|
Beryllium-9
Beryllium (4Be) has 11 known isotopes and 3 known isomers, but only one of these isotopes () is stable and a primordial nuclide. As such, beryllium is considered a monoisotopic element. It is also a mononuclidic element, because its other isotopes have such short half-lives that none are primordial and their abundance is very low (standard atomic weight is ). Beryllium is unique as being the only monoisotopic element with both an even number of protons and an odd number of neutrons. There are 25 other monoisotopic elements but all have odd atomic numbers, and even numbers of neutrons. Of the 10 radioisotopes of beryllium, the most stable are with a half-life of million years and with a half-life of . All other radioisotopes have half-lives under , most under . The least stable isotope is , with a half-life of . The 1:1 neutron–proton ratio seen in stable isotopes of many light elements (up to oxygen, and in elements with even atomic number up to calcium) is prevented i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form minerals. Notable gemstones high in beryllium include beryl ( aquamarine, emerald) and chrysoberyl. It is a relatively rare element in the universe, usually occurring as a product of the spallation of larger atomic nuclei that have collided with cosmic rays. Within the cores of stars, beryllium is depleted as it is fused into heavier elements. Beryllium constitutes about 0.0004 percent by mass of Earth's crust. The world's annual beryllium production of 220 tons is usually manufactured by extraction from the mineral beryl, a difficult process because beryllium bonds strongly to oxygen. In structural applications, the combination of high flexural rigidity, thermal stability, thermal conductivity and low density (1.85 times that of wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmogenic Nuclide
Cosmogenic nuclides (or cosmogenic isotopes) are rare nuclides ( isotopes) created when a high-energy cosmic ray interacts with the nucleus of an '' in situ'' Solar System atom, causing nucleons (protons and neutrons) to be expelled from the atom (see cosmic ray spallation). These nuclides are produced within Earth materials such as rocks or soil, in Earth's atmosphere, and in extraterrestrial items such as meteoroids. By measuring cosmogenic nuclides, scientists are able to gain insight into a range of geological and astronomical processes. There are both radioactive and stable cosmogenic nuclides. Some of these radionuclides are tritium, carbon-14 and phosphorus-32. Certain light (low atomic number) primordial nuclides (isotopes of lithium, beryllium and boron) are thought to have been created not only during the Big Bang, but also (and perhaps primarily) to have been made after the Big Bang, but before the condensation of the Solar System, by the process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmogenic
Cosmogenic nuclides (or cosmogenic isotopes) are rare nuclides (isotopes) created when a high-energy cosmic ray interacts with the nucleus of an ''in situ'' Solar System atom, causing nucleons (protons and neutrons) to be expelled from the atom (see cosmic ray spallation). These nuclides are produced within Earth materials such as rocks or soil, in Earth's atmosphere, and in extraterrestrial items such as meteoroids. By measuring cosmogenic nuclides, scientists are able to gain insight into a range of geological and astronomical processes. There are both radioactive and stable cosmogenic nuclides. Some of these radionuclides are tritium, carbon-14 and phosphorus-32. Certain light (low atomic number) primordial nuclides (isotopes of lithium, beryllium and boron) are thought to have been created not only during the Big Bang, but also (and perhaps primarily) to have been made after the Big Bang, but before the condensation of the Solar System, by the process of cosmic ray s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoisotopic Element
A monoisotopic element is an element which has only a single stable isotope (nuclide). There are only 26 elements that have this property. A list is given in a following section. Stability is experimentally defined for chemical elements, as there are a number of stable nuclides with atomic numbers over ~40 which are theoretically unstable, but apparently have half-lives so long that they have not been observed directly or indirectly (from measurement of products) to decay. Monoisotopic elements are characterized, except in a single case, by odd numbers of protons (odd ''Z''), and even numbers of neutrons. Because of the energy gain from nuclear pairing effects, the odd number of protons imparts instability to isotopes of an odd ''Z'', which in heavier elements requires a completely paired set of neutrons to offset this tendency into stability. (The five stable nuclides with odd ''Z'' and odd neutron numbers are hydrogen-2, lithium-6, boron-10, nitrogen-14, and tantalum-180m1.) T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beryllium-8
Beryllium-8 (8Be, Be-8) is a radionuclide with 4 neutrons and 4 protons. It is an unbound resonance and nominally an isotope of beryllium. It decays into two alpha particles with a half-life on the order of 8.19 seconds. This has important ramifications in stellar nucleosynthesis as it creates a bottleneck in the creation of heavier chemical elements. The properties of 8Be have also led to speculation on the fine tuning of the Universe, and theoretical investigations on cosmological evolution had 8Be been stable. Discovery The discovery of beryllium-8 occurred shortly after the construction of the first particle accelerator in 1932. British physicists John Douglas Cockcroft and Ernest Walton performed their first experiment with their accelerator at the Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge, in which they irradiated lithium-7 with protons. They reported that this populated a nucleus with ''A'' = 8 that near-instantaneously decays into two alpha particles. This act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon-12
