|
Berend George Escher
Berend George Escher (4 April 1885 – 11 October 1967) was a Dutch geologist. Escher had a broad interest, but his research was mainly on crystallography, mineralogy and volcanology. He was a pioneer in experimental geology. He was a half-brother of the artist M.C. Escher, and had some influence on his work due to his knowledge of crystallography. M.C. Escher created a woodcut ''ex libris'' for his brother 'Beer' with a stylized image of a volcano around 1922 (Bool number 91). Escher was the son of the civil engineer G. A. Escher, a director of the Dutch watermanagement (''Rijkswaterstaat'') and his first wife, Charlotte Marie Hartitzsch. Escher spent his youth in Switzerland. He studied geology at the Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule (Technical University) of Zürich, where he was a pupil of Albert Heim. He finished his studies in 1911 and returned to the Netherlands where he first became the assistant of M.E.F.T. Dubois at the University of Amsterdam and then cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorinchem
Gorinchem ( or ), also spelled Gorkum, is a city and municipality in the western Netherlands, in the province of South Holland. The municipality covers an area of of which is water. It had a population of in . The municipality of Gorinchem also includes the population centre of Dalem. History It is assumed that Gorinchem was founded circa 1000 CE by fishermen and farmers on the raised land near the mouth of the river Linge at the Merwede. "''Goriks Heem''" (Home of Gorik) is first mentioned in a document from 1224 in which Floris IV granted people from Gorinchem exemption of toll payments throughout Holland. Somewhere between 1247 and 1267, Gorinchem became property of the Lords of Arkel. At the end of the 13th century earthen mounts reinforced with palisades were built around the settlement to protect it from domination by the neighboring counties of Holland and Gelre. Half a century later real city walls were built complete with 7 gates and 23 watchtowers. Otto van Arke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurits Cornelis Escher
Maurits Cornelis Escher (; 17 June 1898 – 27 March 1972) was a Dutch graphic artist who made mathematically inspired woodcuts, lithographs, and mezzotints. Despite wide popular interest, Escher was for most of his life neglected in the art world, even in his native Netherlands. He was 70 before a retrospective exhibition was held. In the late twentieth century, he became more widely appreciated, and in the twenty-first century he has been celebrated in exhibitions around the world. His work features mathematical objects and operations including impossible objects, explorations of infinity, reflection, symmetry, perspective, truncated and stellated polyhedra, hyperbolic geometry, and tessellations. Although Escher believed he had no mathematical ability, he interacted with the mathematicians George Pólya, Roger Penrose, Harold Coxeter and crystallographer Friedrich Haag, and conducted his own research into tessellation. Early in his career, he drew inspiration f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Henry Kuenen
Philip Henry Kuenen (22 July 1902, in Dundee – 17 December 1976, in Leiden) was a Dutch geologist. Kuenen spent his earliest youth in Scotland, as his father ( Johannes Petrus Kuenen) was professor of physics at University College, Dundee until 1906. He studied geology at Leiden University, where he was a pupil of K. Martin and B.G. Escher. He finished his studies in 1925 and then became assistant to Escher. He worked on paleontology and experimental geology. In 1929-1930 Kuenen participated in the Snellius expedition to the seas surrounding the Sunda Islands of the Dutch East Indies. In 1934 he became lecturer at Groningen University. Because the Dutch government had decided that geology would not be a major subject at Groningen University Kuenen was able to dedicate most of his time to research. Only in 1946 he became a full professor, during the German occupation in World War II the nazis had prevented this because he had British ancestors. The same year he became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Andries Vening Meinesz
Felix Andries Vening Meinesz (30 July 1887 – 10 August 1966) was a Dutch geophysicist and geodesist. He is known for his invention of a precise method for measuring gravity (gravimetry). Thanks to his invention, it became possible to measure gravity at sea, which led him to the discovery of gravity anomalies above the ocean floor. He later attributed these anomalies to continental drift. He was a Fellow of the Royal Society. Biography Vening Meinesz's father, Sjoerd Anne Vening Meinesz, was mayor, first of Rotterdam, then of Amsterdam. Felix was born in The Hague grew up in a protected environment. In 1910 he graduated in civil engineering in Delft. The same year he started working for the Dutch gravity survey. In 1915 he wrote his dissertation on the defects of the gravimeters used at that time. Vening Meinesz then designed a new gravimeter, which the KNMI (Royal Dutch Meteorological Institute) built. The apparatus has two pendula of the same size hanging in a frame but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiden
Leiden (; in English and archaic Dutch also Leyden) is a city and municipality in the province of South Holland, Netherlands. The municipality of Leiden has a population of 119,713, but the city forms one densely connected agglomeration with its suburbs Oegstgeest, Leiderdorp, Voorschoten and Zoeterwoude with 206,647 inhabitants. The Netherlands Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) further includes Katwijk in the agglomeration which makes the total population of the Leiden urban agglomeration 270,879, and in the larger Leiden urban area also Teylingen, Noordwijk, and Noordwijkerhout are included with in total 348,868 inhabitants. Leiden is located on the Oude Rijn, at a distance of some from The Hague to its south and some from Amsterdam to its north. The recreational area of the Kaag Lakes ( Kagerplassen) lies just to the northeast of Leiden. A university city since 1575, Leiden has been one of Europe's most prominent scientific centres for more than four centuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers ( strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy (lithologic stratigraphy), biostratigraphy (biologic stratigraphy), and chronostratigraphy (stratigraphy by age). Historical development Catholic priest Nicholas Steno established the theoretical basis for stratigraphy when he introduced the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality and the principle of lateral continuity in a 1669 work on the fossilization of organic remains in layers of sediment. The first practical large-scale application of stratigraphy was by William Smith in the 1790s and early 19th century. Known as the "Father of English geology", Smith recognized the significance of strata or rock layering and the importance of fossil markers for correlating strata; he created the first ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontology
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek (, "old, ancient"), (, (gen. ), "being, creature"), and (, "speech, thought, study"). Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of anatomically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics, and enginee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Martin
Johann Karl Ludwig Martin (24 November 1851, Jever ( Ostfriesland) – 14 November 1942, Leiden) was a German geologist. He was professor in geology at Leiden University from 1877 to 1922. From 1880 to 1922 he also was director of the Geological Museum of Leiden. As a scientist he is known for his paleontological and stratigraphical research on the Cenozoic fauna of the Dutch East Indies, especially on mollusks. Karl Martin was student at Göttingen, where he became PhD in 1874. He then worked as a teacher at Wismar, where he studied the glacial deposits of Northern Europe. He visited the Museum of Natural History at Leiden to see the collection of Winand Staring, thus meeting the zoologist Hermann Schlegel, the director of the museum. When a chair in geology was created at Leiden University in 1877, Schlegel remembered Martin as a good candidate. As a professor at Leiden, Martins' research was on the collections of the (in 1880 newly created) Geological Museum, especially on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
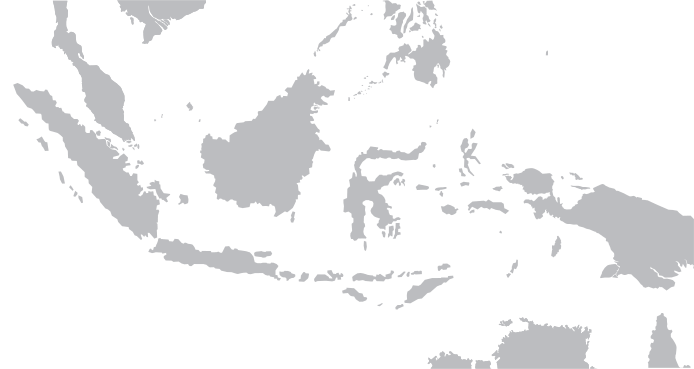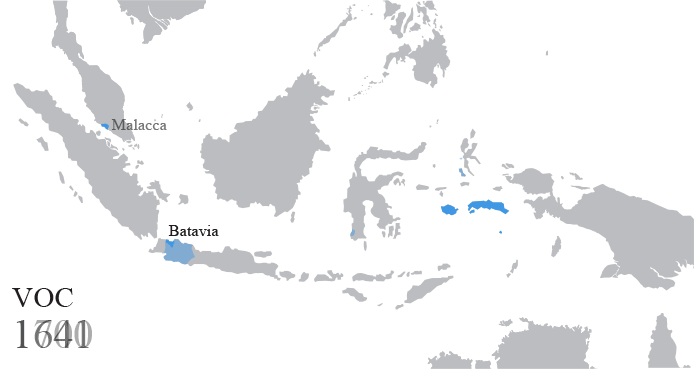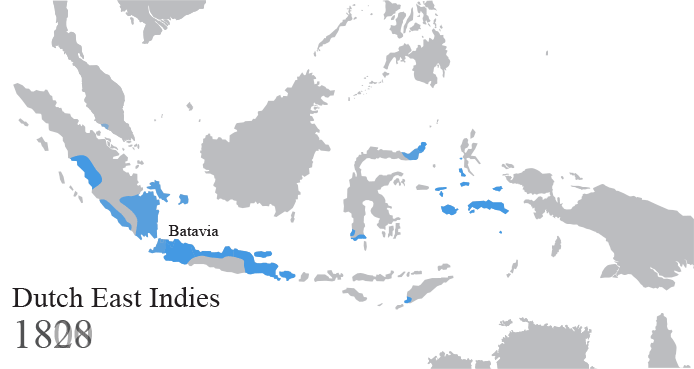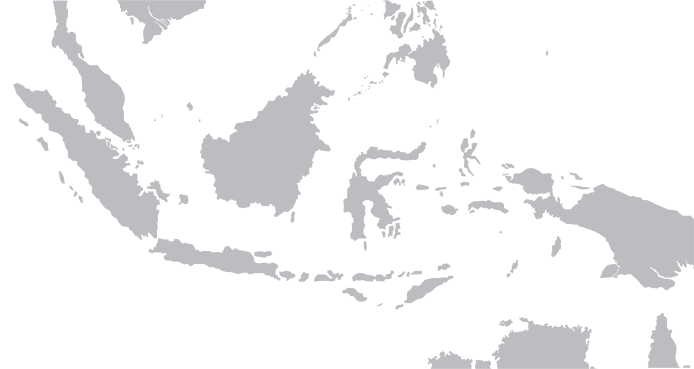
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curator
A curator (from la, cura, meaning "to take care") is a manager or overseer. When working with cultural organizations, a curator is typically a "collections curator" or an "exhibitions curator", and has multifaceted tasks dependent on the particular institution and its mission. In recent years the role of curator has evolved alongside the changing role of museums, and the term "curator" may designate the head of any given division. More recently, new kinds of curators have started to emerge: "community curators", "literary curators", " digital curators" and " biocurators". Collections curator A "collections curator", a "museum curator" or a "keeper" of a cultural heritage institution (e.g., gallery, museum, library or archive) is a content specialist charged with an institution's collections and involved with the interpretation of heritage material including historical artifacts. A collections curator's concern necessarily involves tangible objects of some sort—artwork, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugène Dubois
Marie Eugène François Thomas Dubois (; 28 January 1858 – 16 December 1940) was a Dutch paleoanthropologist and geologist. He earned worldwide fame for his discovery of ''Pithecanthropus erectus'' (later redesignated ''Homo erectus''), or "Java Man". Although hominid fossils had been found and studied before, Dubois was the first anthropologist to embark upon a purposeful search for them. Life and work MEFT. Dubois was born and raised in the village of Eijsden, Limburg, where his father, Jean Joseph Balthazar Dubois, an immigrant from Thimister-Clermont, Liège, Belgium, was an apothecary, later the mayor. Interested in all phenomena of the world of nature, Eugène explored the "caves" ("''grotten''", actually underground limestone mines) of Mount Saint Peter and amassed collections of plant parts, stones, insects, shells, and animal skulls. From age 12-13 on, he attended school in the Limburg city of Roermond, boarding with a family there and then he dropped out. In Roer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)