|
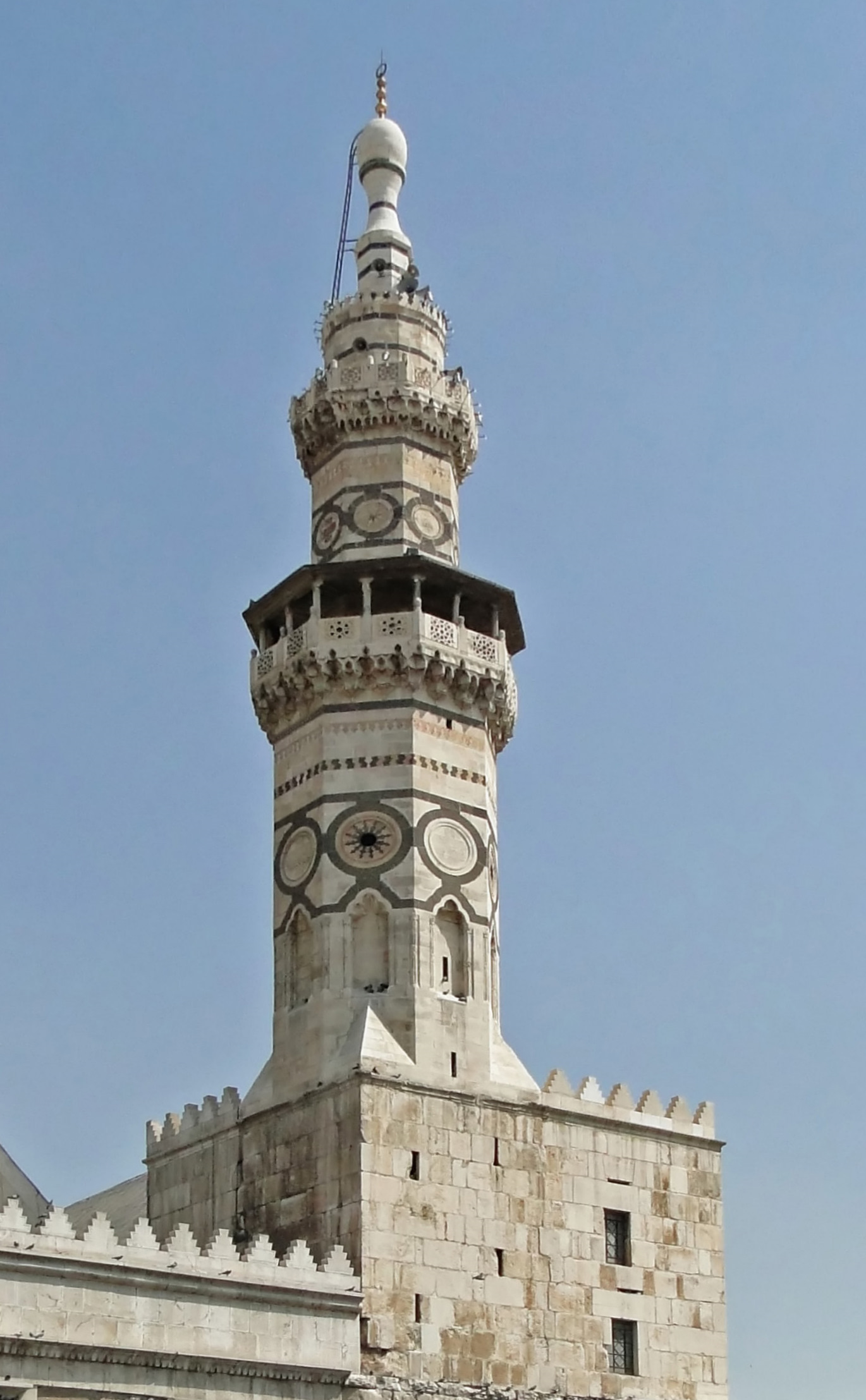
Beni Hammad Fort
Qal'at Bani Hammad ( ar, قلعة بني حماد), also known as Qal'a Bani Hammad or Qal'at of the Beni Hammad (among other variants), is a fortified palatine city in Algeria. Now in ruins, in the 11th century, it served as the first capital of the Hammadid dynasty. It is in the Hodna Mountains northeast of M'Sila, at an elevation of , and receives abundant water from the surrounding mountains. The site is near the town of Maadid (aka Maadhid), about southeast of Algiers, in the Maghreb. In 1980, it was inscribed as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO under the name Al Qal'a of Beni Hammad, and described as "an authentic picture of a fortified Muslim city". The town includes a long line of walls. Inside the walls are four residential complexes, and the largest mosque built in Algeria after that of Mansurah. It is similar in design to the Grand Mosque of Kairouan, with a tall minaret, . Excavations have brought to light numerous terracotta, jewels, coins and ceramics testifyi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M'Sila Province
ber, ⵎⵙⵉⵍⴰ ') is a province (''wilaya'') of northern Algeria. It has a population of 1 million people and an area of 18,718 km², while its capital, also called M'sila, home to M'Sila University, has a population of about 100,000. Localities include Bou Saada and Maadid. Chott El Hodna, a salt lake, crosses into M'Sila. However, most of the region is semi-arid and undeveloped. Additionally, M'Sila was the location of the first village constructed as part of a government-run program to transition nomadic Algerians to sedentary life using local materials. The village, now complete, was dubbed Maader and consists of houses, public and trading areas, and a mosque. History The province was created from parts of Batna (département), Médéa (département) and Sétif (département) in 1974. Administrative divisions The province is divided into 15 districts (''daïras''), which are further divided into 47 ''communes'' or municipalities. Districts # Aïn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berber People
, image = File:Berber_flag.svg , caption = The Berber flag, Berber ethnic flag , population = 36 million , region1 = Morocco , pop1 = 14 million to 18 million , region2 = Algeria , pop2 = 9 million to ~13 million , region3 = Mauritania , pop3 = 2.9 million , region4 = Niger , pop4 = 2.6 million, Niger: 11% of 23.6 million , region5 = France , pop5 = 2 million , region6 = Mali , pop6 = 850,000 , region7 = Libya , pop7 = 600,000 , region8 = Belgium , pop8 = 500,000 (including descendants) , region9 = Netherlands , pop9 = 467,455 (including descendants) , region10 = Burkina Faso , pop10 = 406,271, Burkina Faso: 1.9% of 21.4 million , region11 = Egypt , pop11 = 23,000 or 1,826,580 , region12 = Tunisia , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
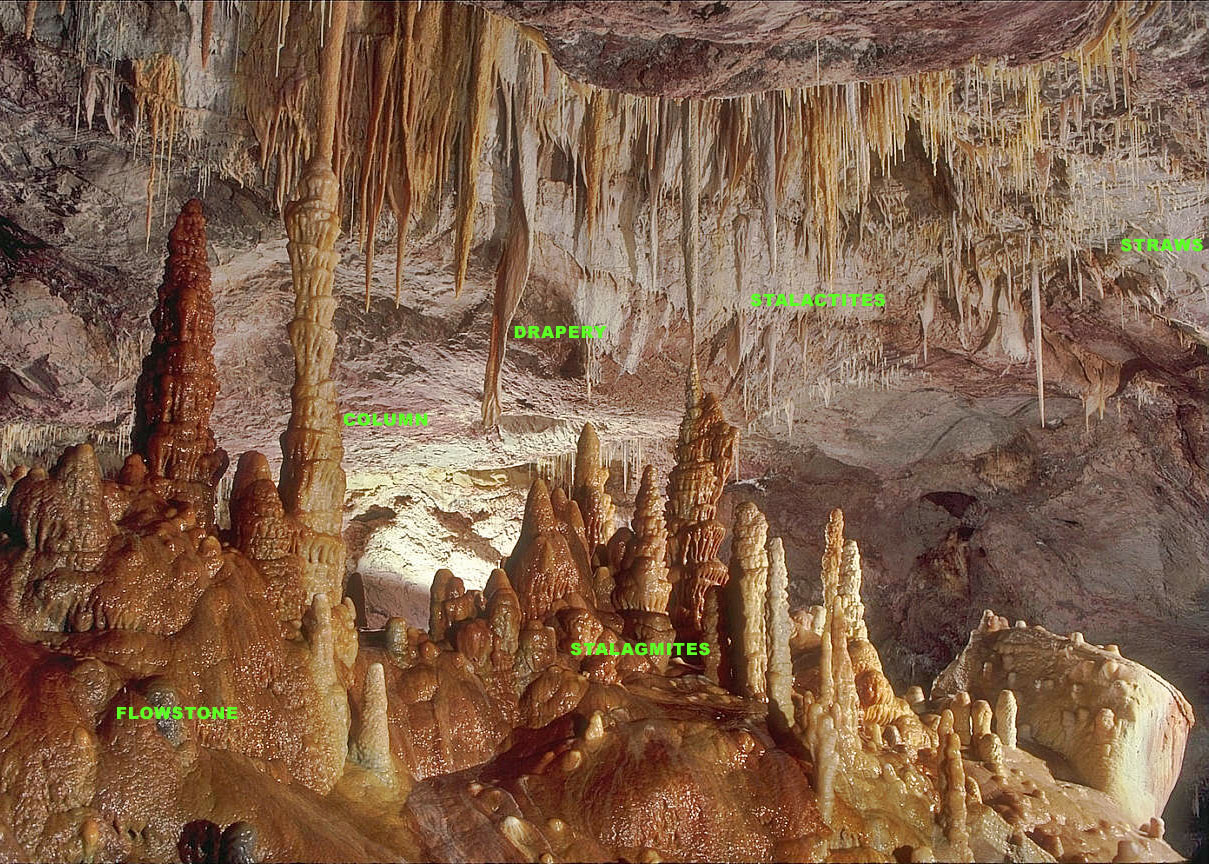
Stalactites
A stalactite (, ; from the Greek 'stalaktos' ('dripping') via ''stalassein'' ('to drip') is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension, or is capable of being melted, may form a stalactite. Stalactites may be composed of lava, minerals, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). A stalactite is not necessarily a speleothem, though speleothems are the most common form of stalactite because of the abundance of limestone caves. The corresponding formation on the floor of the cave is known as a stalagmite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground". Another example is that ''stalactites'' "hang on ''T''ight" and ''stalagmites'' "''M''ight grow up" � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terra-cotta
Terracotta, terra cotta, or terra-cotta (; ; ), in its material sense as an earthenware substrate, is a clay-based unglazed or glazed ceramic where the fired body is porous. In applied art, craft, construction, and architecture, terracotta is the term normally used for sculpture made in earthenware and also for various practical uses, including vessels (notably flower pots), water and waste water pipes, roofing tiles, bricks, and surface embellishment in building construction. The term is also used to refer to the natural brownish orange color of most terracotta. In archaeology and art history, "terracotta" is often used to describe objects such as figurines not made on a potter's wheel. Vessels and other objects that are or might be made on a wheel from the same material are called earthenware pottery; the choice of term depends on the type of object rather than the material or firing technique. Unglazed pieces, and those made for building construction and industry, are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faience
Faience or faïence (; ) is the general English language term for fine tin-glazed pottery. The invention of a white pottery glaze suitable for painted decoration, by the addition of an oxide of tin to the slip of a lead glaze, was a major advance in the history of pottery. The invention seems to have been made in Iran or the Middle East before the ninth century. A kiln capable of producing temperatures exceeding was required to achieve this result, the result of millennia of refined pottery-making traditions. The term is now used for a wide variety of pottery from several parts of the world, including many types of European painted wares, often produced as cheaper versions of porcelain styles. English generally uses various other terms for well-known sub-types of faience. Italian tin-glazed earthenware, at least the early forms, is called maiolica in English, Dutch wares are called Delftware, and their English equivalents English delftware, leaving "faience" as the normal te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly popular in the Ancient Roman world. Mosaic today includes not just murals and pavements, but also artwork, hobby crafts, and industrial and construction forms. Mosaics have a long history, starting in Mesopotamia in the 3rd millennium BC. Pebble mosaics were made in Tiryns in Mycenean Greece; mosaics with patterns and pictures became widespread in classical times, both in Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome. Early Christian basilicas from the 4th century onwards were decorated with wall and ceiling mosaics. Mosaic art flourished in the Byzantine Empire from the 6th to the 15th centuries; that tradition was adopted by the Norman Kingdom of Sicily in the 12th century, by the eastern-influenced Republic of Venice, and among the Rus. Mosaic fell ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises mainly from vitrification and formation of the mineral mullite within the body at these high temperatures. Though definitions vary, porcelain can be divided into three main categories: hard-paste, soft-paste, and bone china. The category that an object belongs to depends on the composition of the paste used to make the body of the porcelain object and the firing conditions. Porcelain slowly evolved in China and was finally achieved (depending on the definition used) at some point about 2,000 to 1,200 years ago; it slowly spread to other East Asian countries, then to Europe, and eventually to the rest of the world. Its manufacturing process is more demanding than that for earthenware and stoneware, the two other main types of pottery, and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giralda
The Giralda ( es, La Giralda ) is the bell tower of Seville Cathedral in Seville, Spain. It was built as the minaret for the Great Mosque of Seville in al-Andalus, Moorish Spain, during the reign of the Almohad dynasty, with a Renaissance-style belfry added by the Catholics after the expulsion of the Muslims from the area. The Cathedral, including the Giralda, was registered in 1987 as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO, along with the Alcázar and the General Archive of the Indies. The tower is in height and remains one of the most important symbols of the city, as it has been since the Middle Ages. Origin Initial construction The mosque was built to replace the older Mosque of Ibn 'Addabas, built in the 9th century under Umayyad rule, since the congregation had grown larger than that modest mosque could accommodate. It was commissioned in 1171 by caliph Abu Ya'qub Yusuf. Sevillian architect Ahmad Ibn Baso, who had led other construction projects for the caliph, was in charge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula. Seville has a municipal population of about 685,000 , and a metropolitan population of about 1.5 million, making it the largest city in Andalusia, the fourth-largest city in Spain and the 26th most populous municipality in the European Union. Its old town, with an area of , contains three UNESCO World Heritage Sites: the Alcázar palace complex, the Cathedral and the General Archive of the Indies. The Seville harbour, located about from the Atlantic Ocean, is the only river port in Spain. The capital of Andalusia features hot temperatures in the summer, with daily maximums routinely above in July and August. Seville was founded as the Roman city of . Known as ''Ishbiliyah'' after the Islamic conquest in 711, Seville became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minaret
A minaret (; ar, منارة, translit=manāra, or ar, مِئْذَنة, translit=miʾḏana, links=no; tr, minare; fa, گلدسته, translit=goldaste) is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generally used to project the Muslim call to prayer ('' adhan''), but they also served as landmarks and symbols of Islam's presence. They can have a variety of forms, from thick, squat towers to soaring, pencil-thin spires. Etymology Two Arabic words are used to denote the minaret tower: ''manāra'' and ''manār''. The English word "minaret" originates from the former, via the Turkish version (). The Arabic word ''manāra'' (plural: ''manārāt'') originally meant a "lamp stand", a cognate of Hebrew '' menorah''. It is assumed to be a derivation of an older reconstructed form, ''manwara''. The other word, ''manār'' (plural: ''manā'ir'' or ''manāyir''), means "a place of light". Both words derive from the Arabic root ''n-w-r'', which has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keep
A keep (from the Middle English ''kype'') is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in castles that were fortified residences, used as a refuge of last resort should the rest of the castle fall to an adversary. The first keeps were made of timber and formed a key part of the motte-and-bailey castles that emerged in Normandy and Anjou during the 10th century; the design spread to England, south Italy and Sicily. As a result of the Norman invasion of 1066, use spread into Wales during the second half of the 11th century and into Ireland in the 1170s. The Anglo-Normans and French rulers began to build stone keeps during the 10th and 11th centuries; these included Norman keeps, with a square or rectangular design, and circular shell keeps. Stone keeps carried considerable political as well as military importance and could take up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
_IMG_7493_edit.jpg)