Carbon-12 (12C) is the most abundant of the two stable isotopes of carbon ( carbon-13 being the other), amounting to 98.93% of element carbon on Earth; its abundance is due to the triple-alpha process by which it is created in stars. Carbon-12 is of particular importance in its use as the standard from which atomic masses of all nuclides are measured, thus, its atomic mass is exactly 12 daltons by definition. Carbon-12 is composed of 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons. History Before 1959, both the IUPAP and IUPAC used oxygen to define the mole; the chemists defining the mole as the number of atoms of oxygen which had mass 16 g, the physicists using a similar definition but with the oxygen-16 isotope only. The two organizations agreed in 1959/60 to define the mole as follows. ''Mole is the amount of substance of a system which contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 gram of carbon 12; its symbol is "mol".'' This was adopted by the CI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Nucleosynthesis
Stellar nucleosynthesis is the creation (nucleosynthesis) of chemical elements by nuclear fusion reactions within stars. Stellar nucleosynthesis has occurred since the original creation of hydrogen, helium and lithium during the Big Bang. As a predictive theory, it yields accurate estimates of the observed abundances of the elements. It explains why the observed abundances of elements change over time and why some elements and their isotopes are much more abundant than others. The theory was initially proposed by Fred Hoyle in 1946, who later refined it in 1954. Further advances were made, especially to nucleosynthesis by neutron capture of the elements heavier than iron, by Margaret and Geoffrey Burbidge, William Alfred Fowler and Hoyle in their famous 1957 B2FH paper, which became one of the most heavily cited papers in astrophysics history. Stars evolve because of changes in their composition (the abundance of their constituent elements) over their lifespans, first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple Alpha Process
The triple-alpha process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions by which three helium-4 nuclei (alpha particles) are transformed into carbon. Triple-alpha process in stars Helium accumulates in the cores of stars as a result of the proton–proton chain reaction and the carbon–nitrogen–oxygen cycle. Nuclear fusion reaction of two helium-4 nuclei produces beryllium-8, which is highly unstable, and decays back into smaller nuclei with a half-life of , unless within that time a third alpha particle fuses with the beryllium-8 nucleus to produce an excited resonance state of carbon-12, called the Hoyle state, which nearly always decays back into three alpha particles, but once in about 2421.3 times releases energy and changes into the stable base form of carbon-12. When a star runs out of hydrogen to fuse in its core, it begins to contract and heat up. If the central temperature rises to 108 K, six times hotter than the Sun's core, alpha particles can fuse fast enough to get ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
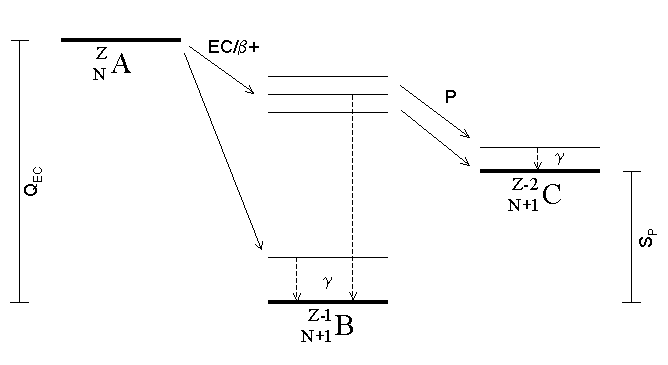
Electron Capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. This process thereby changes a nuclear proton to a neutron and simultaneously causes the emission of an electron neutrino. : : or when written as a nuclear reaction equation, ^_e + ^_p -> ^_n + ^_ ν_e Since this single emitted neutrino carries the entire decay energy, it has this single characteristic energy. Similarly, the momentum of the neutrino emission causes the daughter atom to recoil with a single characteristic momentum. The resulting daughter nuclide, if it is in an excited state, then transitions to its ground state. Usually, a gamma ray is emitted during this transition, but nuclear de-excitation may also take place by internal conversion. Following capture of an inner electron from the atom, an outer el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Bang Nucleosynthesis
In physical cosmology, Big Bang nucleosynthesis (abbreviated BBN, also known as primordial nucleosynthesis) is the production of nuclei other than those of the lightest isotope of hydrogen ( hydrogen-1, 1H, having a single proton as a nucleus) during the early phases of the Universe. Primordial nucleosynthesis is believed by most cosmologists to have taken place in the interval from roughly 10 seconds to 20 minutes after the Big Bang, and is calculated to be responsible for the formation of most of the universe's helium as the isotope helium-4 (4He), along with small amounts of the hydrogen isotope deuterium (2H or D), the helium isotope helium-3 (3He), and a very small amount of the lithium isotope lithium-7 (7Li). In addition to these stable nuclei, two unstable or radioactive isotopes were also produced: the heavy hydrogen isotope tritium (3H or T); and the beryllium isotope beryllium-7 (7Be); but these unstable isotopes later decayed into 3He and 7Li, respectively, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton Emission
Proton emission (also known as proton radioactivity) is a rare type of radioactive decay in which a proton is ejected from a nucleus. Proton emission can occur from high-lying excited states in a nucleus following a beta decay, in which case the process is known as beta-delayed proton emission, or can occur from the ground state (or a low-lying isomer) of very proton-rich nuclei, in which case the process is very similar to alpha decay. For a proton to escape a nucleus, the proton separation energy must be negative—the proton is therefore unbound, and tunnels out of the nucleus in a finite time. Proton emission is not seen in naturally occurring isotopes; proton emitters can be produced via nuclear reactions, usually using linear particle accelerators. Although prompt (i.e. not beta-delayed) proton emission was observed from an isomer in cobalt-53 as early as 1969, no other proton-emitting states were found until 1981, when the proton radioactive ground states of lutetium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |