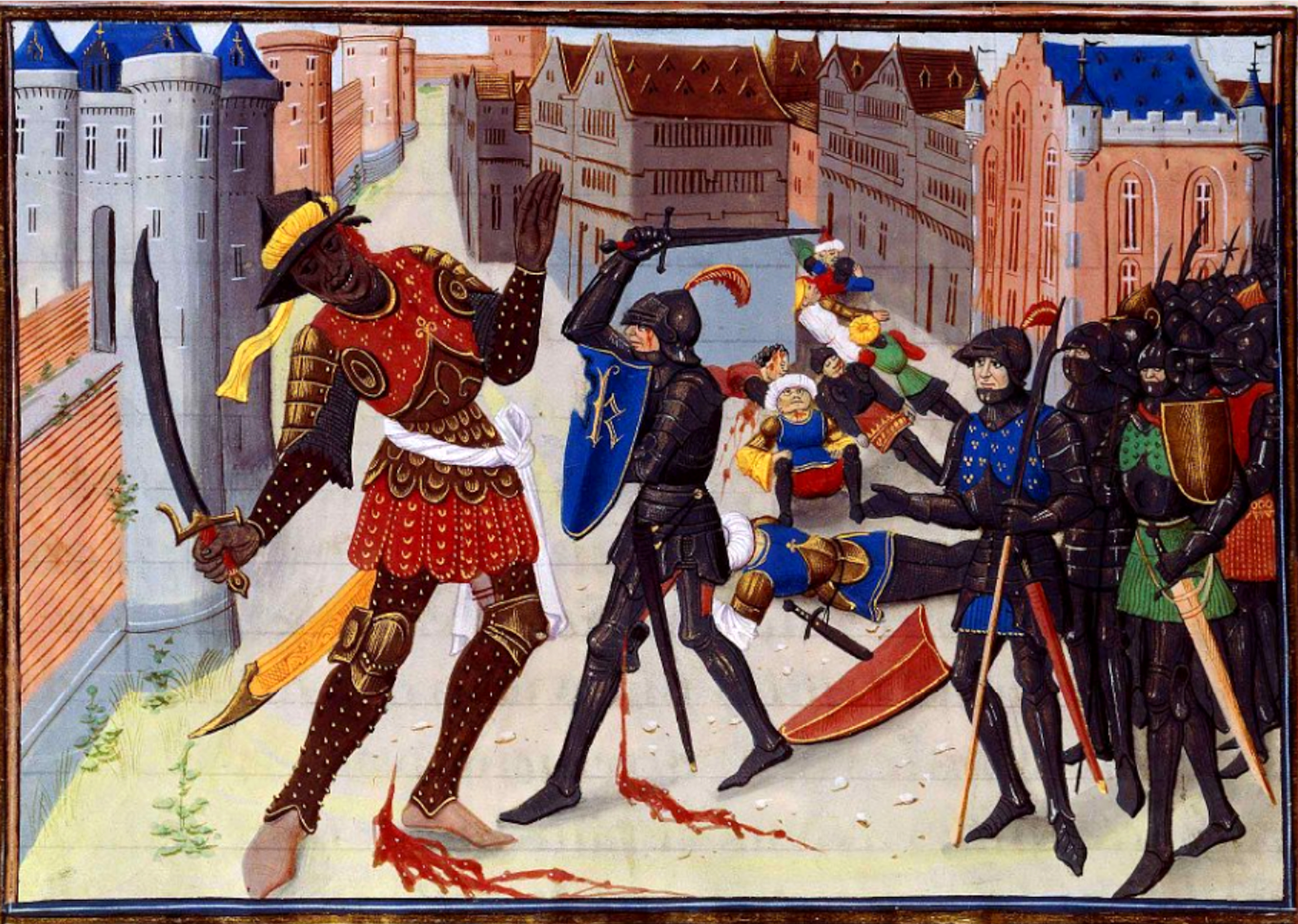
Saracens
file:Erhard Reuwich Sarazenen 1486.png, upright 1.5, Late 15th-century Germany in the Middle Ages, German woodcut depicting Saracens Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek language, Greek and Latin writings, to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Roman Empire, Romans as Arabia Petraea and Arabia Deserta. The term's meaning evolved during its history of usage. During the Early Middle Ages, the term came to be associated with the tribes of Arabia. The oldest known source mentioning "Saracens" in relation to Islam dates back to the 7th century, in the Greek-language Christian tract Teaching of Jacob, ''Doctrina Jacobi''. Among other major events, the tract discusses the Muslim conquest of the Levant, which occurred after the rise of the Rashidun Caliphate following the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The Roman-Catholic church and Christianity in Europe, European Christian leaders used the term during the Middle Ages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Martel
Charles Martel ( – 22 October 741) was a Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of Francia from 718 until his death. He was a son of the Frankish statesman Pepin of Herstal and Pepin's mistress, a noblewoman named Alpaida. Charles, also known as "The Hammer" (in Old French, ''Martel''), successfully asserted his claims to power as successor to his father as the power behind the throne in Frankish politics. Continuing and building on his father's work, he restored centralized government in Francia and began the series of military campaigns that re-established the Franks as the undisputed masters of all Gaul. According to a near-contemporary source, the ''Liber Historiae Francorum'', Charles was "a warrior who was uncommonly ..effective in battle". Martel gained a very consequential victory against an Umayyad invasion of Aquitaine at the Battle of Tours, at a time when the Umayyad Caliphate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
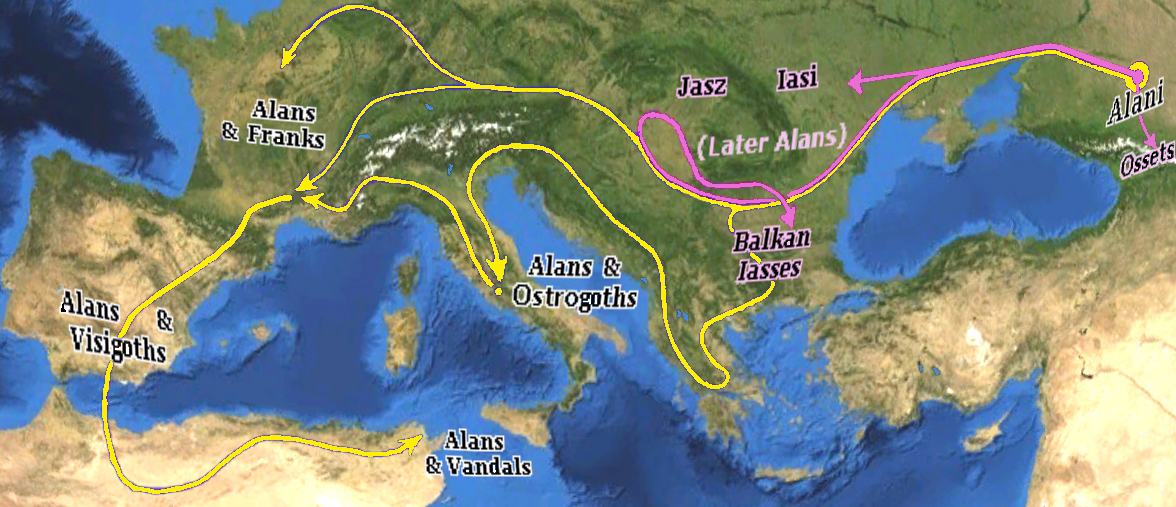
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe. Upon the Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated westwards along with various Germanic tribes. They crossed the Rhine in 406CE along with the Vandals and Suebi, settling in Orléans and Valence. Around 409 CE they joined the Vandals and Suebi in cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |