|
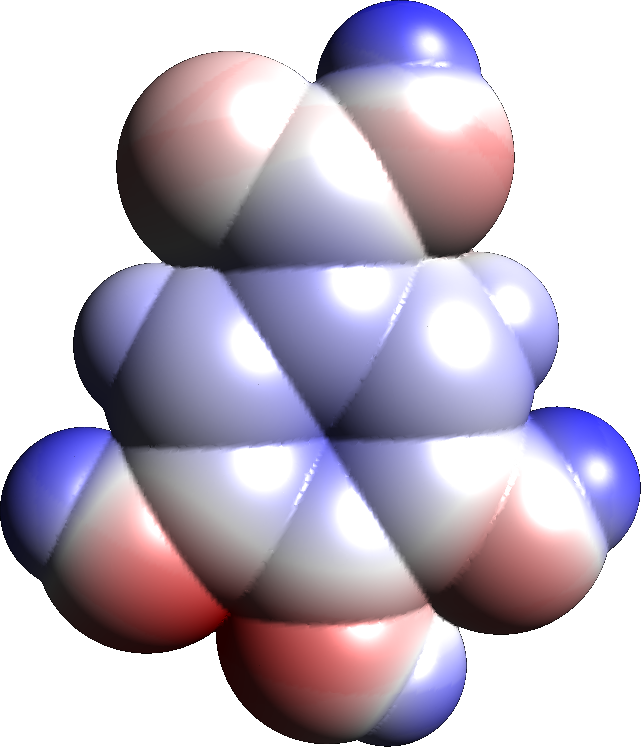
Bergenin
Bergenin, alias cuscutin, is trihydroxybenzoic acid glycoside. It is the C-glycoside of 4-O-methyl gallic acid. It possesses an O-demethylated derivative called norbergenin. These are chemical compounds and drugs of Ayurveda, commonly known as Paashaanbhed. It shows a potent immunomodulatory effect. Bergenin can be isolated from ''Bergenia'' species like '' Bergenia ciliata'' and '' Bergenia ligulata'', from rhizomes of ''Bergenia stracheyi''. It is also found in the stem bark of ''Dryobalanops aromatica'', in ''Ardisia elliptica ''Ardisia elliptica'' is an evergreen tree, also known as the shoebutton ardisia, duck's eye and coralberry, native to the west coast of India, Sri Lanka, Indochina, Malaysia, Indonesia and New Guinea. It is a prolific reproducer which has made i ...'' and in '' Mallotus japonicus''.Hepatoprotective effects of bergenin, a major constituent of Mallotus japonicus, on carbon tetrachloride-intoxicated rats. Lim HwaKyung, Kim HackSeang, Choi HongSerck, Oh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergenia Ciliata
''Bergenia ciliata'' (fringed elephant's ears, winter begonia, hairy bergenia, Hindi & Sanskrit : ''Pashanbheda'', पाषाणभेद) is a plant species in the genus ''Bergenia'', deciduous in Usda zone, USDA Zones 5 to 7, but usually remain semi-evergreen south of Zone 7. It is found in North India, Northern India in Uttarakhand (Chamoli district, Chamoli and other districts of Uttarakhand) and Himachal Pradesh (in district Shimla district, Shimla). This flower is related to the famous Phool Dei Festival (https://www.tourmyindia.com/states/uttarakhand/phool-dei-festival.html) celebrated in Uttarakhand. It is commonly known in India as Pathar phor buti. Also found in mountain areas of West Bengal, like Kalimpong, and Darjeeling. Afghanistan, south Tibet, Northern Nepal, Bhutan (Haa District, Haa and Mongar District, Mongar districts). Bergenin, catechin, gallic acid, gallicin, catechin-7-O-glucoside and β-sitosterol can be found in ''B. ciliata''. It is known for its us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergenia
''Bergenia'' (elephant-eared saxifrage, elephant's ears) is a genus of ten species of flowering plants in the family Saxifragaceae, native to central Asia, from Afghanistan to China and the Himalayan region. Description They are clump-forming, rhizomatous, evergreen perennials with a spirally arranged rosette of leaves 6–35 cm long and 4–15 cm broad, and pink flowers produced in a cyme. The leaves are large, leathery, ovate or cordate, and often have wavy or saw-toothed edges. For most of the year, the leaves have a glossy green colour, but in cooler climates, they turn red or bronze in the fall. The flowers grow on a stem similar in colour to a rhubarb stalk and most varieties have cone-shaped flowers in varying shades of pink. These can range from almost white to ruby red and purple. The common names for ''Bergenia'' are pigsqueak (due to the sound produced when two leaves are rubbed together), elephant's ears (due to the shape of the leaves) and large rockfoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergenia Stracheyi
''Bergenia stracheyi'' is a plant species in the genus ''Bergenia'' found in the Western Himalayas, from 2700 to 4700 m, Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Bergenin and norbergenin Norbergenin is a chemical compound. It is the ''O''-demethylated derivative of bergenin. It can be isolated from rhizomes of ''Bergenia stracheyi ''Bergenia stracheyi'' is a plant species in the genus ''Bergenia'' found in the Western Himalayas ... are chemical compounds that can be isolated from rhizomes of ''B. stracheyi''.Immunomodulatory effect of bergenin and norbergenin against adjuvant-induced arthritis—A flow cytometric study Nighat Nazira, Surrinder Koulb, Mushtaq A. Qurishia, Sachin C. Tanejab, Sheikh F. Ahmadc, Sarang Banic and Ghulam N. Qazi, Journal of Ethnopharmacology, Volume 112, Issue 2, 13 June 2007, pp. 401-405, Cultivars * ''Bergenia stracheyi 'Alba * ''Bergenia stracheyi 'Afghanica References External links stracheyi Plants described in 1868 {{Saxifragaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dryobalanops Aromatica
''Dryobalanops aromatica'', commonly known as Borneo camphor, camphor tree, Malay camphor, or Sumatran camphor, is a species of critically endangered plant in the family Dipterocarpaceae. The species name ''aromatica'' is derived from Latin (''aromaticus'' meaning spice-like) and refers to the smell of the dammar (resin). This species was one of the main sources of camphor and attracted early Arab traders to Borneo, at that time being worth more than gold, and used for incense and perfumes. It is found in Sumatra, peninsular Malaysia, and Borneo. It is a large emergent tree, up to 65 m or even 75 m tall, found in mixed dipterocarp forests on deep humic yellow sandy soils. It is a heavy hardwood sold under the trade names of Kapur. It is recorded from at least two protected areas ( Lambir and Gunung Mulu National Parks). Bergenin, malaysianol A, laevifonol, ampelopsin E, α-viniferin, ε-viniferin and diptoindonesin A can be isolated from the stem bark of ''D. aromatica''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallotus Japonicus
''Mallotus japonicus'' (), also known as East Asian mallotus, the food wrapper plant or "Akamegashiwa" in Japanese, is a plant species in the genus ''Mallotus'' native to China. It is also found in Japan and Korea. This species was first described in 1865, its name was verified by AAS Systematic Botanists on October 2, 2015. The plant is dioecious. The young shoots are red-coloured. The larvae of the moth '' Deoptilia heptadeta'' mine the leaves to feed. Uses The large leaves were used to wrap food. The young leaves, when boiled, are edible. The bark is used in the Japanese pharmacopoeia as a decoction against gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, gastric hyperacidity. In addition, the fruit has anthelmintic properties. Ecology ''Mallotus japonicus'' shows physical, chemical, and biotic resistance traits against herbivores. Trichomes, which are produced on leaf surfaces, serve as a physical resistance trait. Pellucid dots, which also are present on leaf surfaces, typically conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trihydroxybenzoic Acid
Trihydroxybenzoic acid may refer to the following phenolic acids : * Gallic acid (3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) * Phloroglucinol carboxylic acid (2,4,6-trihydroxybenzoic acid) O-methylated trihydroxybenzoic acids are : * Eudesmic acid * Syringic acid Syringic acid is a naturally occurring phenolic compound and dimethoxybenzene that is commonly found as a plant metabolite. Natural occurrence Syringic acid can be found in several plants including ''Ardisia elliptica'' and '' Schumannianthus ... Glycosides : * Theogallin {{Chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoside
In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. These can be activated by enzyme hydrolysis, which causes the sugar part to be broken off, making the chemical available for use. Many such plant glycosides are used as medications. Several species of ''Heliconius'' butterfly are capable of incorporating these plant compounds as a form of chemical defense against predators. In animals and humans, poisons are often bound to sugar molecules as part of their elimination from the body. In formal terms, a glycoside is any molecule in which a sugar group is bonded through its anomeric carbon to another group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides can be linked by an O- (an ''O-glycoside''), N- (a ''glycosylamine''), S-(a ''thioglycoside''), or C- (a '' C-glycoside'') glycosidic bond. According to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallic Acid
Gallic acid (also known as 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) is a trihydroxybenzoic acid with the formula C6 H2( OH)3CO2H. It is classified as a phenolic acid. It is found in gallnuts, sumac, witch hazel, tea leaves, oak bark, and other plants. It is a white solid, although samples are typically brown owing to partial oxidation. Salts and esters of gallic acid are termed "gallates". Isolation and derivatives Gallic acid is easily freed from gallotannins by acidic or alkaline hydrolysis. When heated with concentrated sulfuric acid, gallic acid converts to rufigallol. Hydrolyzable tannins break down on hydrolysis to give gallic acid and glucose or ellagic acid and glucose, known as gallotannins and ellagitannins, respectively. Biosynthesis Gallic acid is formed from 3-dehydroshikimate by the action of the enzyme shikimate dehydrogenase to produce 3,5-didehydroshikimate. This latter compound aromatizes. Reactions Oxidation and oxidative coupling Alkaline solutions of gallic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norbergenin
Norbergenin is a chemical compound. It is the ''O''-demethylated derivative of bergenin. It can be isolated from rhizomes of ''Bergenia stracheyi ''Bergenia stracheyi'' is a plant species in the genus ''Bergenia'' found in the Western Himalayas, from 2700 to 4700 m, Afghanistan and Tajikistan Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Ta ...''. References Pyrogallols Lactones Oxygen heterocycles Heterocyclic compounds with 3 rings {{phenol-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayurveda
Ayurveda () is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. The theory and practice of Ayurveda is pseudoscientific. Ayurveda is heavily practiced in India and Nepal, where around 80% of the population report using it. Ayurveda therapies have varied and evolved over more than two millennia. Therapies include herbal medicines, special diets, meditation, yoga, massage, laxatives, enemas, and medical oils. Ayurvedic preparations are typically based on complex herbal compounds, minerals, and metal substances (perhaps under the influence of early Indian alchemy or ''rasashastra''). Ancient Ayurveda texts also taught surgical techniques, including rhinoplasty, kidney stone extractions, sutures, and the extraction of foreign objects. The main classical Ayurveda texts begin with accounts of the transmission of medical knowledge from the gods to sages, and then to human physicians. Printed editions of the '' Sushruta Samhita'' (''Sushruta's Compen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paashaanbhed
''Bergenia ligulata'' (''Paashaanbhed'', ''Prashanbheda'', and other spellings in Ayurveda traditional Indian medicine) is a plant belonging to the family Saxifragaceae and the genus ''Bergenia''. It is plant is sometimes treated as a form of ''Bergenia ciliata''. It is mostly found in temperate regions of the Himalayas from Kashmir to Bhutan and in Khasia hills at altitude. Chemical constituents ''Bergenia ligulata'' contains a phenolic compound bergenin, and afzelechin Afzelechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in ''Bergenia ligulata'' ( ''Paashaanbhed'' in Ayurveda traditional Indian medicine). It exists as at least 2 major epimers (afzelechin and epi-afzelechin). Metabolism (2R,3S)-cate ..., a type of flavan-3-ol. References ligulata Plants used in Ayurveda {{Saxifragaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunomodulatory
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as ''activation immunotherapies,'' while immunotherapies that reduce or suppress are classified as '' suppression immunotherapies''. Immunotherapy is under preliminary research for its potential to treat various forms of cancer. Cell-based immunotherapies are effective for some cancers. Immune effector cells such as lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes work together to defend the body against cancer by targeting abnormal antigens expressed on the surface of tumor cells. Vaccine-induced immunity to COVID-19 relies mostly on an immunomodulatory T cell response. Therapies such as granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), interferons, imiquimod and cellular membrane fractions from bacteria are licensed for medical use. Others includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |