|
Ben Pekuah
In Jewish law, a ''ben pekuah'' ( he, בֵּן פּקוּעָה) is an animal fetus removed alive from its mother, shortly after the mother was slaughtered in conformance with the rules of ''shechita'' (kosher slaughter). According to Jewish law, a ''ben pekuah'' may later be slaughtered for consumption without adhering to ''shechita''. Status under Jewish law According to the Torah, all ruminants that have split hooves are permitted to be eaten. They must, however, be slaughtered in a manner prescribed by Jewish law, and certain parts of these animals, including certain fats and ''gid hanasheh'' (the sciatic nerve), may not be consumed. Anything that is inside an animal at the point of slaughter is considered an organ of the animal. Therefore, if a mother was pregnant when slaughtered and a live offspring is removed, the offspring is considered a part of the mother. If the mother was slaughtered in adherence to ''shechita'', then the offspring, a ''ben pekuah'', is deemed alre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halakha
''Halakha'' (; he, הֲלָכָה, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical commandments ('' mitzvot''), subsequent Talmudic and rabbinic laws, and the customs and traditions which were compiled in the many books such as the ''Shulchan Aruch''. ''Halakha'' is often translated as "Jewish law", although a more literal translation of it might be "the way to behave" or "the way of walking". The word is derived from the root which means "to behave" (also "to go" or "to walk"). ''Halakha'' not only guides religious practices and beliefs, it also guides numerous aspects of day-to-day life. Historically, in the Jewish diaspora, ''halakha'' served many Jewish communities as an enforceable avenue of law – both civil and religious, since no differentiation of them exists in classical Judaism. Since the Jewish Enlightenment (''Hask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
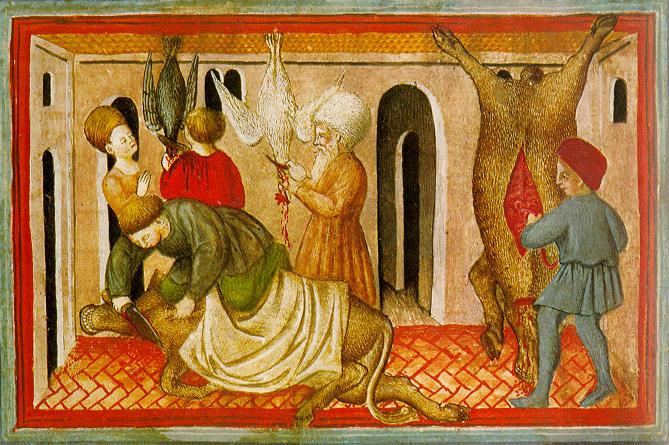
Shechita
In Judaism, ''shechita'' (anglicized: ; he, ; ; also transliterated ''shehitah, shechitah, shehita'') is slaughtering of certain mammals and birds for food according to ''kashrut''. Sources states that sheep and cattle should be slaughtered "as I have instructed you", but nowhere in the Torah are any of the practices of ''shechita'' described. Instead, they have been handed down in Rabbinic Judaism's Oral Torah, and codified in ''halakha''. Species The animal must be of a permitted species. For mammals, this is restricted to ruminants which have split hooves. For birds, although biblically any species of bird not specifically excluded in would be permitted, doubts as to the identity and scope of the species on the biblical list led to rabbinical law permitting only birds with a tradition of being permissible. Fish do not require kosher slaughter to be considered kosher, but are subject to other laws found in which determine whether or not they are kosher (having both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the same as Pentateuch or the Five Books of Moses. It is also known in the Jewish tradition as the Written Torah (, ). If meant for liturgic purposes, it takes the form of a Torah scroll ('' Sefer Torah''). If in bound book form, it is called ''Chumash'', and is usually printed with the rabbinic commentaries (). At times, however, the word ''Torah'' can also be used as a synonym for the whole of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, in which sense it includes not only the first five, but all 24 books of the Hebrew Bible. Finally, Torah can even mean the totality of Jewish teaching, culture, and practice, whether derived from biblical texts or later rabbinic writings. The latter is often known as the Oral Torah. Representing the core of the Jewish spiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are ungulate, hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The process, which takes place in the front part of the digestive system and therefore is called foregut fermentation, typically requires the fermented ingesta (known as cud) to be regurgitated and chewed again. The process of rechewing the cud to further break down plant matter and stimulate digestion is called rumination. The word "ruminant" comes from the Latin ''ruminare'', which means "to chew over again". The roughly 200 species of ruminants include both domestic and wild species. Ruminating mammals include cattle, all domesticated and wild bovines, goats, sheep, giraffes, deer, gazelles, and antelopes.Fowler, M.E. (2010).Medicine and Surgery of Camelids, Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. Chapter 1 General Biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gid Hanasheh
''Gid Hanasheh'' ( he, גִּיד הַנָּשֶׁה ''Gīḏ hanNāše'', literally "forgotten sinew", often translated as "displaced tendon") is the term for sciatic nerve in Judaism. It may not be eaten by Jews according to Halacha (Jewish Law). The laws regarding the prohibition of ''gid hanasheh'' are found in Tractate Chullin, chapter 7. Biblical Source The Torah () recounts that Jacob fought with an angel (according to Rashi, this was Esau's guardian angel) who could not beat him. At the end of the fight, the angel strikes a nerve in Jacob's leg, causing him to limp. The verse then states: "Therefore the Israelites do not eat the displaced nerve (''gid ha-nasheh'') on the hip joint to this very day." () Interpretations The Zohar explains that the thigh is the root location of sexual desire. While most evil urges can be overcome, there is one lust that is so strong that it overpowers even great men - the ''gid ha-nasheh''. Its very name ''nasheh'' means “forgetting” ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
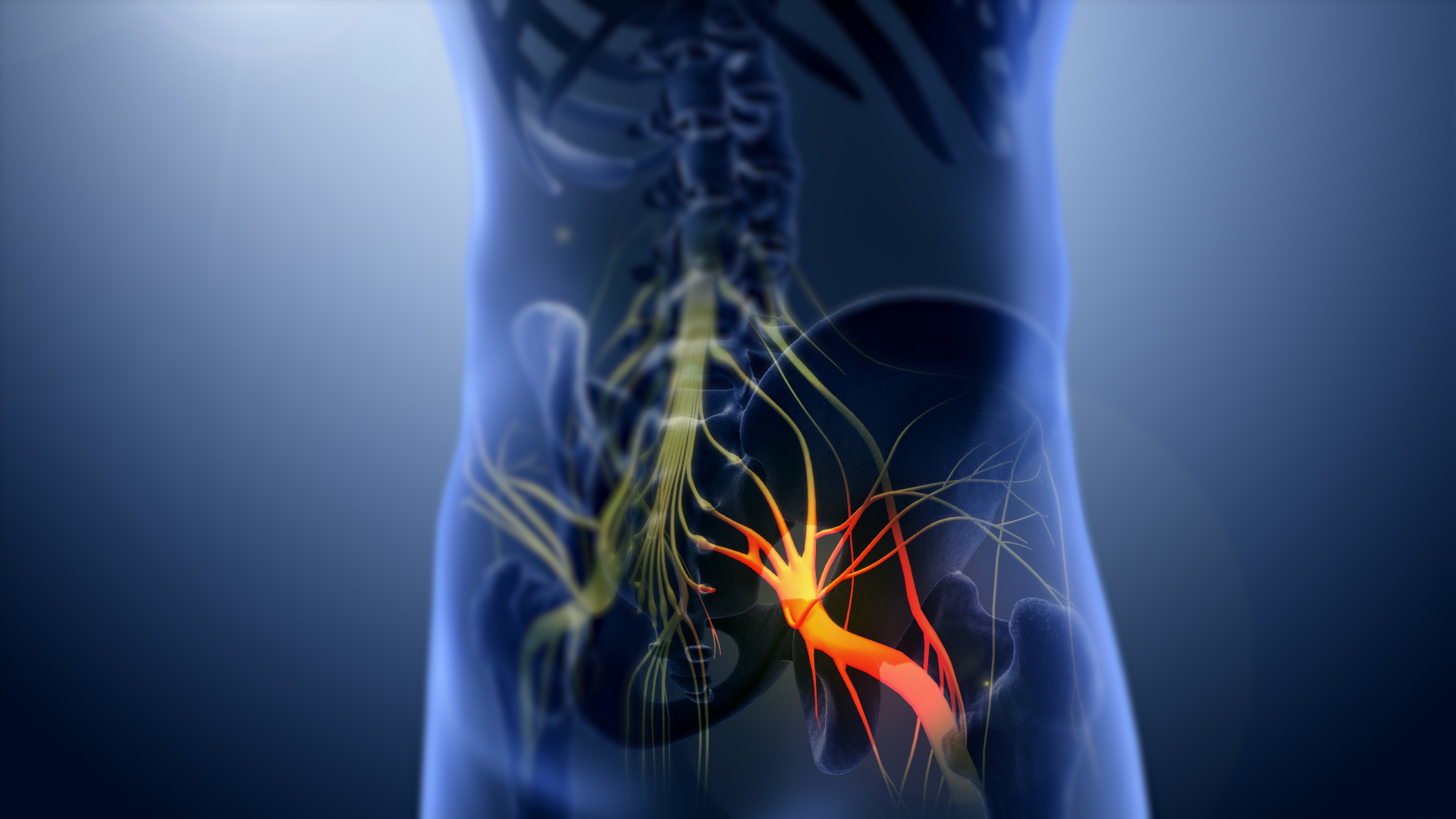
Sciatic Nerve
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals which is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect. The sciatic nerve has no cutaneous branches for the thigh. This nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for the skin of the lateral leg and the whole foot, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from spinal nerves L4 to S3. It contains fibers from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus. Structure In humans, the sciatic nerve is formed from the L4 to S3 segments of the sacral plexus, a collection of nerve fibres that emerge from the sacral part of the spinal cord. The lumbosacral trunk from the L4 and L5 roots descends between the sacral promontory and ala and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glatt Kosher
In Judaism, ''shechita'' (anglicized: ; he, ; ; also transliterated ''shehitah, shechitah, shehita'') is slaughtering of certain mammals and birds for food according to ''kashrut''. Sources states that sheep and cattle should be slaughtered "as I have instructed you", but nowhere in the Torah are any of the practices of ''shechita'' described. Instead, they have been handed down in Rabbinic Judaism's Oral Torah, and codified in ''halakha''. Species The animal must be of a permitted species. For mammals, this is restricted to ruminants which have split hooves. For birds, although biblically any species of bird not specifically excluded in would be permitted, doubts as to the identity and scope of the species on the biblical list led to rabbinical law permitting only birds with a tradition of being permissible. Fish do not require kosher slaughter to be considered kosher, but are subject to other laws found in which determine whether or not they are kosher (having both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gid Hanasheh
''Gid Hanasheh'' ( he, גִּיד הַנָּשֶׁה ''Gīḏ hanNāše'', literally "forgotten sinew", often translated as "displaced tendon") is the term for sciatic nerve in Judaism. It may not be eaten by Jews according to Halacha (Jewish Law). The laws regarding the prohibition of ''gid hanasheh'' are found in Tractate Chullin, chapter 7. Biblical Source The Torah () recounts that Jacob fought with an angel (according to Rashi, this was Esau's guardian angel) who could not beat him. At the end of the fight, the angel strikes a nerve in Jacob's leg, causing him to limp. The verse then states: "Therefore the Israelites do not eat the displaced nerve (''gid ha-nasheh'') on the hip joint to this very day." () Interpretations The Zohar explains that the thigh is the root location of sexual desire. While most evil urges can be overcome, there is one lust that is so strong that it overpowers even great men - the ''gid ha-nasheh''. Its very name ''nasheh'' means “forgetting” ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelev
Chelev ( he, חֵלֶב, ''kheylev'' or ''ẖelev''), or what is also known as "suet", is the animal fats that the Torah prohibits Jews and Israelites from eating (). Only the ''chelev'' of animals that are of the sort from which offerings can be brought in the Tabernacle or Temple are prohibited (). The prohibition of eating ''chelev'' is also, in addition to the Torah, one of the 613 commandments that, according to the Talmud, were given to Moses on Mount Sinai. Hebrew Bible Hebrew language In Biblical Hebrew, the word for fat is ''chelev'' (חֵלֶב), and it is first used for the "fats" of Abel's offering, and most often used for fats of animal sacrifices on the altar of the Tabernacle or Temple. The same word is also used in the phrase "the fat of the land." Rabbinical interpretation The punishment for eating ''chelev'' bemeizid (on purpose) is kareth (exclusion from the after life). The atonement for eating it by mistake is to bring a korban hattath (atonement sacri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is a state in southeastern Australia. It is the second-smallest state with a land area of , the second most populated state (after New South Wales) with a population of over 6.5 million, and the most densely populated state in Australia (28 per km2). Victoria is bordered by New South Wales to the north and South Australia to the west, and is bounded by the Bass Strait to the south (with the exception of a small land border with Tasmania located along Boundary Islet), the Great Australian Bight portion of the Southern Ocean to the southwest, and the Tasman Sea (a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean) to the southeast. The state encompasses a range of climates and geographical features from its temperate coastal and central regions to the Victorian Alps in the northeast and the semi-arid north-west. The majority of the Victorian population is concentrated in the central-south area surrounding Port Phillip Bay, and in particular within the metropolit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oren Duvduvani
Oren ( he, אורן) is a masculine given name, meaning 'pine' or 'ash' in Hebrew. In the Book of Chronicles, Oren is one of the sons of Jerahmeel, the first-born of Hezron, along with Ram, Bunah, Ozem and Ahijah. Oren, as a given name or surname, may also refer to: First name *Oren Aharoni (born 1973), Israeli basketball coach and former basketball player *Oren Ambarchi (born 1969), Australian musician * Oren Biton (born 1994), Israeli football player *Oren Burks (born 1995), American football player * Oren B. Cheney (1816–1903), American college president * Oren S. Copeland (1887–1958), American politician * Oren R. Earl (1813–1901), American politician *Oren Eizenman (born 1985), Israeli-Canadian ice hockey player * Oren Frood (1889–1943), Canadian ice hockey player *Oren Harman (born 1973), Israeli writer *Oren Harris (1903–1997), American politician and judge *Oren Koules (born 1961), American businessman *Oren Lavie (born 1976), Israeli musician and theatre direct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosher Meat
In Judaism, ''shechita'' (anglicized: ; he, ; ; also transliterated ''shehitah, shechitah, shehita'') is slaughtering of certain mammals and birds for food according to '' kashrut''. Sources states that sheep and cattle should be slaughtered "as I have instructed you", but nowhere in the Torah are any of the practices of ''shechita'' described. Instead, they have been handed down in Rabbinic Judaism's Oral Torah, and codified in ''halakha''. Species The animal must be of a permitted species. For mammals, this is restricted to ruminants which have split hooves. For birds, although biblically any species of bird not specifically excluded in would be permitted, doubts as to the identity and scope of the species on the biblical list led to rabbinical law permitting only birds with a tradition of being permissible. Fish do not require kosher slaughter to be considered kosher, but are subject to other laws found in which determine whether or not they are kosher (having b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)