|
Berkelium(III) Chloride
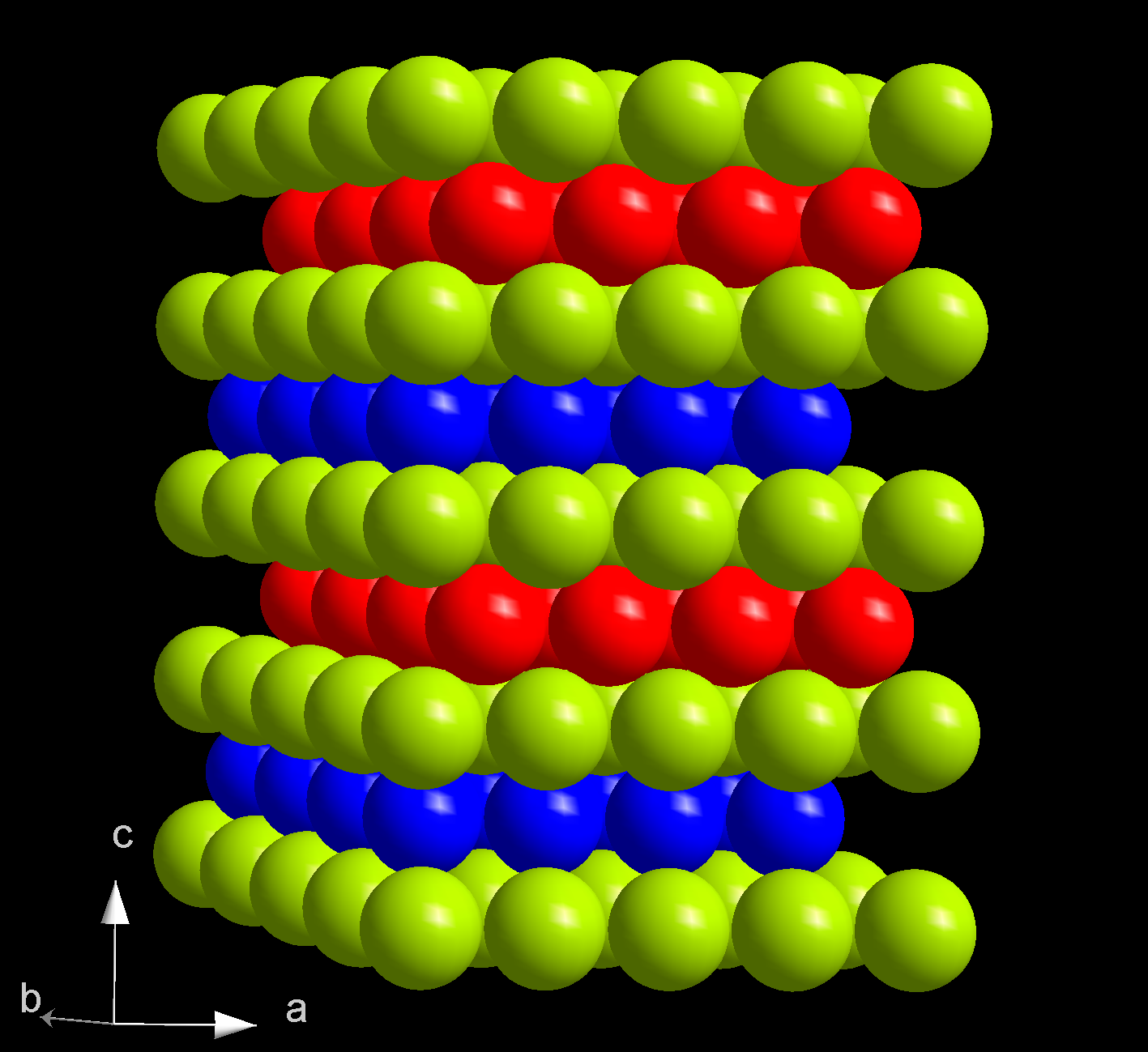
Berkelium(III) chloride also known as berkelium trichloride, is a chemical compound with the formula BkCl3. It is a water-soluble green salt with a melting point of 603 °C. This compound forms the hexahydrate, BkCl3·6H2O. Preparation and reactions This compound was first prepared in 1970 by reacting hydrogen chloride gas and berkelium(IV) oxide or berkelium(III) oxide at 520 °C: :Bk2O3 + 6HCl → 2BkCl3 + 3H2O Berkelium(III) chloride reacts with beryllocene to produce berkelocene(Bk(C5H5)3). It also reacts with oxalic acid to produce berkelium oxalate. This reaction is used to purify this compound, by reacting the oxalate with hydrochloric acid. Structure Anhydrous berkelium(III) chloride has a hexagonal crystal structure, is isostructural to uranium trichloride, and has the person symbol hP6. When heated it its melting point, it converts to an orthorhombic phase. However, the hexahydrate has a monoclinic crystal structure and is isostructural to americium trichlor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry. Hydrochloric acid, the aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride, is also commonly given the formula HCl. Reactions Hydrogen chloride is a diatomic molecule, consisting of a hydrogen atom H and a chlorine atom Cl connected by a polar covalent bond. The chlorine atom is much more electronegative than the hydrogen atom, which makes this bond polar. Consequently, the molecule has a large dipole moment with a negative partial charge (δ−) at the chlorine atom and a positive partial charge (δ+) at the hydrogen atom. In part because of its high polarity, HCl is very soluble in water (and in other polar solvents). Upon contact, and HCl combine to form hydronium cations and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkelium(IV) Oxide
Berkelium(IV) oxide, also known as berkelium dioxide, is a chemical compound with the formula BkO2. This compound slowly decays to californium(IV) oxide. It can be converted to berkelium(III) oxide by hydrogen reduction at 600 °C. :2BkO2 + H2 → Bk2O3 + H2O Production Berkelium(IV) oxide is produced by burning berkelium metal in air at 1200 °C. It can also be produced by reacting berkelium(III) oxide with oxygen at 600 °C. References {{Oxides Berkelium compounds Oxides Fluorite crystal structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkelium(III) Oxide
Berkelium(III) oxide is a binary inorganic compound of berkelium and oxygen with the chemical formula . Synthesis Berkelium(III) oxide can be prepared from berkelium(IV) oxide by reduction with hydrogen Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...: :: Physical properties The compound forms a yellow-green solid with a melting point of 1920 °C. It forms a body-centered cubic crystal lattice with a = 1088.0 ± 0.5 pm. Insoluble in water. References Oxides Berkelium compounds {{inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group 2 Organometallic Chemistry
Magnesium anthracenide with three thf ligands. Group 2 organometallic chemistry refers to the chemistry of compounds containing carbon bonded to any group 2 element. By far the most common group 2 organometallic compounds are the magnesium-containing Grignard reagents which are widely used in organic chemistry. Other organmetallic group 2 compounds are rare and are typically limited to academic interests. Characteristics As the group 2 elements (also referred to as the alkaline earth metals) contain two valence electrons, their chemistries have similarities group 12 organometallic compounds. Both readily assume a +2 oxidation states with higher and lower states being rare, and are less electronegative than carbon. However, as the group two elements (with the exception of beryllium) have considerably low electronegativity the resulting C-M bonds are more highly polarized and ionic-like, if not entirely ionic for the heavier barium compounds. The lighter organoberyllium and organoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalic Acid
Oxalic acid is an organic acid with the systematic name ethanedioic acid and formula . It is the simplest dicarboxylic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that forms a colorless solution in water. Its name comes from the fact that early investigators isolated oxalic acid from flowering plants of the genus ''Oxalis'', commonly known as wood-sorrels. It occurs naturally in many foods. Excessive ingestion of oxalic acid or prolonged skin contact can be dangerous. Oxalic acid has much greater acid strength than acetic acid. It is a reducing agent and its conjugate base, known as oxalate (), is a chelating agent for metal cations. Typically, oxalic acid occurs as the dihydrate with the formula . History The preparation of salts of oxalic acid (crab acid) from plants had been known, at least since 1745, when the Dutch botanist and physician Herman Boerhaave isolated a salt from wood sorrel. By 1773, François Pierre Savary of Fribourg, Switzerland had isolated oxalic acid from i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions .... It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. History In the early tenth century, the Persian physician and alchemist Abu Bakr al-Razi ( 865–925, Latin: Rhazes) conducted experiments with sal ammoniac (ammonium chloride) and vitriol (hydrated sulfates of various metals), which he distilled together, thus producing the gas hydrogen chloride. In doing so, al-Razi may have stumbled upon a primitive method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Trichloride
Uranium(III) chloride, UCl3, is a water soluble salt of uranium. UCl3 is used mostly to reprocess spent nuclear fuel. Uranium(III) chloride is synthesized in various ways from uranium(IV) chloride; however, UCl3 is less stable than UCl4. Preparation There are two ways to synthesize uranium(III) chloride. The following processes describe how to produce uranium(III) chloride. (1) In a mixture of NaCl-KCl at 670–710 °C, add uranium tetrachloride with uranium metal. :3 UCl4 + U → 4UCl3 (2) Heat uranium(IV) chloride in hydrogen gas. :2 UCl4 + H2 → 2UCl3 + 2HCl Properties In solid uranium(III) chloride each uranium atom has nine chlorine atoms as near neighbours, at approximately the same distance, in a tricapped trigonal prismatic configuration. Uranium(III) chloride is a green crystalline solid at room temperature. UCl3 melts at 837 °C and boils at 1657 °C. Uranium(III) chloride has a density of 5500 kg/m3 or 5.500 g/cm3. Its composition by weig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Americium(III) Chloride
Americium(III) chloride or americium trichloride is the chemical compound composed of americium and chlorine with the formula AmCl3. This salt forms pink hexagonal crystals. In the solid state each americium atom has nine chlorine atoms as near neighbours, at approximately the same distance, in a tricapped trigonal prismatic configuration. The hexahydrate has a monocline crystal structure with: a = 970.2 pm, b = 656.7 pm and c = 800.9 pm; β = 93° 37'; space group: ''P''2/''n''.John H. Burns, Joseph Richard Peterson: "The Crystal Structures of Americium Trichloride Hexahydrate and Berkelium Trichloride Hexahydrate", ''Inorg. Chem.'' 1971, ''10 (1)'', 147–151; . Reactions An americium(III) chloride electrorefining method has been investigated to separate mixtures of actinides, since the standard Gibbs free energy of formation of americium(III) chloride is much different than the rest of the actinide chlorides. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkelium(III) Hydroxide
Berkelium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Bk and atomic number 97. It is a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (then the University of California Radiation Laboratory) where it was discovered in December 1949. Berkelium was the fifth transuranium element discovered after neptunium, plutonium, curium and americium. The major isotope of berkelium, 249Bk, is synthesized in minute quantities in dedicated high-flux nuclear reactors, mainly at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee, United States, and at the Research Institute of Atomic Reactors in Dimitrovgrad, Russia. The production of the second-most important isotope, 247Bk, involves the irradiation of the rare isotope 244Cm with high-energy alpha particles. Just over one gram of berkelium has been produced in the United States since 1967. There is no practical ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesium Chloride
Caesium chloride or cesium chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula Cs Cl. This colorless salt is an important source of caesium ions in a variety of niche applications. Its crystal structure forms a major structural type where each caesium ion is coordinated by 8 chloride ions. Caesium chloride dissolves in water. CsCl changes to NaCl structure on heating. Caesium chloride occurs naturally as impurities in carnallite (up to 0.002%), sylvite and kainite. Less than 20 tonnes of CsCl is produced annually worldwide, mostly from a caesium-bearing mineral pollucite. Caesium chloride is widely used medicine structure in isopycnic centrifugation for separating various types of DNA. It is a reagent in analytical chemistry, where it is used to identify ions by the color and morphology of the precipitate. When enriched in radioisotopes, such as 137CsCl or 131CsCl, caesium chloride is used in nuclear medicine applications such as treatment of cancer and diagnosis of myocardial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Julius Emeléus
Harry Julius Emeléus CBE, FRS (22 June 1903 – 2 December 1993) was a leading English inorganic chemist and a professor in the department of chemistry, Cambridge University. Early life Emeléus was born in Poplar, London on 22 June 1903, the son of Karl Henry Emeléus (1869–1948), a pharmacist who was born in Vaasa, Finland. The family moved to the Old Pharmacy in Battle, Sussex shortly after Emeléus was born. His elder brother Karl George Emeléus (1901–1989) went on to become professor of physics at the Queen's University of Belfast. Emeléus was educated at St Leonards Collegiate School, Hastings, and Hastings Grammar School followed by the Royal College of Science, Imperial College, London, graduating in 1923. He gained his PhD in 1926 and a DSc three years later. During his post-graduate studies he spent time at the University of Karlsruhe as a student of Alfred Stock and two years at Princeton University with Professor Hugh Stott Taylor. Among his many students ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkelium Compounds
Berkelium forms a number of chemical compounds, where it normally exists in an Oxidation number, oxidation state of +3 or +4, and behaves similarly to its lanthanide analogue, terbium. Like all actinides, berkelium easily dissolves in various aqueous solution, aqueous inorganic acids, liberating gaseous hydrogen and converting into the trivalent oxidation state. This trivalent state is the most stable, especially in aqueous solutions, but tetravalent berkelium compounds are also known. The existence of divalent berkelium salts is uncertain and has only been reported in mixed lanthanum chloride-strontium chloride melts. Aqueous solutions of Bk3+ ions are green in most acids. The color of the Bk4+ ions is yellow in hydrochloric acid and orange-yellow in sulfuric acid.Peterson, p. 55Holleman, p. 1956 Berkelium does not react rapidly with oxygen at room temperature, possibly due to the formation of a protective oxide surface layer; however, it reacts with molten metals, hydrogen, halog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |